The metabolome regulates the epigenetic landscape during naive-to-primed human embryonic stem cell transition
- PMID: 26571212
- PMCID: PMC4662931
- DOI: 10.1038/ncb3264
The metabolome regulates the epigenetic landscape during naive-to-primed human embryonic stem cell transition
Abstract
For nearly a century developmental biologists have recognized that cells from embryos can differ in their potential to differentiate into distinct cell types. Recently, it has been recognized that embryonic stem cells derived from both mice and humans exhibit two stable yet epigenetically distinct states of pluripotency: naive and primed. We now show that nicotinamide N-methyltransferase (NNMT) and the metabolic state regulate pluripotency in human embryonic stem cells (hESCs). Specifically, in naive hESCs, NNMT and its enzymatic product 1-methylnicotinamide are highly upregulated, and NNMT is required for low S-adenosyl methionine (SAM) levels and the H3K27me3 repressive state. NNMT consumes SAM in naive cells, making it unavailable for histone methylation that represses Wnt and activates the HIF pathway in primed hESCs. These data support the hypothesis that the metabolome regulates the epigenetic landscape of the earliest steps in human development.
Figures
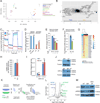




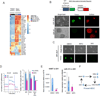


Comment in
-
Metabolic exit from naive pluripotency.Nat Cell Biol. 2015 Dec;17(12):1519-21. doi: 10.1038/ncb3269. Nat Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 26612574
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- UO1HL099993/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL099997/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- R01GM083867/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 1U24DK097154/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01ES019319/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL099993/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01GM097372/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES019319/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- 1P01GM081619/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DK097154/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM097372/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM083867/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01GM97372-03S1/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 GM081619/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01HL099997/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

