Imiquimod-induced apoptosis of melanoma cells is mediated by ER stress-dependent Noxa induction and enhanced by NF-κB inhibition
- PMID: 26578344
- PMCID: PMC4727561
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.12718
Imiquimod-induced apoptosis of melanoma cells is mediated by ER stress-dependent Noxa induction and enhanced by NF-κB inhibition
Abstract
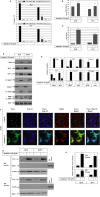
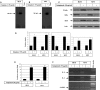
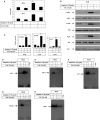
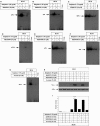
Melanoma is characterized by dysregulated intracellular signalling pathways including an impairment of the cell death machinery, ultimately resulting in melanoma resistance, survival and progression. This explains the tumour's extraordinary resistance to the standard treatment. Imiquimod is a topical immune response modifier (imidazoquinoline) with both antiviral and antitumour activities. The mechanism by which imiquimod triggers the apoptosis of melanoma cells has now been carefully elucidated. Imiquimod-induced apoptosis is associated with the activation of apoptosis signalling regulating kinase1/c-Jun-N-terminal kinase/p38 pathways and the induction of endoplasmic stress characterized by the activation of the protein kinase RNA-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase signalling pathway, increase in intracellular Ca(2+) release, degradation of calpain and subsequent cleavage of caspase-4. Moreover, imiquimod triggers the activation of NF-κB and the expression of the inhibitor of apoptosis proteins (IAPs) such as, X-linked IAP (XIAP) together with the accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Also, imiquimod triggers mitochondrial dysregulation characterized by the loss of mitochondrial membrane potential (Δψm), the increase in cytochrome c release, and cleavage of caspase-9, caspase-3 and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP). Inhibitors of specific pathways, permit the elucidation of possible mechanisms of imiquimod-induced apoptosis. They demonstrate that inhibition of NF-kB by the inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase (IKK) inhibitor Bay 11-782 or knockdown of XIAP induces melanoma apoptosis in cells exposed to imiquimod. These findings support the use of either IKK inhibitors or IAP antagonists as adjuvant therapies to improve the effectiveness topical imiquimod in the treatment of melanoma.
Keywords: ER stress; NF-κB; apoptosis; imiquimod; melanoma.
© 2015 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Bortezomib/proteasome inhibitor triggers both apoptosis and autophagy-dependent pathways in melanoma cells.Cell Signal. 2013 Jan;25(1):308-18. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2012.10.004. Epub 2012 Oct 15. Cell Signal. 2013. PMID: 23079083
-
Apoptosis related protein-1 triggers melanoma cell death via interaction with the juxtamembrane region of p75 neurotrophin receptor.J Cell Mol Med. 2012 Feb;16(2):349-61. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2011.01304.x. J Cell Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 21418516 Free PMC article.
-
Berberine-induced apoptosis in human glioblastoma T98G cells is mediated by endoplasmic reticulum stress accompanying reactive oxygen species and mitochondrial dysfunction.Biol Pharm Bull. 2010;33(10):1644-9. doi: 10.1248/bpb.33.1644. Biol Pharm Bull. 2010. PMID: 20930370
-
Immune modulation and apoptosis induction: two sides of the antitumoral activity of imiquimod.Apoptosis. 2004 May;9(3):291-8. doi: 10.1023/b:appt.0000025805.55340.c3. Apoptosis. 2004. PMID: 15258460 Review.
-
The ER-overload response: activation of NF-kappa B.Trends Biochem Sci. 1997 Feb;22(2):63-7. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(96)10073-6. Trends Biochem Sci. 1997. PMID: 9048485 Review.
Cited by
-
Induction of Apoptosis, Inhibition of MCL-1, and VEGF-A Expression Are Associated with the Anti-Cancer Efficacy of Magnolol Combined with Regorafenib in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Apr 25;13(9):2066. doi: 10.3390/cancers13092066. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33922992 Free PMC article.
-
EAPB0503: An Imiquimod analog with potent in vitro activity against cutaneous leishmaniasis caused by Leishmania major and Leishmania tropica.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2018 Nov 21;12(11):e0006854. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0006854. eCollection 2018 Nov. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2018. PMID: 30462645 Free PMC article.
-
Endoplasmic reticulum stress-a key guardian in cancer.Cell Death Discov. 2024 Jul 30;10(1):343. doi: 10.1038/s41420-024-02110-3. Cell Death Discov. 2024. PMID: 39080273 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of MAPK11/12/13/14 (p38 MAPK) protein in dopamine agonist-resistant prolactinomas.BMC Endocr Disord. 2021 Nov 23;21(1):235. doi: 10.1186/s12902-021-00900-9. BMC Endocr Disord. 2021. PMID: 34814904 Free PMC article.
-
The role of mitochondria in the resistance of melanoma to PD-1 inhibitors.J Transl Med. 2023 May 23;21(1):345. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04200-9. J Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 37221594 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kemper K, Krijgsman O, Cornelissen‐Steijger P, et al Intra‐ and inter‐tumor heterogeneity in a vemurafenib‐resistant melanoma patient and derived xenografts. EMBO. 2015; 7: 1104–18. Doi:10.15252/emmm.201404914. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Partl R, Fastner G, Kaiser J, et al KPS/LDH index: a simple tool for identifying patients with metastatic melanoma who are unlikely to benefit from palliative whole brain radiotherapy. Support Care Cancer. 2015; Doi:10.1007/s00520‐015‐2793‐7. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Massi D, Brusa D, Merelli B, et al The status of PD‐L1 and tumor‐infiltrating immune cells predict resistance and poor prognosis in BRAFi‐treated melanoma patients harboring mutant BRAFV600. Ann Oncol. 2015; 72: 37–46. - PubMed
-
- Kessler DA, Austin RH, Levine H. Resistance to chemotherapy: patient variability and cellular heterogeneity. Cancer Res. 2014; 74: 4663–70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

