Single agent BMS-911543 Jak2 inhibitor has distinct inhibitory effects on STAT5 signaling in genetically engineered mice with pancreatic cancer
- PMID: 26575024
- PMCID: PMC4792572
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.6332
Single agent BMS-911543 Jak2 inhibitor has distinct inhibitory effects on STAT5 signaling in genetically engineered mice with pancreatic cancer
Abstract
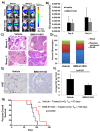
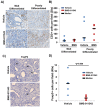
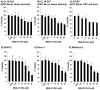
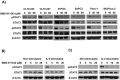
The Jak/STAT pathway is activated in human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) and cooperates with mutant Kras to drive initiation and progression of PDAC in murine models. We hypothesized that the small-molecule Jak2 inhibitor (BMS-911543) would elicit anti-tumor activity against PDAC and decrease immune suppressive features of the disease. We used an aggressive genetically engineered PDAC model with mutant KrasG12D, tp53R270H, and Brca1 alleles (KPC-Brca1 mice). Mice with confirmed tumor burden were treated orally with vehicle or 30 mg/kg BMS-911543 daily for 14 days. Histologic analysis of pancreata from treated mice revealed fewer foci of adenocarcinoma and significantly decreased Ki67+ cells versus controls. In vivo administration of BMS-911543 significantly reduced pSTAT5 and FoxP3 positive cells within the pancreas, but did not alter STAT3 phosphorylation. Continuous dosing of KPC-Brca1 mice with BMS-911543 resulted in a median survival of 108 days, as compared to a median survival of 87 days in vehicle treated animals, a 23% increase (p = 0.055). In vitro experiments demonstrated that PDAC cell lines were poorly sensitive to BMS-911543, requiring high micromolar concentrations to achieve targeted inhibition of Jak/STAT signaling. Similarly, BMS-911543 had little in vitro effect on the viability of both murine and human PDAC-derived stellate cell lines. However, BMS-911543 potently inhibited phosphorylation of pSTAT3 and pSTAT5 at low micromolar doses in human PBMC and reduced in vitro differentiation of Foxp3+ T regulatory cells. These results indicate that single agent Jak2i deserves further study in preclinical models of PDAC and has distinct inhibitory effects on STAT5 mediated signaling.
Keywords: Jak2; STAT3; STAT5; pancreatic cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Loss of P53 Function Activates JAK2-STAT3 Signaling to Promote Pancreatic Tumor Growth, Stroma Modification, and Gemcitabine Resistance in Mice and Is Associated With Patient Survival.Gastroenterology. 2016 Jul;151(1):180-193.e12. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.03.010. Epub 2016 Mar 19. Gastroenterology. 2016. PMID: 27003603
-
Inhibition of Aurora Kinase A Induces Necroptosis in Pancreatic Carcinoma.Gastroenterology. 2017 Nov;153(5):1429-1443.e5. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.07.036. Epub 2017 Jul 29. Gastroenterology. 2017. PMID: 28764929 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of mutant KrasG12D-initiated murine pancreatic carcinoma growth by a dual c-Raf and soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitor t-CUPM.Cancer Lett. 2016 Feb 28;371(2):187-93. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2015.11.042. Epub 2015 Dec 9. Cancer Lett. 2016. PMID: 26683769 Free PMC article.
-
KRAS-related proteins in pancreatic cancer.Pharmacol Ther. 2016 Dec;168:29-42. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2016.09.003. Epub 2016 Sep 3. Pharmacol Ther. 2016. PMID: 27595930 Review.
-
Critical role of oncogenic KRAS in pancreatic cancer (Review).Mol Med Rep. 2016 Jun;13(6):4943-9. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5196. Epub 2016 Apr 27. Mol Med Rep. 2016. PMID: 27121414 Review.
Cited by
-
Five gene signatures were identified in the prediction of overall survival in resectable pancreatic cancer.BMC Surg. 2020 Sep 17;20(1):207. doi: 10.1186/s12893-020-00856-y. BMC Surg. 2020. PMID: 32943033 Free PMC article.
-
Desmoplasia and oncogene driven acinar-to-ductal metaplasia are concurrent events during acinar cell-derived pancreatic cancer initiation in young adult mice.PLoS One. 2019 Sep 6;14(9):e0221810. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0221810. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31490946 Free PMC article.
-
Salmonella-Based Therapy Targeting Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase Restructures the Immune Contexture to Improve Checkpoint Blockade Efficacy.Biomedicines. 2020 Dec 16;8(12):617. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines8120617. Biomedicines. 2020. PMID: 33339195 Free PMC article.
-
5-Azacytidine Potentiates Anti-tumor Immunity in a Model of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma.Front Immunol. 2020 Mar 31;11:538. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00538. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32296439 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of gemcitabine and erlotinib inhibits recurrent pancreatic cancer growth in mice via the JAK-STAT pathway.Oncol Rep. 2018 Mar;39(3):1081-1089. doi: 10.3892/or.2018.6198. Epub 2018 Jan 8. Oncol Rep. 2018. PMID: 29328487 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rahib L, Smith BD, Aizenberg R, Rosenzweig AB, Fleshman JM, Matrisian LM. Projecting cancer incidence and deaths to 2030: the unexpected burden of thyroid, liver, and pancreas cancers in the United States. Cancer Res. 2014;74:2913–2921. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:5–29. - PubMed
-
- Blazer M, Wu C, Goldberg RM, Phillips G, Schmidt C, Muscarella P, Wuthrick E, Williams TM, Reardon J, Ellison EC, Bloomston M, Bekaii-Saab T. Neoadjuvant modified (m) FOLFIRINOX for locally advanced unresectable (LAPC) and borderline resectable (BRPC) adenocarcinoma of the pancreas. Ann Surg Oncol. 2015;22:1153–1159. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

