We should be using nonlinear indices when relating heart-rate dynamics to cognition and mood
- PMID: 26565560
- PMCID: PMC4643265
- DOI: 10.1038/srep16619
We should be using nonlinear indices when relating heart-rate dynamics to cognition and mood
Abstract
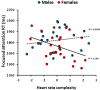
Both heart rate (HR) and brain functioning involve the integrated output of a multitude of regulatory mechanisms, that are not quantified adequately by linear approximations such as means and standard deviations. It was therefore considered whether non-linear measures of HR complexity are more strongly associated with cognition and mood. Whilst resting, the inter-beat (R-R) time series of twenty-one males and twenty-four females were measured for five minutes. The data were summarised using time, frequency and nonlinear complexity measures. Attention, memory, reaction times, mood and cortisol levels were assessed. Nonlinear HR indices captured additional information, enabling a greater percentage of the variance in behaviour to be explained. On occasions non-linear indices were related to aspects for behaviour, for example focused attention and cortisol production, when time or frequency indices were not. These effects were sexually dimorphic with HR complexity being more strongly associated with the behaviour of females. It was concluded that nonlinear rather than linear methods of summarizing the HR times series offers a novel way of relating brain functioning and behaviour. It should be considered whether non-linear measures of HR complexity can be used as a biomarker of the integrated functioning of the brain.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Is the link between depressed mood and heart rate variability explained by disinhibited eating and diet?Biol Psychol. 2017 Feb;123:94-102. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsycho.2016.12.001. Epub 2016 Dec 8. Biol Psychol. 2017. PMID: 27939700
-
Nonlinear measures of heart period variability: decreased measures of symbolic dynamics in patients with panic disorder.Depress Anxiety. 2000;12(2):67-77. doi: 10.1002/1520-6394(2000)12:2<67::AID-DA2>3.0.CO;2-C. Depress Anxiety. 2000. PMID: 11091929
-
Baseline heart rate variability predicts clinical events in heart failure patients implanted with cardiac resynchronization therapy: validation by means of related complexity index.Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2010 Oct;15(4):301-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1542-474X.2010.00384.x. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2010. PMID: 20946551 Free PMC article.
-
Non-linear dynamics of cardiovascular system in humans exposed to repetitive apneas modeling obstructive sleep apnea: aggregated time series data analysis.Auton Neurosci. 2001 Jul 20;90(1-2):106-15. doi: 10.1016/S1566-0702(01)00275-2. Auton Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11485276 Review.
-
Clinical applicability of heart rate variability analysis by methods based on nonlinear dynamics.Card Electrophysiol Rev. 2002 Sep;6(3):250-5. doi: 10.1023/a:1016381025759. Card Electrophysiol Rev. 2002. PMID: 12114847 Review.
Cited by
-
Improvements in Attention and Cardiac Autonomic Modulation After a 2-Weeks Sprint Interval Training Program: A Fidelity Approach.Front Physiol. 2018 Mar 21;9:241. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.00241. eCollection 2018. Front Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29618979 Free PMC article.
-
The influence of EEG oscillations, heart rate variability changes, and personality on self-pain and empathy for pain under placebo analgesia.Sci Rep. 2022 Apr 11;12(1):6041. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-10071-9. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35410362 Free PMC article.
-
Autonomic Inertia as a Proximal Risk Marker for Moments of Perseverative Cognition in Everyday Life in Remitted Depression.Depress Anxiety. 2024 Dec 23;2024:9193159. doi: 10.1155/da/9193159. eCollection 2024. Depress Anxiety. 2024. PMID: 40226686 Free PMC article.
-
Autonomic adaptations mediate the effect of hydration on brain functioning and mood: Evidence from two randomized controlled trials.Sci Rep. 2019 Nov 11;9(1):16412. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-52775-5. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31712590 Free PMC article.
-
Heart Rate Variability and Accelerometry as Classification Tools for Monitoring Perceived Stress Levels-A Pilot Study on Firefighters.Sensors (Basel). 2020 May 16;20(10):2834. doi: 10.3390/s20102834. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32429383 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Benarroch E. E. The central autonomic network: functional organization, dysfunction, and perspective. Mayo Clin. Proc. 68, 988–1001 (1993). - PubMed
-
- Thayer J. F. & Lane R. D. Claude Bernard and the heart-brain connection: further elaboration of a model of neurovisceral integration. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 33, 81–88 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Hansen A. L., Johnsen B. H. & Thayer J. F. Vagal influence on working memory and attention. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 48, 263–274 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Thayer J. F., Åhs F., Fredrikson M., Sollers J. J. III & Wager T. D. A meta-analysis of heart rate variability and neuroimaging studies: implications for heart rate variability as a marker of stress and health. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 36, 747–756 (2012). - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

