Comparing the Effect of Concept Mapping and Conventional Methods on Nursing Students' Practical Skill Score
- PMID: 26576441
- PMCID: PMC4644603
- DOI: 10.17795/nmsjournal27471
Comparing the Effect of Concept Mapping and Conventional Methods on Nursing Students' Practical Skill Score
Abstract
Background: Development of practical skills in the field of nursing education has remained a serious and considerable challenge in nursing education. Moreover, newly graduated nurses may have weak practical skills, which can be a threat to patients' safety.
Objectives: The present study was conducted to compare the effect of concept mapping and conventional methods on nursing students' practical skills.
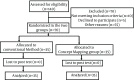
Patients and methods: This quasi-experimental study was conducted on 70 nursing students randomly assigned into two groups of 35 people. The intervention group was taught through concept mapping method, while the control group was taught using conventional method. A two-part instrument was used including a demographic information form and a checklist for direct observation of procedural skills. Descriptive statistics, chi-square, independent samples t-tests and paired t-test were used to analyze data.
Results: Before education, no significant differences were observed between the two groups in the three skills of cleaning (P = 0.251), injection (P = 0.185) and sterilizing (P = 0.568). The students mean scores were significantly increased after the education and the difference between pre and post intervention of students mean scores were significant in the both groups (P < 0.001). However, after education, in all three skills the mean scores of the intervention group were significantly higher than the control group (P < 0.001).
Conclusions: Concept mapping was superior to conventional skill teaching methods. It is suggested to use concept mapping in teaching practical courses such as fundamentals of nursing.
Keywords: Concept Mapping; Conventional Teaching Method; Nursing; Practical Skills; Students.
Similar articles
-
Concept mapping. Does it improve critical thinking ability in practical nursing students?Nurs Educ Perspect. 2011 Jul-Aug;32(4):229-33. doi: 10.5480/1536-5026-32.4.229. Nurs Educ Perspect. 2011. PMID: 21923002 Clinical Trial.
-
Randomized comparison between objective-based lectures and outcome-based concept mapping for teaching neurological care to nursing students.Nurse Educ Today. 2016 Feb;37:83-90. doi: 10.1016/j.nedt.2015.11.032. Epub 2015 Dec 15. Nurse Educ Today. 2016. PMID: 26725013 Clinical Trial.
-
The effects of mentorship and educational videos on nursing students' physical examination skills: a clinical audit.BMC Nurs. 2023 Dec 6;22(1):463. doi: 10.1186/s12912-023-01626-w. BMC Nurs. 2023. PMID: 38057848 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of high fidelity simulation versus low fidelity simulation on practical/clinical skill development in pre-registration physiotherapy students: a systematic review.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2019 Jun;17(6):1229-1255. doi: 10.11124/JBISRIR-2017-003931. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2019. PMID: 30964770
-
The Effect of Concept Maps on Undergraduate Nursing Students' Critical Thinking.Nurs Educ Perspect. 2018 Jul/Aug;39(4):208-214. doi: 10.1097/01.NEP.0000000000000307. Nurs Educ Perspect. 2018. PMID: 29629932 Review.
Cited by
-
Investigating the Effect of Online Gamification on Electrocardiogram Interpretation and Self-Directed Learning in Nursing Students.J Adv Med Educ Prof. 2024 Jul 1;12(3):199-207. doi: 10.30476/JAMP.2024.101396.1925. eCollection 2024 Jul. J Adv Med Educ Prof. 2024. PMID: 39175583 Free PMC article.
-
Concept mapping teaching method and nursing education: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Med Educ. 2025 May 28;25(1):792. doi: 10.1186/s12909-025-07392-4. BMC Med Educ. 2025. PMID: 40437435 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Duchscher JB. A process of becoming: the stages of new nursing graduate professional role transition. J Contin Educ Nurs. 2008;39(10):441–50. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources