Combined ultra-low input mRNA and whole-genome sequencing of human embryonic stem cells
- PMID: 26564201
- PMCID: PMC4643517
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-015-2025-z
Combined ultra-low input mRNA and whole-genome sequencing of human embryonic stem cells
Abstract
Background: Next Generation Sequencing has proven to be an exceptionally powerful tool in the field of genomics and transcriptomics. With recent development it is nowadays possible to analyze ultra-low input sample material down to single cells. Nevertheless, investigating such sample material often limits the analysis to either the genome or transcriptome. We describe here a combined analysis of both types of nucleic acids from the same sample material.
Methods: The method described enables the combined preparation of amplified cDNA as well as amplified whole-genome DNA from an ultra-low input sample material derived from a sub-colony of in-vitro cultivated human embryonic stem cells. cDNA is prepared by the application of oligo-dT coupled magnetic beads for mRNA capture, first strand synthesis and 3'-tailing followed by PCR. Whole-genome amplified DNA is prepared by Phi29 mediated amplification. Illumina sequencing is applied to short fragment libraries prepared from the amplified samples.
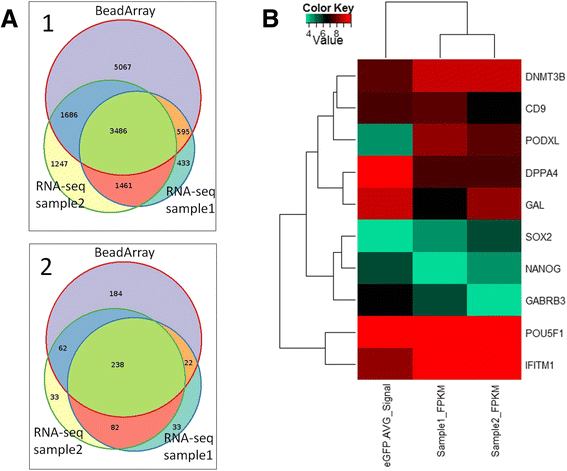
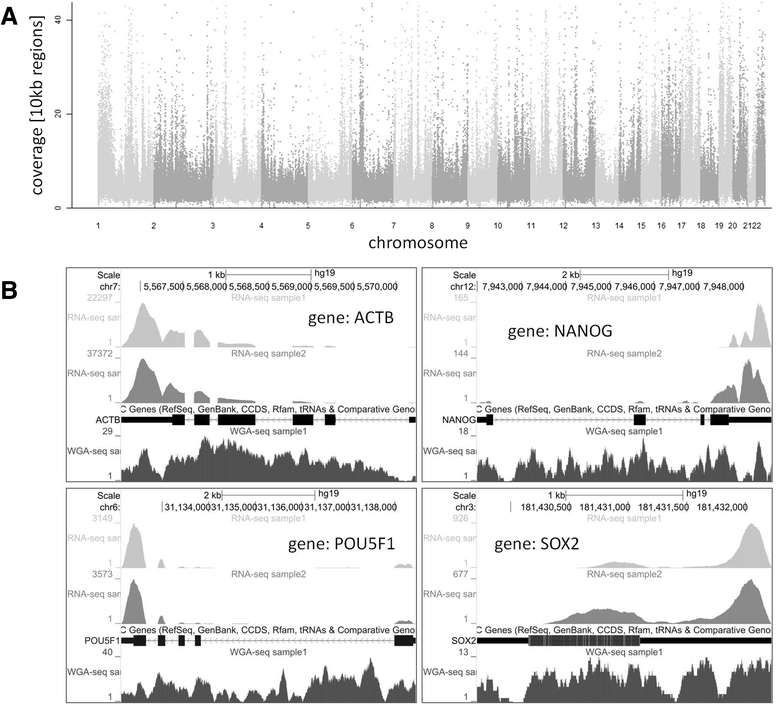
Results: We developed a protocol which enables the combined analysis of the genome as well as the transcriptome by Next Generation Sequencing from ultra-low input samples. The protocol was evaluated by sequencing sub-colony structures from human embryonic stem cells containing 150 to 200 cells. The method can be adapted to any available sequencing system.
Conclusions: To our knowledge, this is the first report where sub-colonies of human embryonic stem cells have been analyzed both at the genomic as well as transcriptome level. The method of this proof of concept study may find useful practical applications for cases where only a limited number of cells are available, e.g. for tissues samples from biopsies, tumor spheres, circulating tumor cells and cells from early embryonic development. The results we present demonstrate that a combined analysis of genomic DNA and messenger RNA from ultra-low input samples is feasible and can readily be applied to other cellular systems with limited material available.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

