Randomized Clinical Trial of Sodium Polystyrene Sulfonate for the Treatment of Mild Hyperkalemia in CKD
- PMID: 26576619
- PMCID: PMC4670766
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.03640415
Randomized Clinical Trial of Sodium Polystyrene Sulfonate for the Treatment of Mild Hyperkalemia in CKD
Abstract
Background and objectives: Hyperkalemia affects up to 10% of patients with CKD. Sodium polystyrene sulfonate has long been prescribed for this condition, although evidence is lacking on its efficacy for the treatment of mild hyperkalemia over several days. This study aimed to evaluate the efficacy of sodium polystyrene sulfonate in the treatment of mild hyperkalemia.
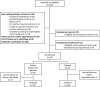
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: In total, 33 outpatients with CKD and mild hyperkalemia (5.0-5.9 mEq/L) in a single teaching hospital were included in this double-blind randomized clinical trial. We randomly assigned these patients to receive either placebo or sodium polystyrene sulfonate of 30 g orally one time per day for 7 days. The primary outcome was the comparison between study groups of the mean difference of serum potassium levels between the day after the last dose of treatment and baseline.
Results: The mean duration of treatment was 6.9 days. Sodium polystyrene sulfonate was superior to placebo in the reduction of serum potassium levels (mean difference between groups, -1.04 mEq/L; 95% confidence interval, -1.37 to -0.71). A higher proportion of patients in the sodium polystyrene sulfonate group attained normokalemia at the end of their treatment compared with those in the placebo group, but the difference did not reach statistical significance (73% versus 38%; P=0.07). There was a trend toward higher rates of electrolytic disturbances and an increase in gastrointestinal side effects in the group receiving sodium polystyrene sulfonate.
Conclusions: Sodium polystyrene sulfonate was superior to placebo in reducing serum potassium over 7 days in patients with mild hyperkalemia and CKD.
Keywords: double-blind method; humans; hyperkalemia; kidney failure, chronic; outpatients; polystyrene sulfonic acid; polystyrenes; potassium; randomized controlled trial; renal insufficiency, chronic.
Copyright © 2015 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures
References
-
- Kovesdy CP: Management of hyperkalaemia in chronic kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol 10: 653–662, 2014 - PubMed
-
- Hudson JQ: Chronic kidney disease: Management of complications. In: Pharmacotherapy: A Pathophysiologic Approach, 7th Ed., edited by Dipiro JT, Talbert RL, Yee GC, Matzke GR, Wells BG, Posey LM, New York, McGraw-Hill Medical, 2008, pp 765–791
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical