Cerebrovascular Damage Mediates Relations Between Aortic Stiffness and Memory
- PMID: 26573713
- PMCID: PMC4679440
- DOI: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.115.06398
Cerebrovascular Damage Mediates Relations Between Aortic Stiffness and Memory
Abstract
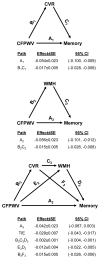
Aortic stiffness is associated with cognitive decline. Here, we examined the association between carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity and cognitive function and investigated whether cerebrovascular remodeling and parenchymal small vessel disease damage mediate the relation. Analyses were based on 1820 (60% women) participants in the Age, Gene/Environment Susceptibility-Reykjavik Study. Multivariable linear regression models adjusted for vascular and demographic confounders showed that higher carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity was related to lower memory score (standardized β: -0.071±0.023; P=0.002). Cerebrovascular resistance and white matter hyperintensities were each associated with carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity and memory (P<0.05). Together, cerebrovascular resistance and white matter hyperintensities (total indirect effect: -0.029; 95% CI, -0.043 to -0.017) attenuated the direct relation between carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity and memory (direct effect: -0.042; 95% CI, -0.087 to 0.003; P=0.07) and explained ≈41% of the observed effect. Our results suggest that in older adults, associations between aortic stiffness and memory are mediated by pathways that include cerebral microvascular remodeling and microvascular parenchymal damage.
Keywords: cognition; dementia; hemodynamics; memory; vascular stiffness.
© 2015 American Heart Association, Inc.
Figures
Comment in
-
Are Hemodynamic Factors Involved in Cognitive Impairment?Hypertension. 2016 Jan;67(1):34-5. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.115.06495. Epub 2015 Nov 16. Hypertension. 2016. PMID: 26573714 No abstract available.
References
-
- Mitchell GF, van Buchem MA, Sigurdsson S, Gotal JD, Jonsdottir MK, Kjartansson O, Garcia M, Aspelund T, Harris TB, Gudnason V, Launer LJ. Arterial stiffness, pressure and flow pulsatility and brain structure and function: the Age, Gene/Environment Susceptibility--Reykjavik Study. Brain. 2011;134:3398–3407. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Poels MM, van Oijen M, Mattace-Raso FU, Hofman A, Koudstaal PJ, Witteman JC, Breteler MM. Arterial stiffness, cognitive decline, and risk of dementia: the Rotterdam Study. Stroke. 2007;38:888–892. - PubMed
-
- Waldstein SR, Rice SC, Thayer JF, Najjar SS, Scuteri A, Zonderman AB. Pulse pressure and pulse wave velocity are related to cognitive decline in the Baltimore Longitudinal Study of Aging. Hypertension. 2008;51:99–104. - PubMed
-
- Kalaria RN, Akinyemi R, Ihara M. Does vascular pathology contribute to alzheimer changes? J Neurol Sci. 2012;322:141–147. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

