First Experience of Ultrasound-guided Percutaneous Ablation for Recurrent Hepatoblastoma after Liver Resection in Children
- PMID: 26578035
- PMCID: PMC4649467
- DOI: 10.1038/srep16805
First Experience of Ultrasound-guided Percutaneous Ablation for Recurrent Hepatoblastoma after Liver Resection in Children
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: First Experience of Ultrasound-guided Percutaneous Ablation for Recurrent Hepatoblastoma after Liver Resection in Children.Sci Rep. 2016 Sep 16;6:33424. doi: 10.1038/srep33424. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27632926 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
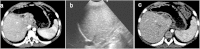
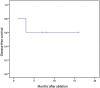
This study aimed to summarize the first experience with ultrasound-guided percutaneous ablation treatment (PAT) for recurrent hepatoblastoma (HB) after liver resection in children. From August 2013 to October 2014, PAT was used to treat 5 children with a total of 8 recurrent HB (mean size, 1.4 ± 0.8 cm; size range, 0.7-3.1 cm), including 4 patients with 7 tumors in the liver and 1 patient with 1 tumor in the lung. Technical success was achieved in all patients (5/5, 100%). The complete ablation rate after the first ablation session was 80% (4/5) on a patient-by-patient basis and 87.5% (7/8) on a tumor-by-tumor basis. Only 1 patient developed a fever with temperature >39 °C; it lasted 4 days after radiofrequency ablation (RFA) and was resolved by conservative therapy. During the follow-up period, new intrahepatic recurrences after PAT were detected in two patients. One died due to tumor progression 4 months after ablation. The median overall survival time after PAT was 13.8 months. PAT is a safe and promising therapy for children with recurrent HB after liver resection, and further investigation in large-scale randomized clinical trials is required to determine its role in the treatment of this disease.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reiterative Radiofrequency Ablation in the Management of Pediatric Patients with Hepatoblastoma Metastases to the Lung, Liver, or Bone.Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2019 Jan;42(1):41-47. doi: 10.1007/s00270-018-2097-7. Epub 2018 Oct 22. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2019. PMID: 30350173
-
Microwave ablation assisted by three-dimensional visualization system as local therapy for relapsed hepatoblastoma: a small pilot study.Abdom Radiol (NY). 2019 Aug;44(8):2909-2915. doi: 10.1007/s00261-019-02011-5. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2019. PMID: 31089779
-
Radiofrequency ablation for recurrent intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma after curative resection.Eur J Radiol. 2011 Dec;80(3):e221-5. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2010.09.019. Epub 2010 Oct 14. Eur J Radiol. 2011. PMID: 20950977
-
Role of interventional radiology in managing pediatric liver tumors : Part 2: percutaneous interventions.Pediatr Radiol. 2018 Apr;48(4):565-580. doi: 10.1007/s00247-018-4072-5. Epub 2018 Feb 2. Pediatr Radiol. 2018. PMID: 29396792 Review.
-
Surgery for hepatoblastoma in children.Curr Opin Pediatr. 1996 Jun;8(3):276-82. doi: 10.1097/00008480-199606000-00016. Curr Opin Pediatr. 1996. PMID: 8814407 Review.
Cited by
-
Radiofrequency Ablation for Cervical Metastatic Lymph Nodes in Children and Adolescents With Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: A Preliminary Study.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 May 18;12:624054. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.624054. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34084150 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor ablation in children.Pediatr Radiol. 2025 Apr;55(4):733-746. doi: 10.1007/s00247-024-06059-4. Epub 2024 Oct 23. Pediatr Radiol. 2025. PMID: 39441218 Review.
-
Immunological effect of local ablation combined with immunotherapy on solid malignancies.Chin J Cancer. 2017 Jun 7;36(1):49. doi: 10.1186/s40880-017-0216-5. Chin J Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28592286 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy analysis of C5V chemotherapy combined with transcatheter subcutaneous radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of children with advanced (Stage III/IV) hepatoblastoma.Pak J Med Sci. 2022 Sep-Oct;38(7):1802-1807. doi: 10.12669/pjms.38.7.5899. Pak J Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 36246706 Free PMC article.
-
Potential therapies for residual hepatoblastoma following incomplete ablation treatment in a nude mouse subcutaneous xenograft model based on lncRNA and mRNA expression profiles.Oncol Rep. 2020 Jun;43(6):1915-1927. doi: 10.3892/or.2020.7545. Epub 2020 Mar 16. Oncol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32186781 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kremer N., Walther A. E. & Tiao G. M. Management of hepatoblastoma: an update. Curr Opin Pediatr 26, 362–369 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Horton J. D., Lee S., Brown S. R., Bader J. & Meier D. E. Survival trends in children with hepatoblastoma. Pediatr Surg Int 25, 407–412 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Qiao G. L. et al. Predictors of survival after resection of children with hepatoblastoma: A single Asian center experience. Eur J Surg Oncol 40, 1533–1539 (2014). - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

