Effects of Lifestyle Modification on Telomerase Gene Expression in Hypertensive Patients: A Pilot Trial of Stress Reduction and Health Education Programs in African Americans
- PMID: 26571023
- PMCID: PMC4646647
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0142689
Effects of Lifestyle Modification on Telomerase Gene Expression in Hypertensive Patients: A Pilot Trial of Stress Reduction and Health Education Programs in African Americans
Abstract
Background: African Americans suffer from disproportionately high rates of hypertension and cardiovascular disease. Psychosocial stress, lifestyle and telomere dysfunction contribute to the pathogenesis of hypertension and cardiovascular disease. This study evaluated effects of stress reduction and lifestyle modification on blood pressure, telomerase gene expression and lifestyle factors in African Americans.
Methods: Forty-eight African American men and women with stage I hypertension who participated in a larger randomized controlled trial volunteered for this substudy. These subjects participated in either stress reduction with the Transcendental Meditation technique and a basic health education course (SR) or an extensive health education program (EHE) for 16 weeks. Primary outcomes were telomerase gene expression (hTERT and hTR) and clinic blood pressure. Secondary outcomes included lifestyle-related factors. Data were analyzed for within-group and between-group changes.
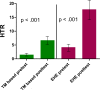
Results: Both groups showed increases in the two measures of telomerase gene expression, hTR mRNA levels (SR: p< 0.001; EHE: p< 0.001) and hTERT mRNA levels (SR: p = 0.055; EHE: p< 0.002). However, no statistically significant between-group changes were observed. Both groups showed reductions in systolic BP. Adjusted changes were SR = -5.7 mm Hg, p< 0.01; EHE = -9.0 mm Hg, p < 0.001 with no statistically significant difference between group difference. There was a significant reduction in diastolic BP in the EHE group (-5.3 mm Hg, p< 0.001) but not in SR (-1.2 mm Hg, p = 0.42); the between-group difference was significant (p = 0.04). The EHE group showed a greater number of changes in lifestyle behaviors.
Conclusion: In this pilot trial, both stress reduction (Transcendental Meditation technique plus health education) and extensive health education groups demonstrated increased telomerase gene expression and reduced BP. The association between increased telomerase gene expression and reduced BP observed in this high-risk population suggest hypotheses that telomerase gene expression may either be a biomarker for reduced BP or a mechanism by which stress reduction and lifestyle modification reduces BP.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00681200.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Lewington S, Clarke R, Qizilbash N, Peto R, Collins R (2002) Age-specific relevance of usual blood pressure to vascular mortality: a meta-analysis of individual data for one million adults in 61 prospective studies. Lancet 360: 1903–1913. - PubMed
-
- Sheats N, Lin Y, Zhao W, Cheek DE, Lackland DT, Egan BM (2005) Prevalence, treatment, and control of hypertension among African Americans and Caucasians at primary care sites for medically under-served patients. Ethn Dis 15: 25–32. - PubMed
-
- Ferdinand KC, Armani AM (2007) The management of hypertension in African Americans. Crit Pathw Cardiol 6: 67–71. - PubMed
-
- Martins D, Norris K (2004) Hypertension treatment in African Americans: physiology is less important than sociology. Cleve Clin J Med 71: 735–743. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

