Hepatic immune tolerance induced by hepatic stellate cells
- PMID: 26576077
- PMCID: PMC4641110
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i42.11887
Hepatic immune tolerance induced by hepatic stellate cells
Abstract
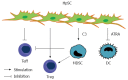
The liver, which is a metabolic organ, plays a pivotal role in tolerance induction. Hepatic stellate cells (HpSCs), which are unique non-parenchymal cells, exert potent immunoregulatory activity during cotransplantation with allogeneic islets effectively protecting the islet allografts from rejection. Multiple mechanisms participate in the immune tolerance induced by HpSCs, including the marked expansion of myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs), attenuation of effector T cell functions and augmentation of regulatory T cells. HpSC conditioned MDSC-based immunotherapy has been conducted in mice with autoimmune disease and the results show that this technique may be promising. This article demonstrates how HpSCs orchestrate both innate immunity and adaptive immunity to build a negative network that leads to immune tolerance.
Keywords: Hepatic stellate cells; Hepatic tolerance; Immunotherapy; Myeloid-derived suppressor cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The role of complement component 3 (C3) in differentiation of myeloid-derived suppressor cells.Blood. 2013 Mar 7;121(10):1760-8. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-06-440214. Epub 2013 Jan 8. Blood. 2013. PMID: 23299310 Free PMC article.
-
Unique aspects of rejection and tolerance in liver transplantation.Semin Liver Dis. 2009 Feb;29(1):91-101. doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1192058. Epub 2009 Feb 23. Semin Liver Dis. 2009. PMID: 19235662 Review.
-
Hepatic immune regulation by stromal cells.Curr Opin Immunol. 2015 Feb;32:1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2014.10.002. Epub 2014 Oct 28. Curr Opin Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25463592 Review.
-
Human hepatic stellate cells inhibit T-cell response through B7-H1 pathway.Transplantation. 2013 Jul 15;96(1):17-24. doi: 10.1097/TP.0b013e318294caae. Transplantation. 2013. PMID: 23756770 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Immunosuppressive Drugs on MDSCs in Transplantation.J Immunol Res. 2018 Jul 3;2018:5414808. doi: 10.1155/2018/5414808. eCollection 2018. J Immunol Res. 2018. PMID: 30057917 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Vitamin A Metabolism and Resistance of Hepatic Metastases to Immunotherapy.Mol Cancer Ther. 2025 Mar 4;24(3):345-353. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-24-0367. Mol Cancer Ther. 2025. PMID: 39363636 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fibrinogen-like protein 2 promotes the accumulation of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in the hepatocellular carcinoma tumor microenvironment.Oncol Lett. 2021 Jan;21(1):47. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.12308. Epub 2020 Nov 17. Oncol Lett. 2021. PMID: 33281958 Free PMC article.
-
The Many Roles of Cell Adhesion Molecules in Hepatic Fibrosis.Cells. 2019 Nov 24;8(12):1503. doi: 10.3390/cells8121503. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31771248 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Cytokines on the Progression of Liver Fibrosis in Mice Infected with Echinococcus multilocularis.Infect Drug Resist. 2021 Dec 24;14:5651-5660. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S344508. eCollection 2021. Infect Drug Resist. 2021. PMID: 34992391 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal stem cells inhibit T cell activation by releasing TGF-β1 from TGF-β1/GARP complex.Oncotarget. 2017 Oct 6;8(59):99784-99800. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.21549. eCollection 2017 Nov 21. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29245940 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Calne RY, Sells RA, Pena JR, Davis DR, Millard PR, Herbertson BM, Binns RM, Davies DA. Induction of immunological tolerance by porcine liver allografts. Nature. 1969;223:472–476. - PubMed
-
- Kamada N, Brons G, Davies HS. Fully allogeneic liver grafting in rats induces a state of systemic nonreactivity to donor transplantation antigens. Transplantation. 1980;29:429–431. - PubMed
-
- Bumgardner GL, Heininger M, Li J, Xia D, Parker-Thornburg J, Ferguson RM, Orosz CG. A functional model of hepatocyte transplantation for in vivo immunologic studies. Transplantation. 1998;65:53–61. - PubMed
-
- Yu MC, Chen CH, Liang X, Wang L, Gandhi CR, Fung JJ, Lu L, Qian S. Inhibition of T-cell responses by hepatic stellate cells via B7-H1-mediated T-cell apoptosis in mice. Hepatology. 2004;40:1312–1321. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

