Multi-Toxin Resistance Enables Pink Bollworm Survival on Pyramided Bt Cotton
- PMID: 26559899
- PMCID: PMC5156061
- DOI: 10.1038/srep16554
Multi-Toxin Resistance Enables Pink Bollworm Survival on Pyramided Bt Cotton
Abstract
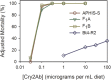
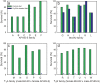
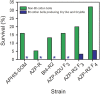
Transgenic crops producing Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) proteins kill key insect pests, providing economic and environmental benefits. However, the evolution of pest resistance threatens the continued success of such Bt crops. To delay or counter resistance, transgenic plant "pyramids" producing two or more Bt proteins that kill the same pest have been adopted extensively. Field populations of the pink bollworm (Pectinophora gossypiella) in the United States have remained susceptible to Bt toxins Cry1Ac and Cry2Ab, but field-evolved practical resistance to Bt cotton producing Cry1Ac has occurred widely in India. Here we used two rounds of laboratory selection to achieve 18,000- to 150,000-fold resistance to Cry2Ab in pink bollworm. Inheritance of resistance to Cry2Ab was recessive, autosomal, conferred primarily by one locus, and independent of Cry1Ac resistance. We created a strain with high resistance to both toxins by crossing the Cry2Ab-resistant strain with a Cry1Ac-resistant strain, followed by one selection with Cry2Ab. This multi-toxin resistant strain survived on field-collected Bt cotton bolls producing both toxins. The results here demonstrate the risk of evolution of resistance to pyramided Bt plants, particularly when toxins are deployed sequentially and refuges are scarce, as seen with Bt cotton and pink bollworm in India.
Conflict of interest statement
This is a cooperative investigation between USDA ARS, the University of Arizona, and DuPont-Pioneer with J.A.F., B.E.T. and Y.C. receiving partial funding from DuPont-Pioneer to support this work (agreement #58-3K95-4-1666). J.A.F. is coauthor of a patent "Cadherin Receptor Peptide for Potentiating Bt Biopesticides" (patent numbers: US20090175974A1, US8354371, WO2009067487A2, WO2009067487A3). B.E.T. is a coauthor of a patent on modified Bt toxins, "Suppression of Resistance in Insects to Bacillus thuringiensis Cry Toxins, Using Toxins that do not Require the Cadherin Receptor" (patent numbers: CA2690188A1, CN101730712A, EP2184293A2, EP2184293A4, EP2184293B1, WO2008150150A2, WO2008150150A3). Bayer CropScience, Dow AgroSciences, Monsanto, and Syngenta did not provide funding to support this work, but may be affected financially by publication of this paper and have funded other work by some of the authors.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Asymmetrical cross-resistance between Bacillus thuringiensis toxins Cry1Ac and Cry2Ab in pink bollworm.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Jul 21;106(29):11889-94. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0901351106. Epub 2009 Jul 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19581574 Free PMC article.
-
Sustained susceptibility of pink bollworm to Bt cotton in the United States.GM Crops Food. 2012 Jul-Sep;3(3):194-200. doi: 10.4161/gmcr.20329. Epub 2012 Jul 1. GM Crops Food. 2012. PMID: 22572905 Review.
-
Early detection of field-evolved resistance to Bt cotton in China: cotton bollworm and pink bollworm.J Invertebr Pathol. 2012 Jul;110(3):301-6. doi: 10.1016/j.jip.2012.04.008. Epub 2012 Apr 16. J Invertebr Pathol. 2012. PMID: 22537835 Review.
-
Responses to Bt toxin Vip3Aa by pink bollworm larvae resistant or susceptible to Cry toxins.Pest Manag Sci. 2022 Oct;78(10):3973-3979. doi: 10.1002/ps.7016. Epub 2022 Jun 13. Pest Manag Sci. 2022. PMID: 35633103
-
Increased frequency of pink bollworm resistance to Bt toxin Cry1Ac in China.PLoS One. 2012;7(1):e29975. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0029975. Epub 2012 Jan 4. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22238687 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Molecular Genetic Basis of Lab- and Field-Selected Bt Resistance in Pink Bollworm.Insects. 2023 Feb 17;14(2):201. doi: 10.3390/insects14020201. Insects. 2023. PMID: 36835770 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transposon insertion causes cadherin mis-splicing and confers resistance to Bt cotton in pink bollworm from China.Sci Rep. 2019 May 16;9(1):7479. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-43889-x. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31097777 Free PMC article.
-
Resistance to Bacillus thuringiensis toxin Cry2Ab and survival on single-toxin and pyramided cotton in cotton bollworm from China.Evol Appl. 2016 Dec 16;10(2):170-179. doi: 10.1111/eva.12438. eCollection 2017 Feb. Evol Appl. 2016. PMID: 28127393 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide analysis reveals distinct global populations of pink bollworm (Pectinophora gossypiella).Sci Rep. 2023 Jul 20;13(1):11762. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-38504-z. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37474628 Free PMC article.
-
Segregation of Cry Genes in the Seeds Produced by F1 Bollgard® II Cotton Differs between Hybrids: Could This Be Linked to the Observed Field Resistance in the Pink Bollworm?Genes (Basel). 2022 Dec 25;14(1):65. doi: 10.3390/genes14010065. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36672806 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mendelsohn M., Kough J., Vaituzis Z. & Matthews K. Are Bt Crops Safe? Nat. Biotechnol. 21, 1003–1009 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Sanahuja G., Banakar R., Twyman R. M., Capell T. & Christou P. Bacillus thuringiensis: A century of research, development and commercial applications. Plant Biotechnol. J. 9, 283–300 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Nicolia A., Manzo A., Vironessi F. & Rosselini D. An overview of the last 10 years of genetically engineered crop safety research. Critical Rev. Biotechnol. 34, 77–88 (2014). - PubMed
-
- James C. Global status of commercialized biotech/GM crops. ISAAA Briefs 49 (ISAAA, Ithaca, NY, 2014) (2014).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

