Selective loss of alpha motor neurons with sparing of gamma motor neurons and spinal cord cholinergic neurons in a mouse model of spinal muscular atrophy
- PMID: 26576026
- PMCID: PMC5341542
- DOI: 10.1111/joa.12419
Selective loss of alpha motor neurons with sparing of gamma motor neurons and spinal cord cholinergic neurons in a mouse model of spinal muscular atrophy
Abstract
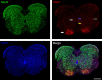
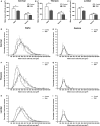
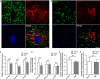
Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is a neuromuscular disease characterised primarily by loss of lower motor neurons from the ventral grey horn of the spinal cord and proximal muscle atrophy. Recent experiments utilising mouse models of SMA have demonstrated that not all motor neurons are equally susceptible to the disease, revealing that other populations of neurons can also be affected. Here, we have extended investigations of selective vulnerability of neuronal populations in the spinal cord of SMA mice to include comparative assessments of alpha motor neuron (α-MN) and gamma motor neuron (γ-MN) pools, as well as other populations of cholinergic neurons. Immunohistochemical analyses of late-symptomatic SMA mouse spinal cord revealed that numbers of α-MNs were significantly reduced at all levels of the spinal cord compared with controls, whereas numbers of γ-MNs remained stable. Likewise, the average size of α-MN cell somata was decreased in SMA mice with no change occurring in γ-MNs. Evaluation of other pools of spinal cord cholinergic neurons revealed that pre-ganglionic sympathetic neurons, central canal cluster interneurons, partition interneurons and preganglionic autonomic dorsal commissural nucleus neuron numbers all remained unaffected in SMA mice. Taken together, these findings indicate that α-MNs are uniquely vulnerable among cholinergic neuron populations in the SMA mouse spinal cord, with γ-MNs and other cholinergic neuronal populations being largely spared.
Keywords: SMA; alpha motor neuron; cholinergic neuron; gamma motor neuron; spinal cord; spinal muscular atrophy.
© 2015 Anatomical Society.
Figures

References
-
- Arai H, Tanabe Y, Hachiya Y, et al. (2005) Finger cold‐induced vasodilatation, sympathetic skin response, and R‐R interval variation in patients with progressive spinal muscular atrophy. J Child Neurol 20, 871–875. - PubMed
-
- Barber RP, Phelps PE, Houser CR, et al. (1984) The morphology and distribution of neurons containing choline acetyltransferase in the adult rat spinal cord: an immunocytochemical study. J Comp Neurol 229, 329–346. - PubMed
-
- Battaglia G, Princivalle A, Forti F, et al. (1997) Expression of the SMN gene, the spinal muscular atrophy determining gene, in the mammalian central nervous system. Hum Mol Genet 6, 1961–1971. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

