Genome-wide survey and comprehensive expression profiling of Aux/IAA gene family in chickpea and soybean
- PMID: 26579165
- PMCID: PMC4621760
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2015.00918
Genome-wide survey and comprehensive expression profiling of Aux/IAA gene family in chickpea and soybean
Abstract
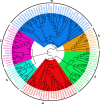
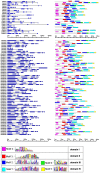
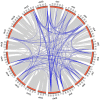
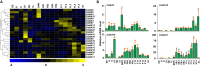
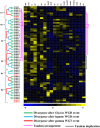
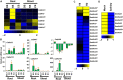
Auxin plays a central role in many aspects of plant growth and development. Auxin/Indole-3-Acetic Acid (Aux/IAA) genes cooperate with several other components in the perception and signaling of plant hormone auxin. An investigation of chickpea and soybean genomes revealed 22 and 63 putative Aux/IAA genes, respectively. These genes were classified into six subfamilies on the basis of phylogenetic analysis. Among 63 soybean Aux/IAA genes, 57 (90.5%) were found to be duplicated via whole genome duplication (WGD)/segmental events. Transposed duplication played a significant role in tandem arrangements between the members of different subfamilies. Analysis of Ka/Ks ratio of duplicated Aux/IAA genes revealed purifying selection pressure with restricted functional divergence. Promoter sequence analysis revealed several cis-regulatory elements related to auxin, abscisic acid, desiccation, salt, seed, and endosperm, indicating their role in development and stress responses. Expression analysis of chickpea and soybean Aux/IAA genes in various tissues and stages of development demonstrated tissue/stage specific differential expression. In soybean, at least 16 paralog pairs, duplicated via WGD/segmental events, showed almost indistinguishable expression pattern, but eight pairs exhibited significantly diverse expression patterns. Under abiotic stress conditions, such as desiccation, salinity and/or cold, many Aux/IAA genes of chickpea and soybean revealed differential expression. qRT-PCR analysis confirmed the differential expression patterns of selected Aux/IAA genes in chickpea. The analyses presented here provide insights on putative roles of chickpea and soybean Aux/IAA genes and will facilitate elucidation of their precise functions during development and abiotic stress responses.
Keywords: Aux/IAA; abiotic stress; chickpea; gene duplication; gene expression; gene family; soybean; transposed duplication.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genome-wide identification and expression pattern analysis of the Aux/IAA (auxin/indole-3-acetic acid) gene family in alfalfa (Medicago sativa) and the potential functions under drought stress.BMC Genomics. 2024 Apr 18;25(1):382. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10313-2. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38637768 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification and salt stress-responsive expression profiling of Aux/IAA gene family in Asparagus officinalis.BMC Plant Biol. 2025 Jun 4;25(1):759. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-06780-8. BMC Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 40468198 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide analysis of primary auxin-responsive Aux/IAA gene family in maize (Zea mays. L.).Mol Biol Rep. 2010 Dec;37(8):3991-4001. doi: 10.1007/s11033-010-0058-6. Epub 2010 Mar 16. Mol Biol Rep. 2010. PMID: 20232157
-
Systematic identification and expression pattern analysis of the Aux/IAA and ARF gene families in moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis).Plant Physiol Biochem. 2018 Sep;130:431-444. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2018.07.033. Epub 2018 Jul 31. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30077919
-
Aux/IAA Gene Family in Plants: Molecular Structure, Regulation, and Function.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Jan 16;19(1):259. doi: 10.3390/ijms19010259. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29337875 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of Candidate Auxin Response Factors Involved in Pomegranate Seed Coat Development.Front Plant Sci. 2020 Sep 15;11:536530. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.536530. eCollection 2020. Front Plant Sci. 2020. PMID: 33042173 Free PMC article.
-
EcoTILLING-Based Association Mapping Efficiently Delineates Functionally Relevant Natural Allelic Variants of Candidate Genes Governing Agronomic Traits in Chickpea.Front Plant Sci. 2016 Apr 19;7:450. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.00450. eCollection 2016. Front Plant Sci. 2016. PMID: 27148286 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification and co-expression network analysis provide insights into the roles of auxin response factor gene family in chickpea.Sci Rep. 2017 Sep 7;7(1):10895. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-11327-5. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28883480 Free PMC article.
-
The SOD Gene Family in Tomato: Identification, Phylogenetic Relationships, and Expression Patterns.Front Plant Sci. 2016 Aug 30;7:1279. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.01279. eCollection 2016. Front Plant Sci. 2016. PMID: 27625661 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive analysis of the B3 superfamily identifies tissue-specific and stress-responsive genes in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.).3 Biotech. 2019 Sep;9(9):346. doi: 10.1007/s13205-019-1875-5. Epub 2019 Aug 26. 3 Biotech. 2019. PMID: 31497464 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cakir B., Kilickaya O., Olcay A. C. (2013). Genome-wide analysis of Aux/IAA genes in Vitis vinifera: cloning and expression profiling of a grape Aux/IAA gene in response to phytohormone and abiotic stresses. Acta Physiol. Plant. 35 365–377.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

