Tropheryma whipplei bivalvular endocarditis and polyarthralgia: a case report
- PMID: 26577283
- PMCID: PMC4650277
- DOI: 10.1186/s13256-015-0746-x
Tropheryma whipplei bivalvular endocarditis and polyarthralgia: a case report
Abstract
Introduction: Tropheryma whipplei infection should be considered in patients with suspected infective endocarditis with negative blood cultures. The case (i) shows how previous symptoms can contribute to the diagnosis of this illness, and (ii) elucidates current recommended diagnostic and therapeutic approaches to Whipple's disease.
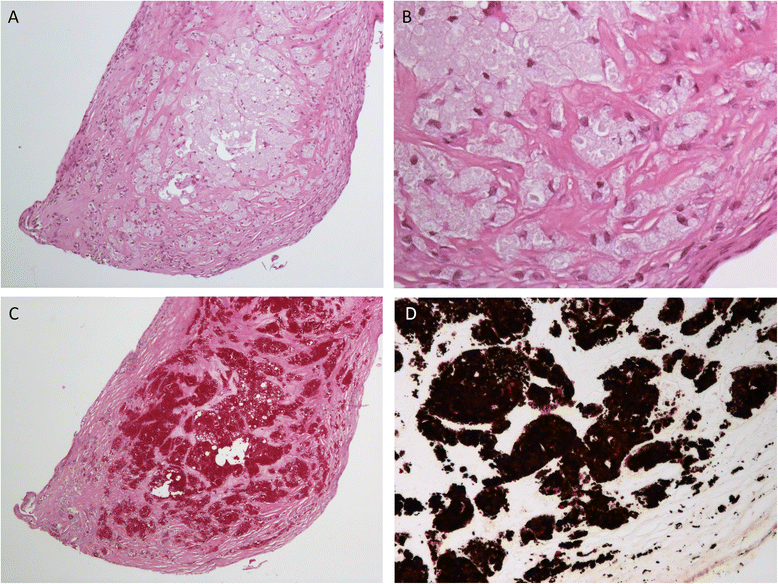
Case presentation: A 71-year-old Swiss man with a past history of 2 years of diffuse arthralgia was admitted for a possible endocarditis with severe aortic and mitral regurgitation. Serial blood cultures were negative. Our patient underwent replacement of his aortic and mitral valve by biological prostheses. T. whipplei was documented by polymerase chain reactions on both removed valves and on stools, as well as by valve histology. A combination of hydroxychloroquine and doxycycline was initiated as lifetime treatment followed by the complete disappearance of his arthralgia.
Conclusions: This case report underlines the importance of considering T. whipplei as a possible causal etiology of blood culture-negative endocarditis. Lifelong antibiotic treatment should be considered for this pathogen (i) due to the significant rate of relapses, and (ii) to the risk of reinfection with another strain since these patients likely have some genetic predisposition.
Figures



References
-
- Smith S, Marrie TJ. Blood-culture-negative endocarditis. In: Chang KL, Embil JM, editors. Endocarditis diagnosis and management. London: Springer; 2006. pp. 185–200.
-
- Lepidi H, Fenollar F, Dumler JS, Gauduchon V, Chalabreysse L, Bammert A, et al. Cardiac valves in patients with Whipple endocarditis: microbiological, molecular, quantitative histologic, and immunohistochemical studies of 5 patients. J Infect Dis. 2004;190:935–45. doi: 10.1086/422845. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fenollar F, Laouira S, Lepidi H, Rolain JM, Raoult D. Value of Tropheryma whipplei quantitative polymerase chain reaction assay for the diagnosis of Whipple disease: usefulness of saliva and stool specimens for first-line screening. Clin Infect Dis. 2008;47:659–67. doi: 10.1086/590559. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

