Longitudinal effect of eteplirsen versus historical control on ambulation in Duchenne muscular dystrophy
- PMID: 26573217
- PMCID: PMC5064753
- DOI: 10.1002/ana.24555
Longitudinal effect of eteplirsen versus historical control on ambulation in Duchenne muscular dystrophy
Abstract
Objective: To continue evaluation of the long-term efficacy and safety of eteplirsen, a phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligomer designed to skip DMD exon 51 in patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD). Three-year progression of eteplirsen-treated patients was compared to matched historical controls (HC).
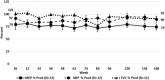
Methods: Ambulatory DMD patients who were ≥7 years old and amenable to exon 51 skipping were randomized to eteplirsen (30/50mg/kg) or placebo for 24 weeks. Thereafter, all received eteplirsen on an open-label basis. The primary functional assessment in this study was the 6-Minute Walk Test (6MWT). Respiratory muscle function was assessed by pulmonary function testing (PFT). Longitudinal natural history data were used for comparative analysis of 6MWT performance at baseline and months 12, 24, and 36. Patients were matched to the eteplirsen group based on age, corticosteroid use, and genotype.
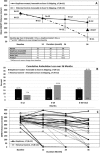
Results: At 36 months, eteplirsen-treated patients (n = 12) demonstrated a statistically significant advantage of 151m (p < 0.01) on 6MWT and experienced a lower incidence of loss of ambulation in comparison to matched HC (n = 13) amenable to exon 51 skipping. PFT results remained relatively stable in eteplirsen-treated patients. Eteplirsen was well tolerated. Analysis of HC confirmed the previously observed change in disease trajectory at age 7 years, and more severe progression was observed in patients with mutations amenable to exon skipping than in those not amenable. The subset of patients amenable to exon 51 skipping showed a more severe disease course than those amenable to any exon skipping.
Interpretation: Over 3 years of follow-up, eteplirsen-treated patients showed a slower rate of decline in ambulation assessed by 6MWT compared to untreated matched HC.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01396239 NCT01540409.
© 2016 The Authors. Annals of Neurology published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of American Neurological Association.
Figures



References
-
- Mendell JR, Rodino‐Klapac LR, Sahenk Z, et al. Eteplirsen for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Ann Neurol 2013;74:637–647. - PubMed
-
- Kole R, Krieg AM. Exon skipping therapy for Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 2015;87:104–107. - PubMed
-
- Henricson EK, Abresch RT, Cnaan A, et al. The cooperative international neuromuscular research group Duchenne natural history study: glucocorticoid treatment preserves clinically meaningful functional milestones and reduces rate of disease progression as measured by manual muscle testing and other commonly used clinical trial outcome measures. Muscle Nerve 2013;48:55–67. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Muntoni F, Wood MJ. Targeting RNA to treat neuromuscular disease. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2011;10:621–637. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

