Treatment of Disseminated Aspergillosis with Posaconazole in 10 Dogs
- PMID: 26566711
- PMCID: PMC4913654
- DOI: 10.1111/jvim.13795
Treatment of Disseminated Aspergillosis with Posaconazole in 10 Dogs
Abstract
Background: Few effective treatments for disseminated Aspergillus infections in dogs are available. Posaconazole has potent and broad-spectrum activity against Aspergillus spp., but its use has not yet been sufficiently evaluated in dogs.
Hypothesis/objectives: The aim of this study was to determine the safety and efficacy of posaconazole for the treatment of naturally occurring disseminated Aspergillus infections in dogs.
Animals: Ten client-owned dogs with disseminated aspergillosis.
Methods: Prospective, nonrandomized, noncontrolled study with posaconazole administered to dogs at dosage of 5 mg/kg p.o. q12h. The primary veterinarian or the veterinary specialist caring for the dogs provided patient data.
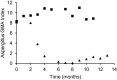
Results: The treatment response for dogs with disseminated disease while receiving posaconazole was defined as clinical remission (n = 4) and clinical improvement (n = 6). There was a high rate of relapse during treatment or after cessation of treatment in both groups, and most dogs died or were euthanized due to progressive disease. Excluding 1 dog concurrently treated with terbinafine that remains alive 5 years after diagnosis, the mean survival time for dogs was 241 days (range 44-516 days). Three other dogs lived >1 year after starting treatment. No clinically relevant adverse events or increases in serum liver enzyme activity occurred during treatment with posaconazole.
Conclusions and clinical importance: Posaconazole appears to be safe and well-tolerated for treatment of disseminated Aspergillus infections in dogs. Long-term survival >1 year is possible with prolonged treatment, but relapse is common.
Keywords: Aspergillus; Diskospondylitis; Fungal; Pyelonephritis.
Copyright © 2015 The Authors. Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of the American College of Veterinary Internal Medicine.
Figures
References
-
- Day MJ. Canine disseminated aspergillosis In: Greene C, ed. Infectious Diseases of the Dog and Cat, 3rd ed St. Louis, MO: Saunders Elsevier; 2006:620–626.
-
- Schultz RM, Johnson EG, Wisner ER, et al. Clinicopathologic and diagnostic imaging characteristics of systemic aspergillosis in 30 dogs. J Vet Intern Med 2008;22:851–859. - PubMed
-
- Walsh TJ, Petraitis V, Petraitiene R, et al. Experimental pulmonary aspergillosis due to Aspergillus terreus: Pathogenesis and treatment of an emerging fungal pathogen resistant to amphotericin B. J Infect Dis 2003;188:305–319. - PubMed
-
- Groll AH, Walsh TJ. Antifungal efficacy and pharmacodynamics of posaconazole in experimental models of invasive fungal infections. Mycoses 2006;49(Suppl 1):7–16. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous