S-thanatin functionalized liposome potentially targeting on Klebsiella pneumoniae and its application in sepsis mouse model
- PMID: 26578959
- PMCID: PMC4621865
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2015.00249
S-thanatin functionalized liposome potentially targeting on Klebsiella pneumoniae and its application in sepsis mouse model
Abstract
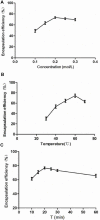
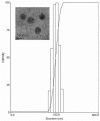
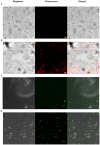
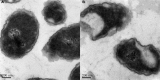
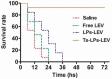
S-thanatin (Ts) was a short antimicrobial peptide with selective antibacterial activity. In this study, we aimed to design a drug carrier with specific bacterial targeting potential. The positively charged Ts was modified onto the liposome surface by linking Ts to the constituent lipids via a PEG linker. The benefits of this design were evaluated by preparing a series of liposomes and comparing their biological effects in vitro and in vivo. The particle size and Zeta potential of the constructed liposomes were measured with a Zetasizer Nano ZS system and a confocal laser scanning microscope. The in vitro drug delivery potential was evaluated by measuring the cellular uptake of encapsulated levofloxacin using HPLC. Ts-linked liposome or its conjugates with quantum dots favored bacterial cells, and increased the bacterial uptake of levofloxacin. In antimicrobial assays, the Ts and levofloxacin combination showed a synergistic effect, and Ts-LPs-LEV exhibited excellent activity against the quality control stain Klebsiella pneumoniae ATCC 700603 and restored the susceptibility of multidrug-resistant K. pneumoniae clinical isolates to levofloxacin in vitro. Furthermore, Ts-LPs-LEV markedly reduced the lethality rate of the septic shock and resulted in rapid bacterial clearance in mouse models receiving clinical multidrug resistant (MDR) isolates. These results suggest that the Ts-functionalized liposome may be a promising antibiotic delivery system for clinical infectious disorders caused by MDR bacteria, in particular the sepsis related diseases.
Keywords: antimicrobial peptide; liposome; multidrug resistance; sepsis; targeting delivery.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Application of S-thanatin, an antimicrobial peptide derived from thanatin, in mouse model of Klebsiella pneumoniae infection.Peptides. 2013 Jul;45:73-7. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2013.04.012. Epub 2013 May 1. Peptides. 2013. PMID: 23643614
-
Activity of the antimicrobial peptide and thanatin analog S-thanatin on clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae resistant to conventional antibiotics with different structures.Curr Microbiol. 2009 Aug;59(2):147-53. doi: 10.1007/s00284-009-9410-2. Epub 2009 May 21. Curr Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19459007
-
Degradable antimicrobial polycarbonates with unexpected activity and selectivity for treating multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae lung infection in mice.Acta Biomater. 2019 Aug;94:268-280. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2019.05.057. Epub 2019 May 24. Acta Biomater. 2019. PMID: 31129359
-
Interaction of antimicrobial peptide s-thanatin with lipopolysaccharide in vitro and in an experimental mouse model of septic shock caused by a multidrug-resistant clinical isolate of Escherichia coli.Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2010 Mar;35(3):250-4. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2009.11.009. Epub 2009 Dec 31. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2010. PMID: 20045294
-
Literature review on the distribution characteristics and antimicrobial resistance of bacterial pathogens in neonatal sepsis.J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2022 Mar;35(5):861-870. doi: 10.1080/14767058.2020.1732342. Epub 2020 Feb 26. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2022. PMID: 32102584 Review.
Cited by
-
Engineered extracellular vesicles coated with an antimicrobial peptide for advanced control of bacterial sepsis.J Extracell Biol. 2024 Aug 23;3(8):e70000. doi: 10.1002/jex2.70000. eCollection 2024 Aug. J Extracell Biol. 2024. PMID: 39185334 Free PMC article.
-
TPGS-based and S-thanatin functionalized nanorods for overcoming drug resistance in Klebsiella pneumonia.Nat Commun. 2022 Jun 29;13(1):3731. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-31500-3. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35768446 Free PMC article.
-
Nanotools for Sepsis Diagnosis and Treatment.Adv Healthc Mater. 2021 Jan;10(1):e2001378. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202001378. Epub 2020 Nov 25. Adv Healthc Mater. 2021. PMID: 33236524 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An infection-microenvironment-targeted and responsive peptide-drug nanosystem for sepsis emergency by suppressing infection and inflammation.Asian J Pharm Sci. 2023 Nov;18(6):100869. doi: 10.1016/j.ajps.2023.100869. Epub 2023 Nov 28. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2023. PMID: 38161786 Free PMC article.
-
Peptides to Overcome the Limitations of Current Anticancer and Antimicrobial Nanotherapies.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Jun 10;14(6):1235. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14061235. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35745807 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anonymous (ed). (2001). National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards (2001) Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria That Grow Aerobically 5th Edn Wayne, PA: National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

