Down, But Not Out: Partial Elimination of Androgen Receptors in the Male Mouse Brain Does Not Affect Androgenic Regulation of Anxiety or HPA Activity
- PMID: 26562258
- PMCID: PMC5393364
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2015-1417
Down, But Not Out: Partial Elimination of Androgen Receptors in the Male Mouse Brain Does Not Affect Androgenic Regulation of Anxiety or HPA Activity
Abstract
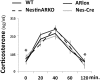
We previously found that androgen receptor (AR) activity mediates two effects of T in adult male mice: reduction of anxiety-like behaviors and dampening of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal response to stress. To determine whether brain ARs mediate these effects, we used the Cre/loxP technology seeking to disable AR throughout the central nervous system (CNS). Female mice carrying the floxed AR allele (ARlox) were crossed with males carrying cre recombinase transgene controlled by the nestin promoter (NesCre), producing cre in developing neurons and glia. Among male offspring, four genotypes resulted: males carrying ARlox and NesCre (NesARko), and three control groups (wild types, NesCre, and ARlox). Reporter mice indicated ubiquitous Cre expression throughout the CNS. Nevertheless, AR immunocytochemistry in NesARko mice revealed efficient knockout (KO) of AR in some brain regions (hippocampus and medial prefrontal cortex [mPFC]), but not others. Substantial AR protein was seen in the amygdala and hypothalamus among other regions, whereas negligible AR remained in others like the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis and dorsal periaqueductal gray. This selective KO allowed for testing the role of AR in hippocampus and mPFC. Males were castrated and implanted with T at postnatal day 60 before testing on postnatal day 90-100. In contrast with males with global KO of AR, T still modulated anxiety-related behavior and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal activity in NesARko males. These results leave open the possibility that AR acting in the CNS mediates these effects of T, but demonstrate that AR is not required in the hippocampus or mPFC for T's anxiolytic effects.
Figures


References
-
- Greenberg PE, Sisitsky T, Kessler RC, et al. . The economic burden of anxiety disorders in the 1990s. J Clin Psychiatry. 1999;60(7):427–435. - PubMed
-
- Zahn-Waxler C, Shirtcliff EA, Marceau K. Disorders of childhood and adolescence: Gender and psychopathology. Annu Rev Clin Psychol. 2008;4:275–303. - PubMed
-
- Menger Y, Bettscheider M, Murgatroyd C, Spengler D. Sex differences in brain epigenetics. Epigenomics. 2010;2(6):807–821. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

