Prone position for acute respiratory failure in adults
- PMID: 26561745
- PMCID: PMC6464920
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD008095.pub2
Prone position for acute respiratory failure in adults
Abstract
Background: Acute hypoxaemia de novo or on a background of chronic hypoxaemia is a common reason for admission to intensive care and for provision of mechanical ventilation. Various refinements of mechanical ventilation or adjuncts are employed to improve patient outcomes. Mortality from acute respiratory distress syndrome, one of the main contributors to the need for mechanical ventilation for hypoxaemia, remains approximately 40%. Ventilation in the prone position may improve lung mechanics and gas exchange and could improve outcomes.
Objectives: The objectives of this review are (1) to ascertain whether prone ventilation offers a mortality advantage when compared with traditional supine or semi recumbent ventilation in patients with severe acute respiratory failure requiring conventional invasive artificial ventilation, and (2) to supplement previous systematic reviews on prone ventilation for hypoxaemic respiratory failure in an adult population.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL; 2014, Issue 1), Ovid MEDLINE (1950 to 31 January 2014), EMBASE (1980 to 31 January 2014), the Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature (CINAHL) (1982 to 31 January 2014) and Latin American Caribbean Health Sciences Literature (LILACS) (1992 to 31 January 2014) in Ovid MEDLINE for eligible randomized controlled trials. We also searched for studies by handsearching reference lists of relevant articles, by contacting colleagues and by handsearching published proceedings of relevant journals. We applied no language constraints, and we reran the searches in CENTRAL, MEDLINE, EMBASE, CINAHL and LILACS in June 2015. We added five new studies of potential interest to the list of "Studies awaiting classification" and will incorporate them into formal review findings during the review update.
Selection criteria: We included randomized controlled trials (RCTs) that examined the effects of prone position versus supine/semi recumbent position during conventional mechanical ventilation in adult participants with acute hypoxaemia.
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently reviewed all trials identified by the search and assessed them for suitability, methods and quality. Two review authors extracted data, and three review authors reviewed the data extracted. We analysed data using Review Manager software and pooled included studies to determine the risk ratio (RR) for mortality and the risk ratio or mean difference (MD) for secondary outcomes; we also performed subgroup analyses and sensitivity analyses.
Main results: We identified nine relevant RCTs, which enrolled a total of 2165 participants (10 publications). All recruited participants suffered from disorders of lung function causing moderate to severe hypoxaemia and requiring mechanical ventilation, so they were fairly comparable, given the heterogeneity of specific disease diagnoses in intensive care. Risk of bias, although acceptable in the view of the review authors, was inevitable: Blinding of participants and carers to treatment allocation was not possible (face-up vs face-down).Primary analyses of short- and longer-term mortality pooled from six trials demonstrated an RR of 0.84 to 0.86 in favour of the prone position (PP), but findings were not statistically significant: In the short term, mortality for those ventilated prone was 33.4% (363/1086) and supine 38.3% (395/1031). This resulted in an RR of 0.84 (95% confidence interval (CI) 0.69 to 1.02) marginally in favour of PP. For longer-term mortality, results showed 41.7% (462/1107) for prone and 47.1% (490/1041) for supine positions, with an RR of 0.86 (95% CI 0.72 to 1.03). The quality of the evidence for both outcomes was rated as low as a result of important potential bias and serious inconsistency.Subgroup analyses for mortality identified three groups consistently favouring PP: those recruited within 48 hours of meeting entry criteria (five trials; 1024 participants showed an RR of 0.75 (95% CI 0.59 to 94)); those treated in the PP for 16 or more hours per day (five trials; 1005 participants showed an RR of 0.77 (95% CI 0.61 to 0.99)); and participants with more severe hypoxaemia at trial entry (six trials; 1108 participants showed an RR of 0.77 (95% CI 0.65 to 0.92)). The quality of the evidence for these outcomes was rated as moderate as a result of potentially important bias.Prone positioning appeared to influence adverse effects: Pressure sores (three trials; 366 participants) with an RR of 1.37 (95% CI 1.05 to 1.79) and tracheal tube obstruction with an RR of 1.78 (95% CI 1.22 to 2.60) were increased with prone ventilation. Reporting of arrhythmias was reduced with PP, with an RR of 0.64 (95% CI 0.47 to 0.87).
Authors' conclusions: We found no convincing evidence of benefit nor harm from universal application of PP in adults with hypoxaemia mechanically ventilated in intensive care units (ICUs). Three subgroups (early implementation of PP, prolonged adoption of PP and severe hypoxaemia at study entry) suggested that prone positioning may confer a statistically significant mortality advantage. Additional adequately powered studies would be required to confirm or refute these possibilities of subgroup benefit but are unlikely, given results of the most recent study and recommendations derived from several published subgroup analyses. Meta-analysis of individual patient data could be useful for further data exploration in this regard. Complications such as tracheal obstruction are increased with use of prone ventilation. Long-term mortality data (12 months and beyond), as well as functional, neuro-psychological and quality of life data, are required if future studies are to better inform the role of PP in the management of hypoxaemic respiratory failure in the ICU.
Conflict of interest statement
Roxanna Bloomfield: none known.
David W Noble: none known.
Alexis Sudlow: none known.
