Hypoxia Potentiates Palmitate-induced Pro-inflammatory Activation of Primary Human Macrophages
- PMID: 26578520
- PMCID: PMC4697177
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M115.686709
Hypoxia Potentiates Palmitate-induced Pro-inflammatory Activation of Primary Human Macrophages
Abstract
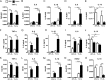
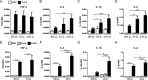
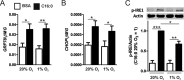
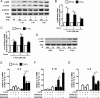
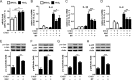
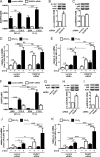
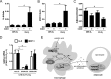
Pro-inflammatory cytokines secreted by adipose tissue macrophages (ATMs) contribute to chronic low-grade inflammation and obesity-induced insulin resistance. Recent studies have shown that adipose tissue hypoxia promotes an inflammatory phenotype in ATMs. However, our understanding of how hypoxia modulates the response of ATMs to free fatty acids within obese adipose tissue is limited. We examined the effects of hypoxia (1% O2) on the pro-inflammatory responses of human monocyte-derived macrophages to the saturated fatty acid palmitate. Compared with normoxia, hypoxia significantly increased palmitate-induced mRNA expression and protein secretion of IL-6 and IL-1β. Although palmitate-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress and nuclear factor κB pathway activation were not enhanced by hypoxia, hypoxia increased the activation of JNK and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling in palmitate-treated cells. Inhibition of JNK blocked the hypoxic induction of pro-inflammatory cytokine expression, whereas knockdown of hypoxia-induced transcription factors HIF-1α and HIF-2α alone or in combination failed to reduce IL-6 and only modestly reduced IL-1β gene expression in palmitate-treated hypoxic macrophages. Enhanced pro-inflammatory cytokine production and JNK activity under hypoxia were prevented by inhibiting reactive oxygen species generation. In addition, silencing of dual-specificity phosphatase 16 increased normoxic levels of IL-6 and IL-1β and reduced the hypoxic potentiation in palmitate-treated macrophages. The secretome of hypoxic palmitate-treated macrophages promoted IL-6 and macrophage chemoattractant protein 1 expression in primary human adipocytes, which was sensitive to macrophage JNK inhibition. Our results reveal that the coexistence of hypoxia along with free fatty acids exacerbates macrophage-mediated inflammation.
Keywords: cytokine; fatty acid; hypoxia; inflammation; macrophage.
© 2016 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures
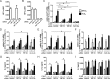
Similar articles
-
Vitamin D inhibits palmitate-induced macrophage pro-inflammatory cytokine production by targeting the MAPK pathway.Immunol Lett. 2018 Oct;202:23-30. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2018.07.009. Epub 2018 Aug 1. Immunol Lett. 2018. PMID: 30076857
-
Effect of arachidonic acid on hypoxia-induced IL-6 production in mouse ES cells: Involvement of MAPKs, NF-kappaB, and HIF-1alpha.J Cell Physiol. 2010 Mar;222(3):574-85. doi: 10.1002/jcp.21973. J Cell Physiol. 2010. PMID: 19950212
-
The Tpl2 Kinase Regulates the COX-2/Prostaglandin E2 Axis in Adipocytes in Inflammatory Conditions.Mol Endocrinol. 2015 Jul;29(7):1025-36. doi: 10.1210/me.2015-1027. Epub 2015 May 28. Mol Endocrinol. 2015. PMID: 26020725 Free PMC article.
-
Adipocyte-Macrophage Cross-Talk in Obesity.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;960:327-343. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-48382-5_14. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 28585206 Review.
-
Message Transmission Between Adipocyte and Macrophage in Obesity.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024;1460:273-295. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-63657-8_9. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 39287855 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of tumor-associated macrophages in primary hepatocellular carcinoma and its related targeting therapy.Int J Med Sci. 2021 Mar 15;18(10):2109-2116. doi: 10.7150/ijms.56003. eCollection 2021. Int J Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 33859517 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Macrophage-Specific Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α Contributes to Impaired Autophagic Flux in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis.Hepatology. 2019 Feb;69(2):545-563. doi: 10.1002/hep.30215. Epub 2019 Jan 4. Hepatology. 2019. PMID: 30102772 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial destiny in type 2 diabetes: the effects of oxidative stress on the dynamics and biogenesis of mitochondria.PeerJ. 2020 Aug 25;8:e9741. doi: 10.7717/peerj.9741. eCollection 2020. PeerJ. 2020. PMID: 32904391 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia in Aging and Aging-Related Diseases: Mechanism and Therapeutic Strategies.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 25;23(15):8165. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158165. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35897741 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Macrophage-Driven Inflammation in Metabolic Osteoarthritis: Implications for Biomarker and Therapy Development.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 24;24(7):6112. doi: 10.3390/ijms24076112. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37047082 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

