Bystander hyperactivation of preimmune CD8+ T cells in chronic HCV patients
- PMID: 26568315
- PMCID: PMC4752008
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.07916
Bystander hyperactivation of preimmune CD8+ T cells in chronic HCV patients
Abstract
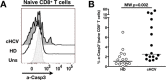
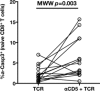
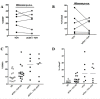
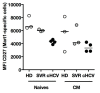
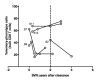
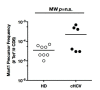
Chronic infection perturbs immune homeostasis. While prior studies have reported dysregulation of effector and memory cells, little is known about the effects on naïve T cell populations. We performed a cross-sectional study of chronic hepatitis C (cHCV) patients using tetramer-associated magnetic enrichment to study antigen-specific inexperienced CD8(+) T cells (i.e., tumor or unrelated virus-specific populations in tumor-free and sero-negative individuals). cHCV showed normal precursor frequencies, but increased proportions of memory-phenotype inexperienced cells, as compared to healthy donors or cured HCV patients. These observations could be explained by low surface expression of CD5, a negative regulator of TCR signaling. Accordingly, we demonstrated TCR hyperactivation and generation of potent CD8(+) T cell responses from the altered T cell repertoire of cHCV patients. In sum, we provide the first evidence that naïve CD8(+) T cells are dysregulated during cHCV infection, and establish a new mechanism of immune perturbation secondary to chronic infection.
Keywords: CD8 T cell dysfunction; Pre-immune repertoire; TCR signaling; chronic inflammation; human; human biology; immunology; medicine; viral immunology.
Conflict of interest statement
The other authors declare that no competing interests exist.
SP: Has received consulting and lecturing fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim, Janssen, Vertex, Gilead, Roche, MSD, Novartis, Abbvie, Sanofi and Glaxo Smith Kline, and grants from Bristol-Myers Squibb, Gilead, Roche and MSD.
Figures







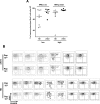
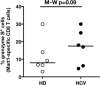


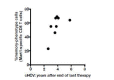
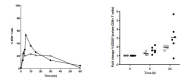
References
-
- Ahmed R, Rouse BT. Immunological memory. Immunological Reviews. 2006;211:5–7. doi: 10.1111/j.0105-2896.2006.00424.x. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

