Effect of PCI on Long-Term Survival in Patients with Stable Ischemic Heart Disease
- PMID: 26559572
- PMCID: PMC5656049
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1505532
Effect of PCI on Long-Term Survival in Patients with Stable Ischemic Heart Disease
Abstract
Background: Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) relieves angina in patients with stable ischemic heart disease, but clinical trials have not shown that it improves survival. Between June 1999 and January 2004, we randomly assigned 2287 patients with stable ischemic heart disease to an initial management strategy of optimal medical therapy alone (medical-therapy group) or optimal medical therapy plus PCI (PCI group) and did not find a significant difference in the rate of survival during a median follow-up of 4.6 years. We now report the rate of survival among the patients who were followed for up to 15 years.
Methods: We obtained permission from the patients at the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) sites and some non-VA sites in the United States to use their Social Security numbers to track their survival after the original trial period ended. We searched the VA national Corporate Data Warehouse and the National Death Index for survival information and the dates of death from any cause. We calculated survival according to the Kaplan-Meier method and used a Cox proportional-hazards model to adjust for significant between-group differences in baseline characteristics.
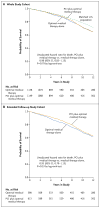
Results: Extended survival information was available for 1211 patients (53% of the original population). The median duration of follow-up for all patients was 6.2 years (range, 0 to 15); the median duration of follow-up for patients at the sites that permitted survival tracking was 11.9 years (range, 0 to 15). A total of 561 deaths (180 during the follow-up period in the original trial and 381 during the extended follow-up period) occurred: 284 deaths (25%) in the PCI group and 277 (24%) in the medical-therapy group (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.03; 95% confidence interval, 0.83 to 1.21; P=0.76).
Conclusions: During an extended-follow-up of up to 15 years, we did not find a difference in survival between an initial strategy of PCI plus medical therapy and medical therapy alone in patients with stable ischemic heart disease. (Funded by the VA Cooperative Studies Program and others; COURAGE ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT00007657.).
Figures

Comment in
-
[Efficacy of percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with chronic ischaemic heart disease].Semergen. 2016 Nov-Dec;42(8):586-587. doi: 10.1016/j.semerg.2015.12.010. Epub 2016 Feb 1. Semergen. 2016. PMID: 26837858 Spanish. No abstract available.
References
-
- Fihn SD, Blankenship JC, Alexander KP, et al. 2014 ACC/AHA/AATS/PCNA/SCAI/STS focused update of the guideline for the diagnosis and management of patients with stable ischemic heart disease. Circulation. 2014;130:1749–67. - PubMed
-
- Patel MR, Dehmer GJ, Hirshfeld JW, Smith PK, Spertus JA. ACCF/SCAI/STS/AATS/AHA/ASNC 2009 Appropriateness criteria for coronary revascularization: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation Appropriateness Criteria Task Force, Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, Society of Thoracic Surgeons, American Association for Thoracic Surgery, American Heart Association, and the American Society of Nuclear Cardiology: endorsed by the American Society of Echocardiography, the Heart Failure Society of America, and the Society of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography. Circulation. 2009;119:1330–52. - PubMed
-
- Bavry AA, Kumbhani DJ, Rassi AN, Bhatt DL, Askari AT. Benefit of early invasive therapy in acute coronary syndromes: a meta-analysis of contemporary randomized clinical trials. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;48:1319–25. - PubMed
-
- Mehta SR, Cannon CP, Fox KA, et al. Routine vs selective invasive strategies in patients with acute coronary syndromes: a collaborative meta-analysis of randomized trials. JAMA. 2005;293:2908–17. - PubMed
-
- Boden WE, O’Rourke RA, Teo KK, et al. Optimal medical therapy with or without PCI for stable coronary disease. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:1503–16. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
