The pathogenicity of splicing defects: mechanistic insights into pre-mRNA processing inform novel therapeutic approaches
- PMID: 26566663
- PMCID: PMC4693517
- DOI: 10.15252/embr.201541116
The pathogenicity of splicing defects: mechanistic insights into pre-mRNA processing inform novel therapeutic approaches
Abstract
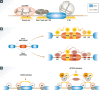
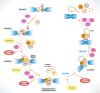
Removal of introns from pre-mRNA precursors (pre-mRNA splicing) is a necessary step for the expression of most genes in multicellular organisms, and alternative patterns of intron removal diversify and regulate the output of genomic information. Mutation or natural variation in pre-mRNA sequences, as well as in spliceosomal components and regulatory factors, has been implicated in the etiology and progression of numerous pathologies. These range from monogenic to multifactorial genetic diseases, including metabolic syndromes, muscular dystrophies, neurodegenerative and cardiovascular diseases, and cancer. Understanding the molecular mechanisms associated with splicing-related pathologies can provide key insights into the normal function and physiological context of the complex splicing machinery and establish sound basis for novel therapeutic approaches.
Keywords: RNA; alternative splicing; disease; mutation; spliceosome.
© 2015 The Authors.
Figures


References
-
- Moore MJ, Proudfoot NJ (2009) Pre‐mRNA processing reaches back to transcription and ahead to translation. Cell 136: 688–700 - PubMed
-
- Pan Q, Shai O, Lee LJ, Frey BJ, Blencowe BJ (2008) Deep surveying of alternative splicing complexity in the human transcriptome by high‐throughput sequencing. Nat Genet 40: 1413–1415 - PubMed
-
- Barbosa‐Morais NL, Irimia M, Pan Q, Xiong HY, Gueroussov S, Lee LJ, Slobodeniuc V, Kutter C, Watt S, Colak R et al (2012) The evolutionary landscape of alternative splicing in vertebrate species. Science 338: 1587–1593 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

