NK-92: an 'off-the-shelf therapeutic' for adoptive natural killer cell-based cancer immunotherapy
- PMID: 26559813
- PMCID: PMC11029582
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-015-1761-x
NK-92: an 'off-the-shelf therapeutic' for adoptive natural killer cell-based cancer immunotherapy
Abstract
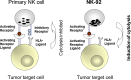
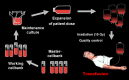
Natural killer (NK) cells are increasingly considered as immunotherapeutic agents in particular in the fight against cancers. NK cell therapies are potentially broadly applicable and, different from their T cell counterparts, do not cause graft-versus-host disease. Efficacy and clinical in vitro or in vivo expansion of primary NK cells will however always remain variable due to individual differences of donors or patients. Long-term storage of clinical NK cell lots to allow repeated clinical applications remains an additional challenge. In contrast, the established and well-characterized cell line NK-92 can be easily and reproducibly expanded from a good manufacturing practice (GMP)-compliant cryopreserved master cell bank. Moreover, no cost-intensive cell purification methods are required. To date, NK-92 has been intensively studied. The cells displayed superior cytotoxicity against a number of tumor types tested, which was confirmed in preclinical mouse studies. Subsequent clinical testing demonstrated safety of NK-92 infusions even at high doses. Despite the phase I nature of the trials conducted so far, some efficacy was noted, particularly against lung tumors. Furthermore, to overcome tumor resistance and for specific targeting, NK-92 has been engineered to express a number of different chimeric antigen receptors (CARs), including targeting, for example, CD19 or CD20 (anti-B cell malignancies), CD38 (anti-myeloma) or human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2; ErbB2; anti-epithelial cancers). The concept of an NK cell line as an allogeneic cell therapeutic produced 'off-the-shelf' on demand holds great promise for the development of effective treatments.
Keywords: CAR; Cellular immunotherapy; Clinical trial; NK cell line; NK-92; Tumor targeting.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. H. G. Klingemann is affiliated with NantKwest Inc, CA, USA (formerly known as Conkwest, Inc.). All other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Gong JH, Maki G, Klingemann HG. Characterization of a human cell line (nk-92) with phenotypical and functional characteristics of activated natural killer cells. Leukemia. 1994;8:652–658. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

