Patient Perspectives in OMERACT Provide an Anchor for Future Metric Development and Improved Approaches to Healthcare Delivery in Connective Tissue Disease Related Interstitial Lung Disease (CTD-ILD)
- PMID: 26568747
- PMCID: PMC4643941
- DOI: 10.2174/1573398X11666150619182624
Patient Perspectives in OMERACT Provide an Anchor for Future Metric Development and Improved Approaches to Healthcare Delivery in Connective Tissue Disease Related Interstitial Lung Disease (CTD-ILD)
Abstract
Objective: The impact and natural history of connective tissue disease related interstitial lung disease (CTD-ILD) are poorly understood; and have not been previously described from the patient's perspective. This investigation sought insight into CTD-ILD from the patients' perspective to add to our knowledge of CTD-ILD, identify disease-specific areas of unmet need and gather potentially meaningful information towards development of disease-specific patient-reported outcome measures (PROMs).
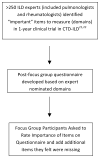
Methods: A mixed methods design incorporating patient focus groups (FGs) querying disease progression and life impact followed by questionnaires with items of importance generated by >250 ILD specialists were implemented among CTD-ILD patients with rheumatoid arthritis, idiopathic inflammatory myopathies, systemic sclerosis, and other CTD subtypes. FG data were analyzed through inductive analysis with five independent analysts, including a patient research partner. Questionnaires were analyzed through Fisher's Exact tests and hierarchal cluster analysis.
Results: Six multicenter FGs included 45 patients. Biophysiologic themes were cough and dyspnea, both pervasively impacting health related quality of life (HRQoL). Language indicating dyspnea was unexpected, unique and contextual. Psycho-social themes were Living with Uncertainty, Struggle over Self-Identity, and Self-Efficacy - with education and clinician communication strongly emphasised. All questionnaire items were rated 'moderately' to 'extremely' important with 10 items of highest importance identified by cluster analysis.
Conclusion: Patients with CTD-ILD informed our understanding of symptoms and impact on HRQoL. Cough and dyspnea are central to the CTD-ILD experience. Initial FGs have provided disease-specific content, context and language essential for reliable PROM development with questionnaires adding value in recognition of patients' concerns.
Keywords: Communication; connective tissue disease; focus groups; interstitial lung disease; patient experience; patient reported outcome measures; questionnaire.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors confirm that this article content has no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Fischer A, du Bois R. Interstitial lung disease in connective tissue disorders. Lancet. 2012;380:689–98. - PubMed
-
- Tyndall AJ, Bannert B, Vonk M, et al. Causes and risk factors for death in systemic sclerosis: a study from the EULAR Scleroderma Trials and Research (EUSTAR) database. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69:1809–15. - PubMed
-
- Maldonado F, Patel RR, Iyer VN, Yi ES, Ryu JH. Are respiratory complications common causes of death in inflammatory myopathies? An autopsy study. Respirology. 2012;17:455–60. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources