Novel Activities of Select NSAID R-Enantiomers against Rac1 and Cdc42 GTPases
- PMID: 26558612
- PMCID: PMC4641600
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0142182
Novel Activities of Select NSAID R-Enantiomers against Rac1 and Cdc42 GTPases
Abstract
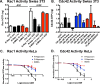
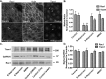
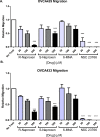
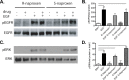
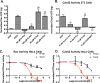
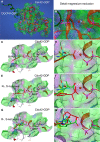
Rho family GTPases (including Rac, Rho and Cdc42) collectively control cell proliferation, adhesion and migration and are of interest as functional therapeutic targets in numerous epithelial cancers. Based on high throughput screening of the Prestwick Chemical Library® and cheminformatics we identified the R-enantiomers of two approved drugs (naproxen and ketorolac) as inhibitors of Rac1 and Cdc42. The corresponding S-enantiomers are considered the active component in racemic drug formulations, acting as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) with selective activity against cyclooxygenases. Here, we show that the S-enantiomers of naproxen and ketorolac are inactive against the GTPases. Additionally, more than twenty other NSAIDs lacked inhibitory action against the GTPases, establishing the selectivity of the two identified NSAIDs. R-naproxen was first identified as a lead compound and tested in parallel with its S-enantiomer and the non-chiral 6-methoxy-naphthalene acetic acid (active metabolite of nabumetone, another NSAID) as a structural series. Cheminformatics-based substructure analyses-using the rotationally constrained carboxylate in R-naproxen-led to identification of racemic [R/S] ketorolac as a suitable FDA-approved candidate. Cell based measurement of GTPase activity (in animal and human cell lines) demonstrated that the R-enantiomers specifically inhibit epidermal growth factor stimulated Rac1 and Cdc42 activation. The GTPase inhibitory effects of the R-enantiomers in cells largely mimic those of established Rac1 (NSC23766) and Cdc42 (CID2950007/ML141) specific inhibitors. Docking predicts that rotational constraints position the carboxylate moieties of the R-enantiomers to preferentially coordinate the magnesium ion, thereby destabilizing nucleotide binding to Rac1 and Cdc42. The S-enantiomers can be docked but are less favorably positioned in proximity to the magnesium. R-naproxen and R-ketorolac have potential for rapid translation and efficacy in the treatment of several epithelial cancer types on account of established human toxicity profiles and novel activities against Rho-family GTPases.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
Dual Actions of Ketorolac in Metastatic Ovarian Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Jul 24;11(8):1049. doi: 10.3390/cancers11081049. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31344967 Free PMC article. Review.
-
R-Ketorolac Targets Cdc42 and Rac1 and Alters Ovarian Cancer Cell Behaviors Critical for Invasion and Metastasis.Mol Cancer Ther. 2015 Oct;14(10):2215-27. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-15-0419. Epub 2015 Jul 23. Mol Cancer Ther. 2015. PMID: 26206334 Free PMC article.
-
The R-enantiomer of ketorolac reduces ovarian cancer tumor burden in vivo.BMC Cancer. 2021 Jan 7;21(1):40. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-07716-1. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33413202 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Pharmacologic Activity of Ketorolac for Therapeutic Benefit in Ovarian Cancer Patients.Clin Cancer Res. 2015 Nov 15;21(22):5064-72. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-0461. Epub 2015 Jun 12. Clin Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 26071482 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The role of Rho GTPases' substrates Rac and Cdc42 in osteoclastogenesis and relevant natural medicinal products study.Biosci Rep. 2020 Jul 31;40(7):BSR20200407. doi: 10.1042/BSR20200407. Biosci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32578854 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Organoid-on-a-chip model of human ARPKD reveals mechanosensing pathomechanisms for drug discovery.Sci Adv. 2022 Sep 23;8(38):eabq0866. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abq0866. Epub 2022 Sep 21. Sci Adv. 2022. PMID: 36129975 Free PMC article.
-
Agent-based modeling predicts RAC1 is critical for ovarian cancer metastasis.Mol Biol Cell. 2022 Dec 1;33(14):ar138. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E21-11-0540. Epub 2022 Oct 6. Mol Biol Cell. 2022. PMID: 36200848 Free PMC article.
-
Ovarian Tumor Microenvironment Signaling: Convergence on the Rac1 GTPase.Cancers (Basel). 2018 Sep 27;10(10):358. doi: 10.3390/cancers10100358. Cancers (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30261690 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dual Actions of Ketorolac in Metastatic Ovarian Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Jul 24;11(8):1049. doi: 10.3390/cancers11081049. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31344967 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulating Cdc42 and Its Signaling Pathways in Cancer: Small Molecules and MicroRNA as New Treatment Candidates.Molecules. 2018 Mar 29;23(4):787. doi: 10.3390/molecules23040787. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 29596304 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

