Retina-on-a-chip: a microfluidic platform for point access signaling studies
- PMID: 26559199
- PMCID: PMC4707151
- DOI: 10.1007/s10544-015-0019-x
Retina-on-a-chip: a microfluidic platform for point access signaling studies
Abstract
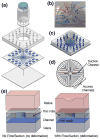
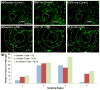
We report on a microfluidic platform for culture of whole organs or tissue slices with the capability of point access reagent delivery to probe the transport of signaling events. Whole mice retina were maintained for multiple days with negative pressure applied to tightly but gently bind the bottom of the retina to a thin poly-(dimethylsiloxane) membrane, through which twelve 100 μm diameter through-holes served as fluidic access points. Staining with toluidine blue, transport of locally applied cholera toxin beta, and transient response to lipopolysaccharide in the retina demonstrated the capability of the microfluidic platform. The point access fluidic delivery capability could enable new assays in the study of various kinds of excised tissues, including retina.
Keywords: Microenvironment; Microfluidic tissue culture; Retina.
Figures




Similar articles
-
A Microfluidic Cancer-on-Chip Platform Predicts Drug Response Using Organotypic Tumor Slice Culture.Cancer Res. 2022 Feb 1;82(3):510-520. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-21-0799. Epub 2021 Dec 6. Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 34872965 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment and characterization of a primary murine adipose tissue-chip.Biotechnol Bioeng. 2018 Aug;115(8):1979-1987. doi: 10.1002/bit.26711. Epub 2018 May 2. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2018. PMID: 29689639
-
Rapid spheroid clearing on a microfluidic chip.Lab Chip. 2017 Dec 19;18(1):153-161. doi: 10.1039/c7lc01114h. Lab Chip. 2017. PMID: 29192297
-
Microfluidic platforms for lab-on-a-chip applications.Lab Chip. 2007 Sep;7(9):1094-110. doi: 10.1039/b706364b. Epub 2007 Jul 27. Lab Chip. 2007. PMID: 17713606 Review.
-
A review of digital microfluidics as portable platforms for lab-on a-chip applications.Lab Chip. 2016 Jul 7;16(13):2376-96. doi: 10.1039/c6lc00387g. Epub 2016 Jun 8. Lab Chip. 2016. PMID: 27272540 Review.
Cited by
-
A Microfluidic Eye Facsimile System to Examine the Migration of Stem-like Cells.Micromachines (Basel). 2022 Mar 2;13(3):406. doi: 10.3390/mi13030406. Micromachines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35334698 Free PMC article.
-
Microfluidic and Microscale Assays to Examine Regenerative Strategies in the Neuro Retina.Micromachines (Basel). 2020 Dec 9;11(12):1089. doi: 10.3390/mi11121089. Micromachines (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33316971 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tissue engineering of the retina: from organoids to microfluidic chips.J Tissue Eng. 2021 Dec 10;12:20417314211059876. doi: 10.1177/20417314211059876. eCollection 2021 Jan-Dec. J Tissue Eng. 2021. PMID: 34917332 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Coculture techniques for modeling retinal development and disease, and enabling regenerative medicine.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2020 Dec;9(12):1531-1548. doi: 10.1002/sctm.20-0201. Epub 2020 Aug 7. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 32767661 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ex Vivo Tumor-on-a-Chip Platforms to Study Intercellular Interactions within the Tumor Microenvironment.Adv Healthc Mater. 2019 Feb;8(4):e1801198. doi: 10.1002/adhm.201801198. Epub 2018 Dec 5. Adv Healthc Mater. 2019. PMID: 30516355 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

