Interaction between Glucose and Lipid Metabolism: More than Diabetic Dyslipidemia
- PMID: 26566492
- PMCID: PMC4641964
- DOI: 10.4093/dmj.2015.39.5.353
Interaction between Glucose and Lipid Metabolism: More than Diabetic Dyslipidemia
Abstract
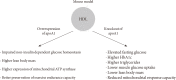
Glucose and lipid metabolism are linked to each other in many ways. The most important clinical manifestation of this interaction is diabetic dyslipidemia, characterized by elevated triglycerides, low high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), and predominance of small-dense LDL particles. However, in the last decade we have learned that the interaction is much more complex. Hypertriglyceridemia and low HDL-C cannot only be the consequence but also the cause of a disturbed glucose metabolism. Furthermore, it is now well established that statins are associated with a small but significant increase in the risk for new onset diabetes. The underlying mechanisms are not completely understood but modulation of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG CoA)-reductase may play a central role as genetic data indicate that mutations resulting in lower HMG CoA-reductase activity are also associated with obesity, higher glucose concentrations and diabetes. Very interestingly, this statin induced increased risk for new onset type 2 diabetes is not detectable in subjects with familial hypercholesterolemia. Furthermore, patients with familial hypercholesterolemia seem to have a lower risk for type 2 diabetes, a phenomenon which seems to be dose-dependent (the higher the low density lipoprotein cholesterol, the lower the risk). Whether there is also an interaction between lipoprotein(a) and diabetes is still a matter of debate.
Keywords: Diabetes mellitus; Diabetic dyslipidemia; Hyperlipoproteinemia type II; Hyperlipoproteinemias; Statin.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Wu L, Parhofer KG. Diabetic dyslipidemia. Metabolism. 2014;63:1469–1479. - PubMed
-
- Avramoglu RK, Basciano H, Adeli K. Lipid and lipoprotein dysregulation in insulin resistant states. Clin Chim Acta. 2006;368:1–19. - PubMed
-
- Adiels M, Olofsson SO, Taskinen MR, Boren J. Overproduction of very low-density lipoproteins is the hallmark of the dyslipidemia in the metabolic syndrome. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2008;28:1225–1236. - PubMed
-
- Duez H, Lamarche B, Uffelman KD, Valero R, Cohn JS, Lewis GF. Hyperinsulinemia is associated with increased production rate of intestinal apolipoprotein B-48-containing lipoproteins in humans. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2006;26:1357–1363. - PubMed
-
- Guerin M, Le Goff W, Lassel TS, Van Tol A, Steiner G, Chapman MJ. Atherogenic role of elevated CE transfer from HDL to VLDL(1) and dense LDL in type 2 diabetes: impact of the degree of triglyceridemia. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2001;21:282–288. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

