Mirror neuron system based therapy for aphasia rehabilitation
- PMID: 26579046
- PMCID: PMC4627352
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2015.01665
Mirror neuron system based therapy for aphasia rehabilitation
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the effect of hand action observation training, i.e., mirror neuron system (MNS) based training, on language function of aphasic patients after stroke. In addition, to reveal the tentative mechanism underlying this effect.
Methods: Six aphasic patients after stroke, meeting the criteria, undergo 3 weeks' training protocol (30 min per day, 6 days per week). Among them, four patients accepted an ABA training design, i.e., they implemented Protocol A (hand action observation combined with repetition) in the first and third weeks and carried out Protocol B (static object observation combined with repetition) in the second week. Conversely, for the other two patients, BAB training design was adopted, i.e., patients took Protocol B in the first and third weeks and accepted Protocol A in the second week. Picture naming test, western aphasia battery (WAB) and Token Test were applied to evaluate the changes of language function before and after each week's training. Furthermore, two subjects (one aphasic patient and one healthy volunteer) attended a functional MRI (fMRI) experiment, by which we tried to reveal the mechanism underlying possible language function changes after training.
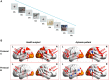
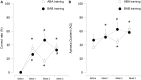
Results: Compared with static object observation and repetition training (Protocol B), hand action observation and repetition training (Protocol A) effectively improved most aspects of the language function in all six patients, as demonstrated in the picture naming test, subtests of oral language and aphasia quotient (AQ) of WAB. In addition, the fMRI experiment showed that Protocol A induced more activations in the MNS of one patient and one healthy control when compared to Protocol B.
Conclusion: The mirror neuron based therapy may facilitate the language recovery for aphasic patients and this, to some extent, provides a novel direction of rehabilitation for aphasia patients.
Keywords: action observation treatment (AOT); aphasia; fMRI; mirror neuron system (MNS); rehabilitation; stroke; therapy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Aphasia rehabilitation based on mirror neuron theory: a randomized-block-design study of neuropsychology and functional magnetic resonance imaging.Neural Regen Res. 2019 Jun;14(6):1004-1012. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.250580. Neural Regen Res. 2019. PMID: 30762012 Free PMC article.
-
The Effectiveness of Action Observation Therapy Based on Mirror Neuron Theory in Chinese Patients with Apraxia of Speech after Stroke.Eur Neurol. 2019;81(5-6):278-286. doi: 10.1159/000503960. Epub 2019 Oct 29. Eur Neurol. 2019. PMID: 31661693 Clinical Trial.
-
A relative weight analysis of the Chinese version of WAB.Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2025 Mar-Apr;60(2):e70002. doi: 10.1111/1460-6984.70002. Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2025. PMID: 39970393
-
The mirror neuron system and treatment of stroke.Dev Psychobiol. 2012 Apr;54(3):293-310. doi: 10.1002/dev.20504. Epub 2010 Nov 24. Dev Psychobiol. 2012. PMID: 22415917 Review.
-
Action observation as a tool for neurorehabilitation to moderate motor deficits and aphasia following stroke.Neural Regen Res. 2012 Sep 15;7(26):2063-74. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5374.2012.26.008. Neural Regen Res. 2012. PMID: 25624838 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dubbing language-therapy CINEma-based in aphasia post-stroke (DULCINEA): A feasibility randomized crossover controlled trial.Digit Health. 2024 Oct 10;10:20552076241288311. doi: 10.1177/20552076241288311. eCollection 2024 Jan-Dec. Digit Health. 2024. PMID: 39421311 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of Interhemispheric Inhibition between Primary Motor Cortices Induced by Manual Motor Imitation: A Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Study.Brain Sci. 2021 Feb 19;11(2):266. doi: 10.3390/brainsci11020266. Brain Sci. 2021. PMID: 33669827 Free PMC article.
-
Aphasia rehabilitation based on mirror neuron theory: a randomized-block-design study of neuropsychology and functional magnetic resonance imaging.Neural Regen Res. 2019 Jun;14(6):1004-1012. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.250580. Neural Regen Res. 2019. PMID: 30762012 Free PMC article.
-
Thinking on Treating Echolalia in Aphasia: Recommendations and Caveats for Future Research Directions.Front Hum Neurosci. 2017 Apr 3;11:164. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2017.00164. eCollection 2017. Front Hum Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28420974 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Harnessing Mirror Neurons: Improving Balance and Quality of Life After a Stroke.Cureus. 2025 Mar 27;17(3):e81290. doi: 10.7759/cureus.81290. eCollection 2025 Mar. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40291301 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bonifazi S., Tomaiuolo F., Altoè G., Ceravolo M. G., Provinciali L., Marangolo P. (2013). Action observation as a useful approach for enhancing recovery of verb production: new evidence from aphasia. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 49, 473–481. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

