Involuntary reflexive pelvic floor muscle training in addition to standard training versus standard training alone for women with stress urinary incontinence: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 26573847
- PMCID: PMC4647572
- DOI: 10.1186/s13063-015-1051-0
Involuntary reflexive pelvic floor muscle training in addition to standard training versus standard training alone for women with stress urinary incontinence: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Pelvic floor muscle training is effective and recommended as first-line therapy for female patients with stress urinary incontinence. However, standard pelvic floor physiotherapy concentrates on voluntary contractions even though the situations provoking stress urinary incontinence (for example, sneezing, coughing, running) require involuntary fast reflexive pelvic floor muscle contractions. Training procedures for involuntary reflexive muscle contractions are widely implemented in rehabilitation and sports but not yet in pelvic floor rehabilitation. Therefore, the research group developed a training protocol including standard physiotherapy and in addition focused on involuntary reflexive pelvic floor muscle contractions.
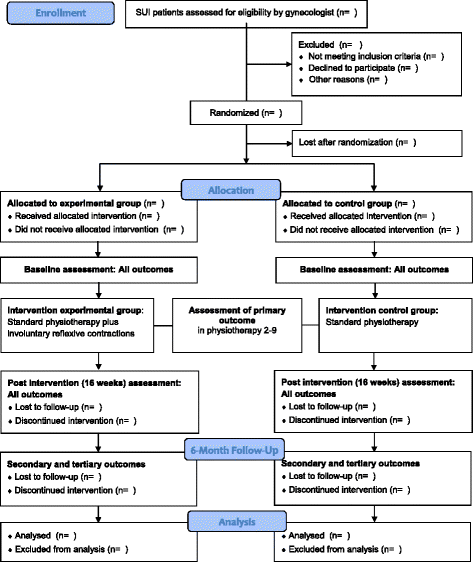
Methods/design: The aim of the planned study is to compare this newly developed physiotherapy program (experimental group) and the standard physiotherapy program (control group) regarding their effect on stress urinary incontinence. The working hypothesis is that the experimental group focusing on involuntary reflexive muscle contractions will have a higher improvement of continence measured by the International Consultation on Incontinence Modular Questionnaire Urinary Incontinence (short form), and - regarding secondary and tertiary outcomes - higher pelvic floor muscle activity during stress urinary incontinence provoking activities, better pad-test results, higher quality of life scores (International Consultation on Incontinence Modular Questionnaire) and higher intravaginal muscle strength (digitally tested) from before to after the intervention phase. This study is designed as a prospective, triple-blinded (participant, investigator, outcome assessor), randomized controlled trial with two physiotherapy intervention groups with a 6-month follow-up including 48 stress urinary incontinent women per group. For both groups the intervention will last 16 weeks and will include 9 personal physiotherapy consultations and 78 short home training sessions (weeks 1-5 3x/week, 3x/day; weeks 6-16 3x/week, 1x/day). Thereafter both groups will continue with home training sessions (3x/week, 1x/day) until the 6-month follow-up. To compare the primary outcome, International Consultation on Incontinence Modular Questionnaire (short form) between and within the two groups at ten time points (before intervention, physiotherapy sessions 2-9, after intervention) ANOVA models for longitudinal data will be applied.
Discussion: This study closes a gap, as involuntary reflexive pelvic floor muscle training has not yet been included in stress urinary incontinence physiotherapy, and if shown successful could be implemented in clinical practice immediately.
Trial registration: NCT02318251 ; 4 December 2014 First patient randomized: 11 March 2015.
References
-
- Haylen BT, de Ridder D, Freeman RM, Swift SE, Berghmans B, Lee J, et al. An International Urogynecological Association (IUGA)/International Continence Society (ICS) joint report on the terminology for female pelvic floor dysfunction. Neurourol Urodyn. 2010;29(1):4–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous