Production of ergothioneine by Methylobacterium species
- PMID: 26579093
- PMCID: PMC4621440
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.01185
Production of ergothioneine by Methylobacterium species
Abstract
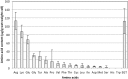
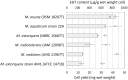
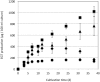
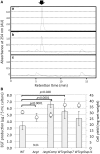
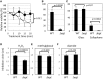
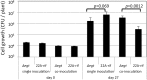
Metabolomic analysis revealed that Methylobacterium cells accumulate a large amount of ergothioneine (EGT), which is a sulfur-containing, non-proteinogenic, antioxidative amino acid derived from histidine. EGT biosynthesis and its role in methylotrophy and physiology for plant surface-symbiotic Methylobacterium species were investigated in this study. Almost all Methylobacterium type strains can synthesize EGT. We selected one of the most productive strains (M. aquaticum strain 22A isolated from a moss), and investigated the feasibility of fermentative EGT production through optimization of the culture condition. Methanol as a carbon source served as the best substrate for production. The productivity reached up to 1000 μg/100 ml culture (1200 μg/g wet weight cells, 6.3 mg/g dry weight) in 38 days. Next, we identified the genes (egtBD) responsible for EGT synthesis, and generated a deletion mutant defective in EGT production. Compared to the wild type, the mutant showed better growth on methanol and on the plant surface as well as severe susceptibility to heat treatment and irradiation of ultraviolet (UV) and sunlight. These results suggested that EGT is not involved in methylotrophy, but is involved in their phyllospheric lifestyle fitness of the genus in natural conditions.
Keywords: Methylobacterium species; antioxidant; ergothioneine; glutathione; methanol; methylotroph; reactive oxygen species.
Figures

References
-
- Bazela K., Solyga-Zurek A., Debowska R., Rogiewicz K., Bartnik E., Eris I. (2014). L-Ergothioneine protects skin cells against UV-induced damage—a preliminary study. Cosmetics 1, 51–60. 10.3390/cosmetics1010051 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

