New aspects in fenestrated capillary and tissue dynamics in the sensory circumventricular organs of adult brains
- PMID: 26578857
- PMCID: PMC4621430
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2015.00390
New aspects in fenestrated capillary and tissue dynamics in the sensory circumventricular organs of adult brains
Abstract
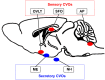
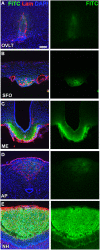
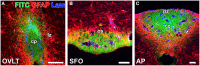
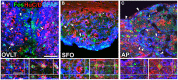
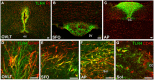
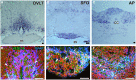
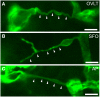
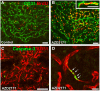
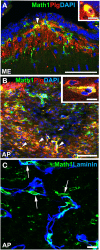
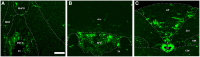
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) generally consists of endothelial tight junction barriers that prevent the free entry of blood-derived substances, thereby maintaining the extracellular environment of the brain. However, the circumventricular organs (CVOs), which are located along the midlines of the brain ventricles, lack these endothelial barriers and have fenestrated capillaries; therefore, they have a number of essential functions, including the transduction of information between the blood circulation and brain. Previous studies have demonstrated the extensive contribution of the CVOs to body fluid and thermal homeostasis, energy balance, the chemoreception of blood-derived substances, and neuroinflammation. In this review, recent advances have been discussed in fenestrated capillary characterization and dynamic tissue reconstruction accompanied by angiogenesis and neurogliogenesis in the sensory CVOs of adult brains. The sensory CVOs, including the organum vasculosum of the lamina terminalis (OVLT), subfornical organ (SFO), and area postrema (AP), have size-selective and heterogeneous vascular permeabilities. Astrocyte-/tanycyte-like neural stem cells (NSCs) sense blood- and cerebrospinal fluid-derived information through the transient receptor potential vanilloid 1, a mechanical/osmotic receptor, Toll-like receptor 4, a lipopolysaccharide receptor, and Nax, a Na-sensing Na channel. They also express tight junction proteins and densely and tightly surround mature neurons to protect them from blood-derived neurotoxic substances, indicating that the NSCs of the CVOs perform BBB functions while maintaining the capacity to differentiate into new neurons and glial cells. In addition to neurogliogenesis, the density of fenestrated capillaries is regulated by angiogenesis, which is accompanied by the active proliferation and sprouting of endothelial cells. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) signaling may be involved in angiogenesis and neurogliogenesis, both of which affect vascular permeability. Thus, recent findings advocate novel concepts for the CVOs, which have the dynamic features of vascular and parenchymal tissues.
Keywords: TLR4; TRPV1; VEGF; angiogenesis; blood-brain barrier (BBB); homeostasis; inflammation; neural stem cells (NSCs).
Figures

Similar articles
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor-dependent angiogenesis and dynamic vascular plasticity in the sensory circumventricular organs of adult mouse brain.Cell Tissue Res. 2015 Mar;359(3):865-84. doi: 10.1007/s00441-014-2080-9. Epub 2015 Jan 10. Cell Tissue Res. 2015. PMID: 25573819
-
Changes in pericytic expression of NG2 and PDGFRB and vascular permeability in the sensory circumventricular organs of adult mouse by osmotic stimulation.Cell Biochem Funct. 2014 Jan;32(1):51-61. doi: 10.1002/cbf.2971. Epub 2013 Apr 29. Cell Biochem Funct. 2014. PMID: 23629811
-
Heterogeneous vascular permeability and alternative diffusion barrier in sensory circumventricular organs of adult mouse brain.Cell Tissue Res. 2016 Feb;363(2):497-511. doi: 10.1007/s00441-015-2207-7. Epub 2015 Jun 6. Cell Tissue Res. 2016. PMID: 26048259
-
Glial functions in the blood-brain communication at the circumventricular organs.Front Neurosci. 2022 Oct 6;16:991779. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.991779. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36278020 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sensory circumventricular organs and brain homeostatic pathways.FASEB J. 1993 May;7(8):678-86. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.8.8500693. FASEB J. 1993. PMID: 8500693 Review.
Cited by
-
The Coding Logic of Interoception.Annu Rev Physiol. 2024 Feb 12;86:301-327. doi: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-042222-023455. Epub 2023 Dec 7. Annu Rev Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38061018 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Hypothalamic Reactive Astrocytes in Diet-Induced Obesity.Mol Cells. 2022 Feb 28;45(2):65-75. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2022.2044. Mol Cells. 2022. PMID: 35236781 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Leukemia Inhibitory Factor Represses GnRH Gene Expression via cFOS during Inflammation in Male Mice.Neuroendocrinology. 2019;108(4):291-307. doi: 10.1159/000496754. Epub 2019 Jan 10. Neuroendocrinology. 2019. PMID: 30630179 Free PMC article.
-
Adult Neurogenesis in Sheep: Characterization and Contribution to Reproduction and Behavior.Front Neurosci. 2017 Oct 23;11:570. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2017.00570. eCollection 2017. Front Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 29109674 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Basic physiology of the blood-brain barrier in health and disease: a brief overview.Tissue Barriers. 2021 Jan 2;9(1):1840913. doi: 10.1080/21688370.2020.1840913. Epub 2020 Nov 15. Tissue Barriers. 2021. PMID: 33190576 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

