Medical 3D Printing for the Radiologist
- PMID: 26562233
- PMCID: PMC4671424
- DOI: 10.1148/rg.2015140320
Medical 3D Printing for the Radiologist
Abstract
While use of advanced visualization in radiology is instrumental in diagnosis and communication with referring clinicians, there is an unmet need to render Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine (DICOM) images as three-dimensional (3D) printed models capable of providing both tactile feedback and tangible depth information about anatomic and pathologic states. Three-dimensional printed models, already entrenched in the nonmedical sciences, are rapidly being embraced in medicine as well as in the lay community. Incorporating 3D printing from images generated and interpreted by radiologists presents particular challenges, including training, materials and equipment, and guidelines. The overall costs of a 3D printing laboratory must be balanced by the clinical benefits. It is expected that the number of 3D-printed models generated from DICOM images for planning interventions and fabricating implants will grow exponentially. Radiologists should at a minimum be familiar with 3D printing as it relates to their field, including types of 3D printing technologies and materials used to create 3D-printed anatomic models, published applications of models to date, and clinical benefits in radiology. Online supplemental material is available for this article.
(©)RSNA, 2015.
Figures

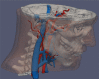
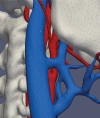
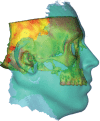

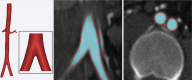

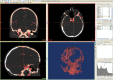




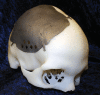
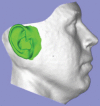
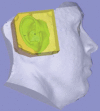



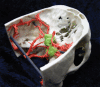
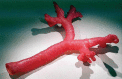
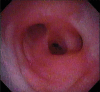

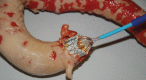
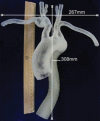


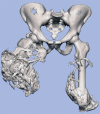

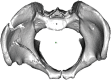



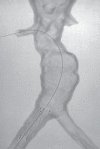



Comment in
-
Three-dimensional Physical Modeling: Applications and Experience at Mayo Clinic.Radiographics. 2015 Nov-Dec;35(7):1989-2006. doi: 10.1148/rg.2015140260. Radiographics. 2015. PMID: 26562234
-
RadioGraphics Update: Medical 3D Printing for the Radiologist.Radiographics. 2020 Jul-Aug;40(4):E21-E23. doi: 10.1148/rg.2020190217. Radiographics. 2020. PMID: 32609597
References
-
- Fishman EK, Drebin B, Magid D, et al. . Volumetric rendering techniques: applications for three-dimensional imaging of the hip. Radiology 1987;163(3):737–738. - PubMed
-
- Rubin GD, Dake MD, Napel SA, McDonnell CH, Jeffrey RB, Jr. Three-dimensional spiral CT angiography of the abdomen: initial clinical experience. Radiology 1993;186(1): 147–152. - PubMed
-
- Wohlers Associates, Inc . Wohlers report 2013: additive manufacturing and 3D printing state of the industry. Fort Collins, Colo: Wohlers Associates, Inc, 2013.
-
- Mitsouras D, Dill KE, Kumamaru KK, Steigner ML, Rybicki FJ, III. 3-D printing: bridging the gap between theory and practice [abstr]. In: Radiological Society of North America Scientific Assembly and Annual Meeting Program. Oak Brook, Ill: Radiological Society of North America, 2013; 109.
-
- Hiller J, Lipson H. STL 2.0: a proposal for a universal multi-material Additive Manufacturing File format. Proceedings of the Solid Freeform Fabrication Symposium 2009. Austin, Texas, 2009; 266–278.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

