Analyzing the molecular mechanism of lipoprotein localization in Brucella
- PMID: 26579096
- PMCID: PMC4623201
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.01189
Analyzing the molecular mechanism of lipoprotein localization in Brucella
Abstract
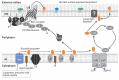
Bacterial lipoproteins possess diverse structure and functionality, ranging from bacterial physiology to pathogenic processes. As such many lipoproteins, originating from Brucella are exploited as potential vaccines to countermeasure brucellosis infection in the host. These membrane proteins are translocated from the cytoplasm to the cell membrane where they are anchored peripherally by a multifaceted targeting mechanism. Although much research has focused on the identification and classification of Brucella lipoproteins and their potential use as vaccine candidates for the treatment of Brucellosis, the underlying route for the translocation of these lipoproteins to the outer surface of the Brucella (and other pathogens) outer membrane (OM) remains mostly unknown. This is partly due to the complexity of the organism and evasive tactics used to escape the host immune system, the variation in biological structure and activity of lipoproteins, combined with the complex nature of the translocation machinery. The biosynthetic pathway of Brucella lipoproteins involves a distinct secretion system aiding translocation from the cytoplasm, where they are modified by lipidation, sorted by the lipoprotein localization machinery pathway and thereafter equipped for export to the OM. Surface localized lipoproteins in Brucella may employ a lipoprotein flippase or the β-barrel assembly complex for translocation. This review provides an overview of the characterized Brucella OM proteins that form part of the OM, including a handful of other characterized bacterial lipoproteins and their mechanisms of translocation. Lipoprotein localization pathways in gram negative bacteria will be used as a model to identify gaps in Brucella lipoprotein localization and infer a potential pathway. Of particular interest are the dual topology lipoproteins identified in Escherichia coli and Haemophilus influenza. The localization and topology of these lipoproteins from other gram negative bacteria are well characterized and may be useful to infer a solution to better understand the translocation process in Brucella.
Keywords: Brucella lipoprotein; Brucella vaccine target; Lol pathway; lipoprotein localization; lipoprotein secretion; outer membrane protein; pathogen-associated molecular patterns; toll-like receptors.
Figures


References
-
- Bang B. (1897). The etiology of epizootic abortion. J. Comp. Pathol. Ther. 10 125–IN2 10.1016/S0368-1742(97)80014-8 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