Figures
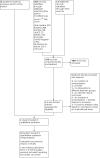



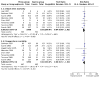

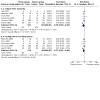
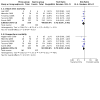
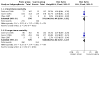
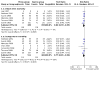
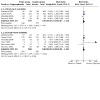

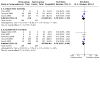
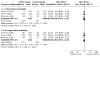

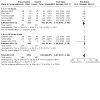
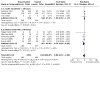
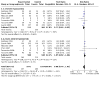

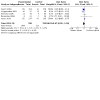




Update of
- doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008095
References
References to studies included in this review
Ayzac 2016 {published data only}
Chan 2007 {published data only}
-
- Chan MC, Hsu JY, Liu HH, Lee YL, Pong SC, Chang LY, et al. Effects of prone position on inflammatory parkers in patients with ARDS due to community-acquired pneumonia. Journal of the Formosan Medical Association 2007;106(9):708-16. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Chiumello 2012 {published data only}
Fernandez 2008 {published data only}
-
- Fernandez R, Trenchs X, Klamburg J, Castedo J, Serrano JM, Besso G, et al. Prone positioning in acute respiratory distress syndrome: a multicenter randomized clinical trial. Intensive Care Medicine 2008;34(8):1487-91. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Gattinoni 2001 {published data only}
-
- Gattinoni L, Tognoni G, Pesenti A, Taccone P, Mascheroni D, Labarta V, et al. Effect of prone positioning on the survival of patients with acute respiratory failure. New England Journal of Medicine 2001;345(8):568-73. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Girard 2014 {published data only}
-
- Girard R, Baboi L, Ayzac L, Richard J-C, Guerin C. The impact of patient positioning on pressure ulcers in patients with severe ARDS: results from a multicentre randomised controlled trial on prone positioning. Intensive Care Medicine 2014;40(3):397-403. [DOI: 10.1007/s00134-013-3188-1 ] [PMID: 24352484] - PubMed
Guerin 2004 {published data only}
-
- Guerin C, Gaillard S, Lemasson S, Ayzac L, Girard R, Beuret P, et al. Effects of systematic prone positioning in hypoxemic acute respiratory failure: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2004;292(19):2379-87. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Guerin 2013 {published data only}
Leal 1997 {published data only}
-
- Leal RP, Gonzales R, Gaona C, Garcia G, Maldonado A, Dominguez-Cherit G. Randomized trial compares prone v supine position in patients with ARDS. American Journal of Respiratory & Critical Care Medicine 1997;155:A745.
Mancebo 2006 {published data only}
-
- Mancebo J, Fernandez R, Blanch L, Rialp G, Gordo F, Ferrer M, et al. A multicenter trial of prolonged prone ventilation in severe acute respiratory distress syndrome. American Journal of Respiratory & Critical Care Medicine 2006;173(11):1233-9. [DOI: 10.1164/rccm.200503-353OC ] [PMID: ] - PubMed
Taccone 2009 {published data only}
-
- Taccone P, Pesenti A, Latini R, Polli F, Vagginelli F, Mietto C, et al. Prone positioning in patients with moderate and severe acute respiratory distress syndrome: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2009;302(18):1977-84. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Voggenreiter 2005 {published data only}
-
- Voggenreiter G, Aufmkolk M, Stiletto MJ, Baacke MG, Waydhas C, Ose C, et al. Prone positioning improves oxygenation in post-traumatic lung injury—A prospective randomized trial. Journal of Trauma 2005;59(2):333-43. [PMID: ] - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Beuret 2002 {published data only}
Cao 2014 {published data only}
-
- Cao FT, Wan F, Fan XC, et al. Effects of ventilation under prone position in the elderly with severe pneumonia combined with acute respiratory failure [俯卧位通气对合并急性呼吸衰竭的老年重症肺炎的影响]. Jiangsu Medical Journal 2014;40(5):578-80.
Charron 2011 {published data only}
-
- Charron C, Bouferrache K, Caille V, Castro S, Aegerter P, Page B, et al. Routine prone positioning in patients with severe ARDS: feasibility and impact on prognosis. Intensive Care Medicine 2011;37(5):785–90. [DOI: DOI 10.1007/s00134-011-2180-x] [PMID: ] - PubMed
Cheng 2016 {published data only}
-
- Cheng FQ, Zhao LH, Lan F, Jiang L,Zhao Xue Q,Wang H-Z. The application of prone position ventilation on elderly patients with severe pneumonia and respiratory failure [俯卧位通气在老年重症肺炎合并呼 吸衰竭中的应用]. Today Nurse 2016;10:20-1.
Curley 2005 {published data only}
Demory 2007 {published data only}
Li G 2015 {published data only}
-
- Li GZ. Clinical research of prone position ventilation on severe pneumonia patients [俯卧位与仰卧位机械通气治疗重症肺炎临床疗 效的比较研究]. Medical Frontier 2015;5(23):166-7. [DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1752.2015.23.155] - DOI
Li J 2015 {published data only}
-
- Li J, Xi JY. Comparative study for clinical effect on severe pneumonia between prone-position and supine-position mechanical ventilation [俯卧位机械通气应用于重症肺炎治疗的临床研究]. Practical Journal of Cardiac Cerebral Pneumal and Vascular Disease 2015;23(10):85-7. [DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-5971.2015.10.023.] - DOI
Papazian 2005 {published data only}
-
- Papazian L, Gainnier M, Marin V, Donati S, Arnal J-M, Demory D, et al. Comparison of prone positioning and high-frequency oscillatory ventilation in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Critical Care Medicine 2005;33:2162-71. [DOI: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000181298.05474.2B] [PMID: ] - DOI - PubMed
Peng 2018 {published data only}
-
- Peng X, He L, Chen J. Comparison of the curative effect of supine position and prone position ventilation combined with vibration sputumin* patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome (*sputum)? [急性呼吸窘迫综合征病人仰卧位、俯卧位通气联合振动排痰的疗效比较]. Chinese Nursing Research 2018;32(9):1387-92.
Wang 2015 {published data only}
-
- Wang WX, Dong Y, Xu B, et al. Impact of prone position on patients with late pregnancy combined with severe pneumonia in high altitude area [王文欣,董颖,徐波,等.高海拔地区晚期妊娠并重症肺炎剖宫 产术后患者俯卧位通气的临床应用[J].高原医学杂志]. Journal of High Altitude Medicine 2015;3:38-42.
Watanabe 2002 {published data only}
-
- Watanabe I, Fujihara H, Sato K, Honda T, Ohashi S, Endoh H, et al. Beneficial effect of a prone position for patients with hypoxemia after transthoracic esophagectomy. Critical Care Medicine 2002;30(8):1799-02. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Yan 2015 {published data only}
-
- Yan HS, Wang ZF. Treatment of prone and supine position ventilation on patients with severe pneumonia [俯卧位和仰卧位机械通气在重症肺炎治疗中 的应用效果研究]. Heilongjiang Med 2015;39(9):1021-2. [DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5775. 2015.09.012.]
Zhou 2014 {published data only}
-
- Zhou X, Liu D, Long Y, Zhang Q, Cui N, He H, et al. The effects of prone position ventilation combined with recruitment maneuvers on outcomes in patients with severe acute respiratory distress syndrome [Chinese]. Chung-Hua Nei Ko Tsa Chih Chinese Journal of Internal Medicine 2014;53(6):437-41. [PMID: ] - PubMed
References to ongoing studies
NCT03891212 {published data only}
-
- The Effect of Prone Position Drainage on the Efficacy of Severe Pneumonia, a Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03891212 First Posted 26 March 2019. [CLINICALTRIALS.GOV IDENTIFIER: NCT03891212]
NCT04139733 {published data only}
-
- Early Use of Prone Position in ECMO for Severe ARDS. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04139733 First Posted 25 October 2019. [CLINICALTRIALS.GOV IDENTIFIER: NCT04139733]
NCT04607551 {published data only}
-
- PRONing to Facilitate Weaning From ECMO in Patients With Refractory Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (PRONECMO). https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04607551 First Posted: 29 October 2020. [CLINICALTRIALS.GOV IDENTIFIER: NCT04607551]
Additional references
Abroug 2008
-
- Abroug F, Ouanes-Besbes L, Elatrous S, Brochard L. The effect of prone positioning in acute respiratory distress syndrome or acute lung injury: a meta-analysis. Areas of uncertainty and recommendations for research. Intensive Care Medicine 2008;34(6):1002–11. [DOI: 10.1007/s00134-008-1062-3] [PMID: ] - DOI - PubMed
Abroug 2011
Adhikari 2004
Adhikari 2007
Alsaghir 2008
-
- Alsaghir AH, Martin CM. Effect of prone positioning in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome: a meta-analysis. Critical Care Medicine 2008;36(2):603-9. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Aoyama 2019
-
- Aoyama H, Uchida K, Aoyama K, Pechlivanoglou P, Englesakis M, Yamada Y, et al. Assessment of Therapeutic Interventions and Lung ProtectiveVentilation in Patients With Moderate to Severe Acute RespiratoryDistress Syndrome. A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis. JAMA Network Open 2019;2(7):e198116. [DOI: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.8116] [PMID: ] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
ARDS definition workforce 2012
-
- The ARDS Definition Workforce. Acute respiratory distress syndrome: the Berlin definition. JAMA 2012;307(23):2526-33. [DOI: 10.1001/jama.2012.5669 ] - PubMed
ARDSnet 2006a
-
- The National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) Clinical Trials Network. Comparison of two fluid-management strategies in acute lung injury. New England Journal of Medicine 2006;354(24):2564-75. [PMID: ] - PubMed
ARDSnet 2006b
-
- The National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) Clinical Trials Network. Efficacy and safety of corticosteroids for persistent acute respiratory distress syndrome. New England Journal of Medicine 2006;354(16):1671-84. [PMID: ] - PubMed
ARDS Network 2000
-
- The Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Network. Ventilation with lower tidal volumes as compared with traditional tidal volumes for acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome. New England Journal of Medicine 2000;342(18):1301-8. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Ay 2020
-
- Ay E, Weigand MA, Röhrig R, Gruss M. Dying in the Intensive Care Unit (ICU): A Retrospective Descriptive Analysis of Deaths in the ICU in a Communal Tertiary Hospital in Germany. Anesthesiology Research and Practice 2020;2020:Article ID 2356019. [DOI: 10.1155/2020/2356019] [PMID: ] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Ayoubieh 2014
-
- Ayoubieh H, Alkhalili E, Kassis YE, Faza N, Khalaf S, Lystad L, et al. Ischemic optic neuropathy after prone ventilation for ARDS. Critical Care Medicine 2014;42(Suppl 1):A1641-A1642. [DOI: 10.1097/01.ccm.0000458670.13219.ba] [EMBASE: 71707880] - DOI
Ball 1999
-
- Ball C. Use of prone position in management of acute respiratory failure. Clinical Effectiveness in Nursing 1999;3:36-46.
Bassler 2010
-
- Bassler D, Briel M, Montori VM, Lane M, Glasziou P, Zhou Q, et al. Stopping randomized trials early for benefit and estimation of treatment effects: systematic review and meta-regression analysis. JAMA 2010;303(12):1180-7. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Baston 2019
Beitler 2014
-
- Beitler JR, Shaefi S, Montesi SB, Devlin A, Loring SH, Talmor D, et al. Prone positioning reduces mortality from acute respiratory distress syndrome in the low tidal volume era: a meta-analysis. Intensive Care Medicine 2014;40(3):332-41. [DOI: 10.1007/s00134-013-3194-3 ] [PMID: 24435203] - PMC - PubMed
Bellani 2016
Bent 2006
-
- Bent S, Padula, Avins AL. Brief communication: better ways to question patients about adverse medical events: a randomized, controlled trial. Annals of Internal Medicine 2006;144(4):257-61. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Bernard 2005
Bernard 2017
Bloomfield 2006
-
- Bloomfield R, Steel E, MacLennan G, Noble DW. Accuracy of weight and height estimation in an intensive care unit: implications for clinical practice and research. Critical Care Medicine 2006;34(8):2153-7. [PMID: 16763505 ] - PubMed
Bloomfield 2014
Borenstein 2019
-
- Borenstein M. Common mistakes in meta-analysis and how to avoid to avoid them. 1st edition. New Jersey: Biostat Inc., 2019. [ISBN 978-1-7334367-1-7]
Chan 2008
-
- Chan M, Hsu J, Liu H, Lee Y, Pong S, Chan L, et al. Reply to Friederich et al. Journal of the Formosan Medical Association 2008;107(2):192.
Chang 2014
-
- Chang H-C, Chien H-T, Hwu J-Y. Effects of Prone Positioning on Oxygenation and Complications in Patients With Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) in the Intensive Care Unit: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis [俯臥對加護病房急性呼吸窘迫症候群病人之氧合與合併症成效—系統性回顧暨統合分析]. Journal of Nursing & Healthcare Research 2014;10(3):178-189. [DOI: 10.6225/JNHR.10.3.178 ]
Chatte 1997
-
- Chatte G, Sab JM, Dubois JM, Sirodot M, Gaussorgues P, Robert D. Prone position in mechanically ventilated patients with severe acute respiratory failure. American Journal of Respiratory & Critical Care Medicine 1997;155(2):473-8. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Cheifetz 2017
Cheung 2020
Chiumello 2016
Claesson 2015
-
- Claesson J, Freundlich M, Gunnarsson I, Laake JH, Vandvik PO, Varpula T, et al. Scandinavian clinical practice guideline on mechanical ventilation in adults with the acute respiratory distress syndrome. Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica 2015;59(3):286-97. [DOI: 10.1111/aas.12449] [PMID: ] - DOI - PubMed
Constantin 2019
-
- Constantin J-M, Jabaudon M, Lefrant J-Y, Jaber S, Quenot J-P, Langeron O, et al for the AZUREA network. Personalised mechanical ventilation tailored to lung morphology versus low positive end-expiratory pressure for patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome in France (the LIVE study): a multicentre, single-blind, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Respiratory Medicine 2019;7(10):870-80. [DOI: 10.1016/S2213-2600(19)30138-9] [PMID: ] - DOI - PubMed
Counsell 1994
Cranshaw 2002
Cummings 2013
-
- Cummings SR, Grady D, Hulley SB. Designing a randomized blinded trial. In: Hulley SB, Cummings SR, Browner WS, Grady DG, Newman TB, editors(s). Designing Clinical Research. 4th edition. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2013:145-149. [ISBN 978-1-60831-804-9]
Curley 1999
-
- Curley MAQ. Prone positioning of patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome: a systematic review. American Journal of Critical Care 1999;8(6):397-405. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Dalmedico 2017
-
- Dalmedico MM, Salas D, Maciel de Oliveira A, Baran FDP, Meardi JT, Santos MC. Efficacy of prone position in acute respiratory distress syndrome: overview of systematic reviews. Revista da Escola de Enfermagem da USP (Journal of the School of Nursing, University of Sao Paulo) 2017;51:e03251. [DOI: ] [PMID: ] - PubMed
Deeks 2011
-
- Deeks JJ, Higgins JPT, Altman DG, on behalf of the Cochrane Statistical Methods Group. Chapter 9: Analysing data and undertaking meta-analyses. In: Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. www.cochrane-handbook.org. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 2011.
Deeks 2019
-
- Deeks JJ, Higgins JPT, Altman DG. Analysing data and undertaking meta-analyses. In: Higgins JPT Thomas J, editors(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Second edition. Chichester: Wiley Blackwell, 2019:241-284. [ISBN 9781119536628]
de Hemptinne 2009
Diaz 2010
Du 2018
Faculty of Intensive Care 2019
-
- Bamford P, Denmore C, Newmarch C, Shirley P, Singer B, Webb S, et al. Guidance for: prone positioning in adult critical care. Faculty of Intensive Care Medicine (UK) 2019:1-40.
Fan 2010
Fan 2017
-
- Fan E, Del Sorbo L, Goligher EC, Hodgson CL, Munshi L, Walkey AJ et al. An Official American Thoracic Society / European Society of Intensive Care Medicine / Society of Critical Care Medicine Clinical Practice Guideline: Mechanical Ventilation in Adult Patients with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. American Journal of Respiratory & Crititical Care Medicine 2017;195(9):1253-63. [DOI: 10.1164/rccm.201703-0548ST] [PMID: ] - DOI - PubMed
Ferguson 2013
-
- Ferguson ND, Cook DJ, Guyatt GH, Mehta S, Hand L, Austin P, et al. High-frequency oscillation in early acute respiratory distress syndrome. New England Journal of Medicine 2013;368(9):795-805. [DOI: DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1215554] [PMID: ] - PubMed
Ferrand 2001
-
- Ferrand E, Robert R, Ingrand P, Lemaire F, for the French LATAREA group. Withholding and withdrawal of life support in intensive-care units in France: a prospective survey. Lancet 2001;357(9249):9-14. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Festic 2016
Fielding‐Singh 2018
Fleiss 1986
-
- Fleiss JL. The Design and Analysis of Clinical Experiments. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 1986. [ISBN 0-471-82047-4]
Fletcher 2005
-
- Fletcher RW, Fletcher SW. Cause. In: Clinical Epidemiology. The Essentials. 4th edition. Philadelphia: Lippincott William & Wilkins, 2005:199-201. [ISBN 0-7817-5215-9]
Forbes 2013
Frieden 2017
Friedman 1998
-
- Friedman LM, Furberg CD, DeMets DL. Fundamentals of Clinical Trials. 3rd edition. New York: Springer Verlag, 1998. [ISBN 0-387-98586-7]
Gattinoni 2006
-
- Gattinoni L, Valenza F, Pelosi P, Mascheroni D. Prone positioning in acute respiratory failure. In: Tobin MJ, editors(s). Principles and Practice of Mechanical Ventilation. 2nd edition. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2006:1081-92.
Gattinoni 2010
-
- Gattinoni L, Carlesso E, Taccone P, Pollo F, Guerin C, Mancebo J. Prone positioning improves survival in ARDS: a pathophysiologic review and individual patient meta-analysis. Minerva Anestesiologica 2010;76(6):448-54. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Gattinoni 2012
-
- Gattinoni L, Carlesso E, Caironi P. Stress and strain within the lung. Current Opinion in Critical Care 2012;18(1):42-7. [DOI: ] [PMID: ] - PubMed
Gattinoni 2013
-
- Gattinoni L, Taccone P, Carlesso E, Marini JJ. Prone position in acute respiratory distress syndrome: rationale, indications, and limits. American Journal of Respiratory Critical Care Medicine 2013;188(11):1286-93. [DOI: 10.1164/rccm.201308-1532CI ] [PMID: ] - PubMed
Gillies 2012
Glantz 2005
-
- Glantz SA. Primer of biostatistics: The program version 6.0. 6th edition. New York: McGraw Hill, 2005. [ISBN 0-07-143822-X]
Goettler 2002
Goodwin 2012
Graf 2008
-
- Graf J, Marini JJ. Do airway secretions play an under appreciated role in acute respiratory distress syndrome? Current Opinion in Critical Care 2008;14(1):44-9. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Graham 2020
Griffiths 2019
Gristina 2018
Guerin 2006
-
- Guerin C. Ventilation in the prone position in patients with acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome. Current Opinion in Critical Care 2006;12(1):50-4. [MEDLINE: ] [PMID: ] - PubMed
Guerin 2014
-
- Guerin C, Baboi L, Richard JC. Mechanisms of prone positioning in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Intensive Care Medicine 2014;40(11):1634-42. [DOI: 10.1007/s00134-014-3500-8 ] [PMID: ] - PubMed
Guyatt 2008
Guyatt 2008a
-
- Guyatt G, Rennie D, Meade MO, Cook DJ. Users' Guides to the Medical Literature. Essentials of Evidence-Based Practice. 2nd Edition. Toronto: McGraw-Hill, 2008. [ISBN 978-0-07-159038-9]
Guyatt 2011a
Guyatt 2011b
-
- Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Kunz R, Brozek J, Alonso-Coello P, Rind D, et al. GRADE guidelines 6. Rating the quality of evidence - imprecision. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2011;64(12):1283-93. [PMID: 21839614] - PubMed
Guyatt 2011c
Hanley 1983
-
- Hanley JA, Lippman-Hand A. If nothing goes wrong, is everything all right? Interpreting zero numerators. JAMA 1983;249(13):1743-5. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Hashimoto 2017
Hatala 2005
-
- Hatala R, Keitz S, Wyer P, Guyatt G, Evidence-Based Medicine Teaching Tips Working Group. Tips for learners of evidence-based medicine: 4. Assessing heterogeneity of primary studies in systematic reviews and whether to combine their results. CMAJ : Canadian Medical Association journal = journal de l'Association medicale canadienne 2005;172(5):661-5. [PMID: ] - PMC - PubMed
Hernan 2017
Herridge 2011
-
- Herridge MS, Tansey CM, Matté A, Tomlinson G, Diaz-Granados N, Cooper A, et al. Functional disability 5 years after acute respiratory distress syndrome. New England Journal of Medicine 2011;364(14):1293-304. [PMID: 21470008] - PubMed
Higgins 2003
Higgins 2011a
-
- Higgins JPT, Altman DG, Sterne JC. Assessing risk of bias. In: Higgins JPT, Green S, editors(s). Cochrane Handbook of Systematic Reviews for Interventions. 5.1.0 edition. Chichester: Wiley, March 2011.
