Structural basis of Sorcin-mediated calcium-dependent signal transduction
- PMID: 26577048
- PMCID: PMC4649501
- DOI: 10.1038/srep16828
Structural basis of Sorcin-mediated calcium-dependent signal transduction
Abstract
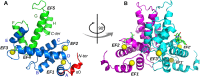
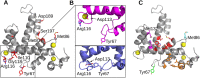
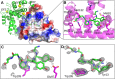
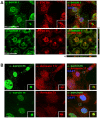
Sorcin is an essential penta-EF hand calcium binding protein, able to confer the multi-drug resistance phenotype to drug-sensitive cancer cells and to reduce Endoplasmic Reticulum stress and cell death. Sorcin silencing blocks cell cycle progression in mitosis and induces cell death by triggering apoptosis. Sorcin participates in the modulation of calcium homeostasis and in calcium-dependent cell signalling in normal and cancer cells. The molecular basis of Sorcin action is yet unknown. The X-ray structures of Sorcin in the apo (apoSor) and in calcium bound form (CaSor) reveal the structural basis of Sorcin action: calcium binding to the EF1-3 hands promotes a large conformational change, involving a movement of the long D-helix joining the EF1-EF2 sub-domain to EF3 and the opening of EF1. This movement promotes the exposure of a hydrophobic pocket, which can accommodate in CaSor the portion of its N-terminal domain displaying the consensus binding motif identified by phage display experiments. This domain inhibits the interaction of sorcin with PDCD6, a protein that carries the Sorcin consensus motif, co-localizes with Sorcin in the perinuclear region of the cell and in the midbody and is involved in the onset of apoptosis.
Figures


References
-
- Nagpal J. K. & Das B. R. Identification of differentially expressed genes in tobacco chewing-mediated oral cancer by differential display-polymerase chain reaction. Eur J Clin Invest 37, 658–64 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Pomeroy S. L. et al. Prediction of central nervous system embryonal tumour outcome based on gene expression. Nature 415, 436–42 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Yokota T. et al. Identification of histological markers for malignant glioma by genome-wide expression analysis: dynein, alpha-PIX and sorcin. Acta Neuropathol 111, 29–38 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Zhao P. et al. Comparative proteomic analysis of anti-benzo(a)pyrene-7,8-dihydrodiol–9,10-epoxide-transformed and normal human bronchial epithelial G0/G1 cells. Chem Biol Interact 186, 166–73 (2010). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

