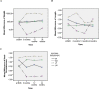
Two-Year Comparison of Growth Indices of Twins with Dissimilar Weight at Birth (Low Birth Weight vs. Normal Twin)
- PMID: 26576375
- PMCID: PMC4645768
Two-Year Comparison of Growth Indices of Twins with Dissimilar Weight at Birth (Low Birth Weight vs. Normal Twin)
Abstract
Background: Twin pregnancies are commonly associated with low birth weight (LBW) infants. Most studies focus on growth of LBW compared with normal infants in singleton. However, there has not been any study on twins to compare LBW with normal birth weight (NBW) infants as a match control of the same twin.
Methods: This cohort study was conducted at Healthcare centers of Kashan, in 2013. Twins differing in birth weight (one with LBW and the other with NBW) were assessed using the care charts in Well Care program in regard to weight, height and head circumference measurements at birth and after 6, 12, 24 months of age and were compared separately between all matched pairs and in four sex-twin subgroups which was defined according to the sex of each twin in pairs; SF (Same-sex: Female), SM (Same-sex: Male), LF (LBW: Female) and LM (LBW: Male).
Results: Incidence of dissimilar twins in birth weight was 28.4%. The weight of LBW was significantly lower than the NBW cohort in SF and LF subgroups up to 24 months. The height of LBW was not significantly different from NBW cohort in SM and LM subgroups up to 24 month. Head circumference was significantly higher in LBW compared to NBW cohort in LM subgroup up to 24 month. However, these indices were significantly lower in LBW compared to NBW cohort in all pairs.
Conclusion: Although LBW cohort was significantly lower than the NBW in growth indices at birth to 2 years old in all twins, however, highly variable results was observed in four subgroups of sex-twin.
Keywords: Growth indicator; Low birth weight; Twins.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Low birth weight babies under village conditions: feeding pattern, growth and motor development.Paediatr Indones. 1991 Mar-Apr;31(3-4):84-98. Paediatr Indones. 1991. PMID: 1956693
-
Growth and neurodevelopment in low birth weight versus normal birth weight infants from birth to 24 months, born in an obstetric emergency hospital in Haiti, a prospective cohort study.BMC Pediatr. 2021 Mar 24;21(1):143. doi: 10.1186/s12887-021-02605-3. BMC Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 33761917 Free PMC article.
-
Are low birth weight neonates at risk for suboptimal renal growth and function during infancy?BMC Nephrol. 2016 Jul 26;17(1):100. doi: 10.1186/s12882-016-0314-7. BMC Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 27460896 Free PMC article.
-
Small for gestational age, term babies, in the first six years of life.Eur J Clin Nutr. 1998 Jan;52 Suppl 1:S59-64. Eur J Clin Nutr. 1998. PMID: 9511021 Review.
-
Association between low birth weight and impaired glucose tolerance in children: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Pediatr. 2024 May 9;12:1362076. doi: 10.3389/fped.2024.1362076. eCollection 2024. Front Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 38783917 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Predictors of Weight Velocity in the First 6 Months of Life in a Rural Block of West Bengal: A Longitudinal Study.Indian J Community Med. 2019 Apr-Jun;44(2):92-96. doi: 10.4103/ijcm.IJCM_150_18. Indian J Community Med. 2019. PMID: 31333283 Free PMC article.
-
Ambient Air Pollution, Housing Context, and Birth Outcomes Among Wisconsin Mothers.Matern Child Health J. 2024 Aug;28(8):1386-1394. doi: 10.1007/s10995-024-03941-3. Epub 2024 Jun 7. Matern Child Health J. 2024. PMID: 38847990 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Matte U, Le Roux MG, Bénichou B, Moisan JP, Giugliani R. ( 1996). Study on possible increase in twinning rate at a small village in south Brazil. Acta Genet Med Gemellol (Roma), 45( 4): 431– 437. - PubMed
-
- Martin JA, Hamilton BE, Osterman MJK. ( 2012). Three Decades of Twin Births in the United States, 1980–2009. NCHS data brief, no 80. Hyattsville, MD: National Center for Health Statistics. - PubMed
-
- Anonymous ( 2011). Multiple pregnancy. The management of twin and triplet pregnancies in the antenatal period. NICE clinical guideline 129. Available from: www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg129/resources/guidance-multiple-pregnancy-pdf - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources