A Novel Function of Molecular Chaperone HSP70: SUPPRESSION OF ONCOGENIC FOXM1 AFTER PROTEOTOXIC STRESS
- PMID: 26559972
- PMCID: PMC4697151
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M115.678227
A Novel Function of Molecular Chaperone HSP70: SUPPRESSION OF ONCOGENIC FOXM1 AFTER PROTEOTOXIC STRESS
Abstract
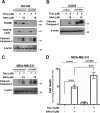
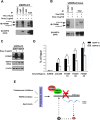
The oncogenic transcription factor FOXM1 is overexpressed in the majority of human cancers, and it is a potential target for anticancer therapy. We identified proteasome inhibitors as the first type of drugs that target FOXM1 in cancer cells. Here we found that HSP90 inhibitor PF-4942847 and heat shock also suppress FOXM1. The common effector, which was induced after treatment with proteasome and HSP90 inhibitors or heat shock, was the molecular chaperone HSP70. We show that HSP70 binds to FOXM1 following proteotoxic stress and that HSP70 inhibits FOXM1 DNA-binding ability. Inhibition of FOXM1 transcriptional autoregulation by HSP70 leads to the suppression of FOXM1 protein expression. In addition, HSP70 suppression elevates FOXM1 expression, and simultaneous inhibition of FOXM1 and HSP70 increases the sensitivity of human cancer cells to anticancer drug-induced apoptosis. Overall, we determined the unique and novel mechanism of FOXM1 suppression by proteasome inhibitors.
Keywords: 70-kD heat shock protein (Hsp70); FOXM1; anticancer drug; cell death; gene expression; protein-protein interaction.
© 2016 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Heat shock proteins and cancer: The FoxM1 connection.Biochem Pharmacol. 2023 May;211:115505. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2023.115505. Epub 2023 Mar 15. Biochem Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36931349 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A new target for proteasome inhibitors: FoxM1.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2010 Feb;19(2):235-42. doi: 10.1517/13543780903563364. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2010. PMID: 20074015 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FoxM1 is a general target for proteasome inhibitors.PLoS One. 2009 Aug 12;4(8):e6593. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0006593. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19672316 Free PMC article.
-
Validation of the Hsp70-Bag3 protein-protein interaction as a potential therapeutic target in cancer.Mol Cancer Ther. 2015 Mar;14(3):642-8. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-14-0650. Epub 2015 Jan 6. Mol Cancer Ther. 2015. PMID: 25564440 Free PMC article.
-
Honokiol is a FOXM1 antagonist.Cell Death Dis. 2018 Jan 24;9(2):84. doi: 10.1038/s41419-017-0156-7. Cell Death Dis. 2018. PMID: 29367668 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Heat shock proteins and cancer: The FoxM1 connection.Biochem Pharmacol. 2023 May;211:115505. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2023.115505. Epub 2023 Mar 15. Biochem Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36931349 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FOXM1 in Cancer: Interactions and Vulnerabilities.Cancer Res. 2017 Jun 15;77(12):3135-3139. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-3566. Epub 2017 Jun 5. Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28584182 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The multifaceted roles of FOXM1 in pulmonary disease.Cell Commun Signal. 2019 Apr 16;17(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s12964-019-0347-1. Cell Commun Signal. 2019. PMID: 30992007 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel FOXM1 inhibitor identified via gene network analysis induces autophagic FOXM1 degradation to overcome chemoresistance of human cancer cells.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Jul 14;12(7):704. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-03978-0. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 34262016 Free PMC article.
-
Bortezomib inhibits growth and sensitizes glioma to temozolomide (TMZ) via down-regulating the FOXM1-Survivin axis.Cancer Commun (Lond). 2019 Dec 3;39(1):81. doi: 10.1186/s40880-019-0424-2. Cancer Commun (Lond). 2019. PMID: 31796105 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Laoukili J., Stahl M., and Medema R. H. (2007) FoxM1: at the crossroads of ageing and cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1775, 92–102 - PubMed
-
- Halasi M., and Gartel A. L. (2013) Targeting FOXM1 in cancer. Biochem. Pharmacol. 85, 644–652 - PubMed
-
- Radhakrishnan S. K., Bhat U. G., Hughes D. E., Wang I. C., Costa R. H., and Gartel A. L. (2006) Identification of a chemical inhibitor of the oncogenic transcription factor Forkhead Box M1. Cancer Res. 66, 9731–9735 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