Higgins 2011b
-
- Higgins JPT, Deeks J. Chapter 7: Selecting studies and collecting data. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. New York: Wiley-Blackwell, Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011].
Ho 2020
Hough 2012
Hu 2014
Iftikhar 2015
IntHout 2014
Ioannidis 2006
-
- Ioannidis JP, Mulrow CD, Goodman SN. Adverse events: the more you search, the more you find. Annals of Internal Medicine 2006;114(4):298-300. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Ioannidis 2016
Iwashyna 2010
-
- Iwasyna TJ. Survivorship will be the defining challenge of critical care in the 21st century. Annals of Internal Medicine 2010;153(3):204-5. [DOI: ] [PMID: 20679565] - PubMed
Jadad 2007
-
- Jadad AR, Enkin MW. Bias in Randomized Controlled Trials. In: Randomized Controlled Trials - Questions, Answers and Musings. 2nd edition. Oxford: Blackwell, BMJ Books, 2007:29-47. [ISBN 978-1-4051-3266-4]
Karanicolas 2010
Klein 2004
-
- Klein Y, Blackbourne L, Barquist ES. Non-ventilatory-based strategies in the management of acute respiratory distress syndrome. Journal of Trauma, Injury, Infection and Critical Care 2004;57(4):915-24. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Klompas 2008
KNAW 2018
-
- KNAW (Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences). Replication studies – Improving reproducibility in the empirical sciences. Amsterdam: KNAW, 2018. [ISBN 978-90-6984-720-7]
Kneyber 2014
Kopterides 2009
-
- Kopterides P, Siempos II, Armaganidis A. Prone positioning in hypoxemic respiratory failure: meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Journal of Critical Care 2009;24(1):89-100. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Lagakos 2006
-
- Lagakos SW. The challenge of subgroup analyses - Reporting without distorting. New England Journal of Medicine 2006;354:1667-9. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Lamas 2014
Lee 2014
-
- Lee JM, Bae W, Lee YJ, Cho Y-J. The efficacy and safety of prone positional ventilation in acute respiratory distress syndrome: updated study-level meta-analysis of 11 randomized controlled trials. Critical Care Medicine 2014;42(5):1252-62. [DOI: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000000122] [PMID: ] - DOI - PubMed
Lefebvre 2019
-
- Lefebvre C, Glanville J, Briscoe S, Littlewood A, Marshall C, Metzendorf M-I, Noel-Storr A, Rader T, Shokraneh F, Thomas J, Wieland LS. Chapter 4: Searching for and selecting studies. In: Higgins JPT, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Welch VA (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 6.0 (updated July 2019). Cochrane, 2019. [AVAILABLE AT:: https://training.cochrane.org/handbook/current/chapter-04]
Lipsey 1990
-
- Lipsey MW. Design sensitivity: Statistical power for experimental research. London: Sage, 1990.
