Regulation of Macrophage, Dendritic Cell, and Microglial Phenotype and Function by the SOCS Proteins
- PMID: 26579124
- PMCID: PMC4621458
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00549
Regulation of Macrophage, Dendritic Cell, and Microglial Phenotype and Function by the SOCS Proteins
Abstract
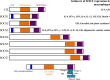
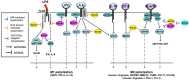
Macrophages are innate immune cells of dynamic phenotype that rapidly respond to external stimuli in the microenvironment by altering their phenotype to respond to and to direct the immune response. The ability to dynamically change phenotype must be carefully regulated to prevent uncontrolled inflammatory responses and subsequently to promote resolution of inflammation. The suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS) proteins play a key role in regulating macrophage phenotype. In this review, we summarize research to date from mouse and human studies on the role of the SOCS proteins in determining the phenotype and function of macrophages. We will also touch on the influence of the SOCS on dendritic cell (DC) and microglial phenotype and function. The molecular mechanisms of SOCS function in macrophages and DCs are discussed, along with how dysregulation of SOCS expression or function can lead to alterations in macrophage/DC/microglial phenotype and function and to disease. Regulation of SOCS expression by microRNA is discussed. Novel therapies and unanswered questions with regard to SOCS regulation of monocyte-macrophage phenotype and function are highlighted.
Keywords: IL-4 and IL-13; M1 macrophage; M2 macrophages; dendritic cells; differentiation; macrophage; macrophages; suppressor of cytokine signaling proteins.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulation of innate immunity by suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS) proteins.Immunobiology. 2008;213(3-4):225-35. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2007.10.008. Epub 2007 Nov 28. Immunobiology. 2008. PMID: 18406369 Review.
-
IL-21 enhances SOCS gene expression and inhibits LPS-induced cytokine production in human monocyte-derived dendritic cells.J Leukoc Biol. 2006 Jun;79(6):1279-85. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0905503. Epub 2006 Mar 21. J Leukoc Biol. 2006. PMID: 16551679
-
Ablation of proximal tubular suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 enhances tubular cell cycling and modifies macrophage phenotype during acute kidney injury.Kidney Int. 2014 Jun;85(6):1357-68. doi: 10.1038/ki.2013.525. Epub 2014 Jan 8. Kidney Int. 2014. PMID: 24402091
-
SOCS proteins, cytokine signalling and immune regulation.Nat Rev Immunol. 2007 Jun;7(6):454-65. doi: 10.1038/nri2093. Epub 2007 May 18. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17525754 Review.
-
Macrophage polarization and function with emphasis on the evolving roles of coordinated regulation of cellular signaling pathways.Cell Signal. 2014 Feb;26(2):192-7. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.11.004. Epub 2013 Nov 9. Cell Signal. 2014. PMID: 24219909 Review.
Cited by
-
TET2 regulates immune tolerance in chronically activated mast cells.JCI Insight. 2022 Apr 8;7(7):e154191. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.154191. JCI Insight. 2022. PMID: 35393954 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of gene expression profiles in children with type 1 diabetes mellitus.Mol Med Rep. 2019 May;19(5):3989-4000. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2019.10099. Epub 2019 Mar 28. Mol Med Rep. 2019. PMID: 30942443 Free PMC article.
-
Negative regulators of STAT3 signaling pathway in cancers.Cancer Manag Res. 2019 May 29;11:4957-4969. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S206175. eCollection 2019. Cancer Manag Res. 2019. PMID: 31213912 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Decoding microglia responses to psychosocial stress reveals blood-brain barrier breakdown that may drive stress susceptibility.Sci Rep. 2018 Jul 26;8(1):11240. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-28737-8. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30050134 Free PMC article.
-
Folic Acid Is Able to Polarize the Inflammatory Response in LPS Activated Microglia by Regulating Multiple Signaling Pathways.Mediators Inflamm. 2016;2016:5240127. doi: 10.1155/2016/5240127. Epub 2016 Sep 25. Mediators Inflamm. 2016. PMID: 27738387 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

