Cytomegalovirus-Associated Gastroduodenal Ulcers in a Patient With Functional Hypercortisolism: A Case Report
- PMID: 26559263
- PMCID: PMC4912257
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000001940
Cytomegalovirus-Associated Gastroduodenal Ulcers in a Patient With Functional Hypercortisolism: A Case Report
Abstract
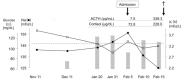
Cytomegalovirus (CMV)-associated gastroduodenal ulcers (GDU) are a rare digestive disease, which principally affect immunocompromised patients. We recently experienced CMV-associated GDU occurring in a seemingly immunocompetent patient. The rarity of such a condition was inimical to a correct clinical diagnosis.A 77-year-old woman with Alzheimer's disease was admitted to our hospital because of vomiting and anorexia. Her general condition was extremely poor due to severe dehydration. Any invasive procedures including gastroduodenal endoscopy could not be performed. Laboratory test results showed electrolyte imbalance, hyperglycemia, and hypercortisolemia. The plasma adrenocorticotropic hormone level was rather low. On her 11th day in hospital, she suddenly fell into shock status. Despite intensive care, the patient could not be rescued. An autopsy was performed and revealed that she had suffered from CMV-associated GDU and died of candidemia that invaded through the ulcer. Her adrenal glands showed neither neoplasm nor hyperplasia, suggesting that her hypercortisolism was a purely functional disorder. We concluded that the severe opportunistic infections were developed in association with functional hypercortisolism.This case suggests that functional hypercortisolism, even though transient, can cause a patient to be immunocompromised.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Prevalence and etiology of gastroduodenal ulcer in HIV-positive patients: a comparative study of 497 symptomatic subjects evaluated by endoscopy.Am J Gastroenterol. 1998 Jun;93(6):935-40. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.1998.00282.x. Am J Gastroenterol. 1998. PMID: 9647023
-
Everolimus-associated cytomegalovirus colitis in a patient with metastasized breast cancer: a case report.Breast Cancer. 2020 Jul;27(4):776-779. doi: 10.1007/s12282-019-01026-6. Epub 2019 Nov 26. Breast Cancer. 2020. PMID: 31773503
-
Low prevalence of Helicobacter pylori but high prevalence of cytomegalovirus-associated peptic ulcer disease in AIDS patients: Comparative study of symptomatic subjects evaluated by endoscopy and CD4 counts.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2004 Apr;19(4):423-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1746.2003.03278.x. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2004. PMID: 15012780
-
Refractory pharyngeal ulceration due to cytomegalovirus in a patient with HIV infection: a case report and literature review.BMC Infect Dis. 2021 Mar 10;21(1):252. doi: 10.1186/s12879-021-05943-w. BMC Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 33691621 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[A case of cytomegalovirus infection with splenic infarction and an esophageal ulcer in an immunocompetent adult].Nihon Shokakibyo Gakkai Zasshi. 2017;114(7):1269-1276. doi: 10.11405/nisshoshi.114.1269. Nihon Shokakibyo Gakkai Zasshi. 2017. PMID: 28679983 Review. Japanese.
References
-
- Maitra A. Kumar V, Abbas AK, Aster JC, Perkins JA. Adrenocortical Hyperfunction (Hyperadrenalism). Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease (9th ed). Philadelphia, PA:Elsevier Saunders; 2015. 1123–1129.
-
- Lionakis MS, Kontoyiannis DP. Glucocorticoids and invasive fungal infections. Lancet 2003; 362:1828–1838. - PubMed
-
- Vermes I, Beishuizen A. The hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal response to critical illness. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 2001; 15:495–511. - PubMed
-
- Gatta B, Chabre O, Cortet C, et al. Reevaluation of the combined dexamethasone suppression-corticotropin-releasing hormone test for differentiation of mild cushing's disease from pseudo-Cushing's syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2007; 92:4290–4293. - PubMed
-
- Alwani RA, Schmit Jongbloed LW, de Jong FH, et al. Differentiating between Cushing's disease and pseudo-Cushing's syndrome: comparison of four tests. Eur J Endocrinol 2014; 170:477–486. - PubMed