MacCallum 2005
-
- MacCallum NS, Evans TE. Epidemiology of acute lung injury. Current Opinion in Critical Care 2005;11(1):43-9. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Marini 2008
Marini 2010
-
- Marini JJ. Can we prevent the spread of focal lung inflammation? Critical Care Medicine 2010;38(10 Suppl):S574-81. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Marini 2020
Mark 2015
Matthay 2019
Mentzelopoulos 2005
-
- Mentzelopoulos SD, Roussos C, Zakynthinos SG. Prone position reduces lung stress in severe acute respiratory distress syndrome. European Respiratory Journal 2005;25(3):534-44. [MEDLINE: 15738300 ] [PMID: ] - PubMed
Moher 2009
Mora‐Arteaga 2015
-
- Mora-Arteaga JA, Bernal-Ramírez OJ, Rodríguez SJ. The effects of prone position ventilation in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome. A systematic review and metaanalysis. Medicina Intensiva 2015;39(6):359-72. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Morgan 2014
Munshi 2017
-
- Munshi L, Del Sorbo L, Adhikari NKJ, Hodgson CL, Wunsch H, Meade MO, et al. Prone position for acute respiratory distress syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Annals of the American Thoracic Society 2017;14(4 Suppl):S280-8. [DOI: DOI: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201704-343OT] - PubMed
Mure 2001
-
- Mure M, Lindahl SGE. Prone position improves gas exchange – but how? Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica 2001;45(2):150-9. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Mustafa 2013
Møller 2017
Needham 2012
Noah 2011
-
- Noah MA, Peek GJ, Finney SJ, Griffiths MJ, Harrison DA, Grieve R, et al. Referral to an extracorporeal membrane oxygenation center and mortality among patients with severe 2009 influenza A(H1N1). JAMA 2011;306(15):1659-68. [PMID: 21976615 ] - PubMed
Noble 2004
Noble 2010
-
- Noble DW, Peek GJ. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for respiratory failure: past, present and future. Anaesthesia 2010;65(10):971-4. [PMID: ] - PubMed
O'Brien 2011
Oxman 1992
-
- Oxman AD, Guyatt GH. A consumer's guide to subgroup analyses. Annals of Internal Medicine 1992;116(1):78-84. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Oxman 2012
Packer 2016
-
- Packer M. The room where it happens: a skeptic’s analysis of the New Heart Failure Guidelines. Journal of Cardiac Failure 2016;22(9):726-30. [DOI: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2016.07.433 ] [PMID: ] - PubMed
Papazian 2010
-
- Papazian L, Forel JM, Gacouin A, Penot-Ragon C, Perrin G, Loundou A, et al. Neuromuscular blockers in early acute respiratory distress syndrome. New England Journal of Medicine 2010;363(12):1107-16. [PMID: 20843245 ] - PubMed
Park 2015
-
- Park SY, Kim HJ, Yoo KH, Park YB, Kim SW, Lee SJ, et al. The efficacy and safety of prone positioning in adults patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Journal of Thoracic Diseases 2015;7(3):356-67. [DOI: 10.3978/j.issn.2072-1439.2014.12.49] [PMID: 25922713] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Petrucci 2013
Phua 2009
-
- Phua J, Badia JR, Adhikari NKJ, Friedrich JO, Fowler RA, Singh JM, et al. Has mortality from acute respiratory distress syndrome decreased over time? A systematic review. American Journal of Respiratory & Critical Care Medicine 2009;179(3):220-7. [DOI: 10.1164/rccm.200805-722OC ] [PMID: ] - PubMed
Porta 2008
-
- Porta M (ed). A Dictionary of Epidemiology. 5th edition. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2008.
Psaty 2010
-
- Psaty BM, Prentice RL. Minimizing bias in randomized trials: the importance of blinding. JAMA 2010;304(7):793-4. [MEDLINE: ] [PMID: ] - PubMed
Reade 2008
Reade 2010
Reilly 2019
RevMan 5.40 [Computer program]
-
- Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.40 for Windows. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2020.
Rezoagli 2017
Riley 2010
Rivas‐Fernandez 2016
Robba 2020
Rubenfeld 2007
Sheiner 1995
-
- Sheiner LB, Rubin DB. Intention-to-treat-analysis and the goals of clinical trials. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 1995;57(1):6-15. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Sim 2014
-
- Sim YS, Jung H, Shin TR, Kim DG, Park SM. The efficacy and safety of prone positioning in adult patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Respirology (2014) 19 (Suppl. 3), 63–253 2014;19(Suppl 3):79. [DOI: doi: 10.1111/resp.12417]
Slutsky 2013
-
- Slutsky AS, Ranieri VM. Ventilator- induced lung injury. New England Journal of Medicine 2013;369(22):2126-36. [DOI: DOI: 10.1056/NEJMra1208707] [PMID: ] - PubMed
Soni 2008
Soni 2010
-
- Soni N. ARDS, acronyms and the Pinocchio effect. Anaesthesia 2010;65(10):976-9. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Soo Hoo 2013
Stapleton 2005
-
- Stapleton RD, Wang BM, Hudson LD, Rubenfeld GD, Caldwell ES, Steinberg KP. Causes and timing of death in patients with ARDS. Chest 2005;128(2):525-32. [PMID: 16100134] - PubMed
Stevens 2014
Stewart 2015
-
- Stewart LA, Clarke M, Rovers M, Riley RD, Simmonds M, Stewart G, et al for the PRISMA-IPD Development Group. Preferred reporting items for a systematic review and meta-analysis of Individual participant data. The PRISMA-IPD Statement. JAMA 2015;313(16):1657-65. [DOI: 10.1001/jama.2015.3656] [PMID: ] - DOI - PubMed
Strachan 2001
-
- Strachan L, Noble DW. Hypoxia and surgical patients - prevention and treatment of an unnecessary cause of morbidity and mortality. Journal of The Royal College of Surgeons of Edinburgh 2001;46(5):297-302. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Strom 2006
Sud 2008
-
- Sud S, Sud M, Friedrich JO, Adhikari NK. Effect of mechanical ventilation in the prone position on clinical outcomes in patients with acute hypoxemic respiratory failure: a systematic review and meta-analysis. CMAJ Canadian Medical Association Journal 2008;178(9):1153-61. [PMID: 18427090 ] - PMC - PubMed
Sud 2008a
-
- Sud S, Sud M, Friedrich JO, Adhikari NKJ. Effect of mechanical ventilation in the prone position on clinical outcomes in patients with acute hypoxemic respiratory failure: a systematic review and meta-analysis. CMAJ : Canadian Medical Association journal = journal de l'Association medicale canadienne 2008;178(9):1153-61. [DOI: 10.1503/cmaj.071802 ] [PMID: 18427090 ] - PMC - PubMed
Sud 2008b
Sud 2010
-
- Sud S, Friedrich JO, Taccone P, Polli F, Adhikari NKJ, Latini R, et al. Prone ventilation reduces mortality in patients with acute respiratory failure and severe hypoxemia: systematic review and meta-analysis. Intensive Care Medicine 2010;36(4):585-99. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Sud 2011
Sud 2011a
-
- Sud S, Friederich J, Sud M, Adhikari N. Meta-Analysis, Meta-Regression, And Patient- And Trial- Level Data Subgroup Analysis: An Example of Ecological Bias In A Meta-Analysis Of Prone Ventilation In Patients With Severe Hypoxemic RespiratoryFailure Due To ALI/ARDS. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2011;183:A3738.
