Targeting a Plk1-Controlled Polarity Checkpoint in Therapy-Resistant Glioblastoma-Propagating Cells
- PMID: 26573800
- PMCID: PMC4698003
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-3689
Targeting a Plk1-Controlled Polarity Checkpoint in Therapy-Resistant Glioblastoma-Propagating Cells
Abstract
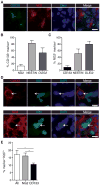
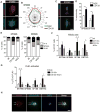
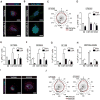
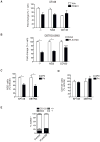
The treatment of glioblastoma (GBM) remains challenging in part due to the presence of stem-like tumor-propagating cells that are resistant to standard therapies consisting of radiation and temozolomide. Among the novel and targeted agents under evaluation for the treatment of GBM are BRAF/MAPK inhibitors, but their effects on tumor-propagating cells are unclear. Here, we characterized the behaviors of CD133(+) tumor-propagating cells isolated from primary GBM cell lines. We show that CD133(+) cells exhibited decreased sensitivity to the antiproliferative effects of BRAF/MAPK inhibition compared to CD133(-) cells. Furthermore, CD133(+) cells exhibited an extended G2-M phase and increased polarized asymmetric cell divisions. At the molecular level, we observed that polo-like kinase (PLK) 1 activity was elevated in CD133(+) cells, prompting our investigation of BRAF/PLK1 combination treatment effects in an orthotopic GBM xenograft model. Combined inhibition of BRAF and PLK1 resulted in significantly greater antiproliferative and proapoptotic effects beyond those achieved by monotherapy (P < 0.05). We propose that PLK1 activity controls a polarity checkpoint and compensates for BRAF/MAPK inhibition in CD133(+) cells, suggesting the need for concurrent PLK1 inhibition to improve antitumor activity against a therapy-resistant cell compartment.
©2015 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors disclose no potential conflicts of interest
Figures


Similar articles
-
Polo-like kinase 1 inhibition kills glioblastoma multiforme brain tumor cells in part through loss of SOX2 and delays tumor progression in mice.Stem Cells. 2012 Jun;30(6):1064-75. doi: 10.1002/stem.1081. Stem Cells. 2012. PMID: 22415968
-
Polo-like kinase 1 inhibition causes decreased proliferation by cell cycle arrest, leading to cell death in glioblastoma.Cancer Gene Ther. 2013 Sep;20(9):499-506. doi: 10.1038/cgt.2013.46. Epub 2013 Jul 26. Cancer Gene Ther. 2013. PMID: 23887645
-
A high-content small molecule screen identifies sensitivity of glioblastoma stem cells to inhibition of polo-like kinase 1.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 30;8(10):e77053. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0077053. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24204733 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Polo-like kinase in cancer therapy.Clin Cancer Res. 2010 Jan 15;16(2):384-9. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-1380. Epub 2010 Jan 12. Clin Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20068088 Review.
-
Polo-like kinase inhibitors: an emerging opportunity for cancer therapeutics.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2010 Jan;19(1):27-43. doi: 10.1517/13543780903483191. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2010. PMID: 20001553 Review.
Cited by
-
miR-509 inhibits cancer stemness properties in oral carcinomas via directly targeting PlK1.J Dent Sci. 2022 Apr;17(2):653-658. doi: 10.1016/j.jds.2021.09.028. Epub 2021 Oct 8. J Dent Sci. 2022. PMID: 35756764 Free PMC article.
-
The polo-like kinase 1 inhibitor volasertib synergistically increases radiation efficacy in glioma stem cells.Oncotarget. 2018 Jan 8;9(12):10497-10509. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.24041. eCollection 2018 Feb 13. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 29535822 Free PMC article.
-
The CINs of Polo-Like Kinase 1 in Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Oct 13;12(10):2953. doi: 10.3390/cancers12102953. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33066048 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Combined Effect of G-Quadruplex and Neuro-Inducers as an Alternative Approach to Human Glioblastoma Therapy.Front Oncol. 2022 Apr 28;12:880740. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.880740. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35586496 Free PMC article.
-
BEERE: a web server for biomedical entity expansion, ranking and explorations.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Jul 2;47(W1):W578-W586. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz428. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 31114876 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Weller M, van den Bent M, Hopkins K, Tonn JC, Stupp R, Falini A, et al. EANO guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of anaplastic gliomas and glioblastoma. Lancet Oncol. 2014 - PubMed
-
- Snuderl M, Fazlollahi L, Le LP, Nitta M, Zhelyazkova BH, Davidson CJ, et al. Mosaic amplification of multiple receptor tyrosine kinase genes in glioblastoma. Cancer Cell Elsevier Inc. 2011;20:810–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

