Troubleshooting Arterial-Phase MR Images of Gadoxetate Disodium-Enhanced Liver
- PMID: 26576109
- PMCID: PMC4644741
- DOI: 10.3348/kjr.2015.16.6.1207
Troubleshooting Arterial-Phase MR Images of Gadoxetate Disodium-Enhanced Liver
Abstract
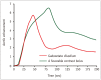
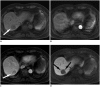
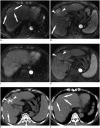
Gadoxetate disodium is a widely used magnetic resonance (MR) contrast agent for liver MR imaging, and it provides both dynamic and hepatobiliary phase images. However, acquiring optimal arterial phase images at liver MR using gadoxetate disodium is more challenging than using conventional extracellular MR contrast agent because of the small volume administered, the gadolinium content of the agent, and the common occurrence of transient severe motion. In this article, we identify the challenges in obtaining high-quality arterial-phase images of gadoxetate disodium-enhanced liver MR imaging and present strategies for optimizing arterial-phase imaging based on the thorough review of recent research in this field.
Keywords: Arterial phase; Gadoxetate disodium; Liver; Magnetic resonance imaging; Transient severe motion.
Figures
References
-
- Kudo M. Will Gd-EOB-MRI change the diagnostic algorithm in hepatocellular carcinoma? Oncology. 2010;78(Suppl 1):87–93. - PubMed
-
- Fowler KJ, Brown JJ, Narra VR. Magnetic resonance imaging of focal liver lesions: approach to imaging diagnosis. Hepatology. 2011;54:2227–2237. - PubMed
-
- Mitchell DG, Bruix J, Sherman M, Sirlin CB. LI-RADS (Liver Imaging Reporting and Data System): summary, discussion, and consensus of the LI-RADS Management Working Group and future directions. Hepatology. 2015;61:1056–1065. - PubMed
-
- Lencioni R, Llovet JM. Modified RECIST (mRECIST) assessment for hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin Liver Dis. 2010;30:52–60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