Sud 2013
-
- Sud S, Sud M, Friederich JO, Wunsch H, Meade MO, Ferguson ND, et al. High-frequency ventilation versus conventional ventilation for treatment of acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2013, Issue 2. Art. No: CD004085. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD004085.pub3] [PMID: ] - DOI - PubMed
Sud 2014
-
- Sud S, Friedrich JO, Adhikari NK, Taccone P, Mancebo J, Polli F, et al. Effect of prone positioning during mechanical ventilation on mortality among patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. CMAJ : Canadian Medical Association journal = journal de l'Association medicale canadienne 2014;186(10):E381-90. [PMID: ] - PMC - PubMed
Sun 2014
Tabula 2015
-
- Tabula J, Ordillo LS, Remalante PP, Wang A. The effect of prone versus supine positioning in mortality among adult patients with moderate to severe acute respiratory distress syndrome: a meta-analysis. Intensive Care Medicine Experimental 2015;3(Suppl 1):A93. [DOI: ]
Tekwani 2014
The Academy of Medical Sciences 2015
-
- Bishop D, Cantrell D, Johnson P, Kapur S, Macleod M, Savage C et al. Reproducibility and reliability of biomedical research: Improving research practice - Symposium Report. The Academy of Medical Sciences 2015:1-77.
Thomas 2013
Tierney 2019
-
- Tierney JF, Stewart LA, Clarke M. Ch 26: Individual Participant Data. In: Higgins JPT Thomas J, editors(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. 2nd edition. Chichester: Wiley Blackwell, 2019:643-658. [ISBN 9781119536628]
Tiruvoipati 2008
-
- Tiruvoipati R, Bangash M, Manktelow B, Peek GJ. Efficacy of prone ventilation in adult patients with acute respiratory failure: a meta-analysis. Journal of Critical Care 2008;23(1):101-10. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Tonelli 2014
-
- Tonelli AR, Zein J, Adams J, Ioannidis JPA. Effects of Interventions on Survival in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: an Umbrella Review of 159 Published Randomized Trials and 29 Meta-analyses. Intensive Care Medicine 2014;40(6):769-87. [DOI: 10.1007/s00134-014-3272-1] [PMID: ] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Turnbull 2014
Uribe 2012
-
- Uribe AA, Baig MA, Puente EG, Viloria A, Mendel E, Bergese SD. Current intraoperative devices to reduce visual loss after spine surgery. Neurosurgical Focus 2012;33(2):E14. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Venet 2003
-
- Venet C, Guyomarc'h S, Pingat J, Michard C, Laporte S, Bertrand M, et al. Prognostic factors in acute respiratory distress syndrome: a retrospective multivariate analysis including prone positioning in management strategy. Intensive Care Medicine 2003;29(9):1435-41. [PMID: 12827238] - PubMed
Verbrugge 2007
-
- Verbrugge SJC, Lachmann B, Kesecioglu J. Lung protective ventilatory strategies in acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome: from experimental findings to clinical application. Clinical Physiology and Functional Imaging 2007;27(2):67-90. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Walkey 2012
Wang 2014
Ware 2000
-
- Ware LB, Matthay MA. Acute respiratory distress syndrome. New England Journal of Medicine 2000;342(18):1334-49. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Weissman 1997
-
- Weissman C. Analyzing intensive care unit length of stay data: problems and possible solutions. Critical Care Medicine 1997;25(9):1594-600. [PMID: ] - PubMed
Williams 2008
Wilson 2020
Wunsch 2010
Yankech 2017
-
- Yankech L, Campbell C. Does the use of prone positioning improve survival in patients with ARDS. Canadian Journal of Respiratory Therapy 2017;53 (poster abstracts)(3):53.
Young 2013
-
- Young D, Lamb SE, Shah S, MacKenzie I, Tunnicliffe W, Lall R, et al. High-frequency oscillation for acute respiratory distress syndrome. New England Journal of Medicine 2013;368(9):806-13. [DOI: DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1215716] [PMID: ] - PubMed
Yue 2017
-
- Yue W, Zhang Z, Zhang C, YangL, He J, Hou Y, et al. Effect of prone positioning ventilation for mortality in severe acute respiratory distress syndrome patients: a cumulative meta-analysis [俯卧位通气治疗急性呼吸窘迫综合征患者病死率的累积 Meta 分析]. Chinese Journal of Evidence-based Medicine 2017;17(7):792-7. [DOI: 10.7507/1672-2531.201702002] - DOI
References to other published versions of this review
Bloomfield 2009
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

