RNA:DNA hybrids in the human genome have distinctive nucleotide characteristics, chromatin composition, and transcriptional relationships
- PMID: 26579211
- PMCID: PMC4647656
- DOI: 10.1186/s13072-015-0040-6
RNA:DNA hybrids in the human genome have distinctive nucleotide characteristics, chromatin composition, and transcriptional relationships
Abstract
Background: RNA:DNA hybrids represent a non-canonical nucleic acid structure that has been associated with a range of human diseases and potential transcriptional regulatory functions. Mapping of RNA:DNA hybrids in human cells reveals them to have a number of characteristics that give insights into their functions.
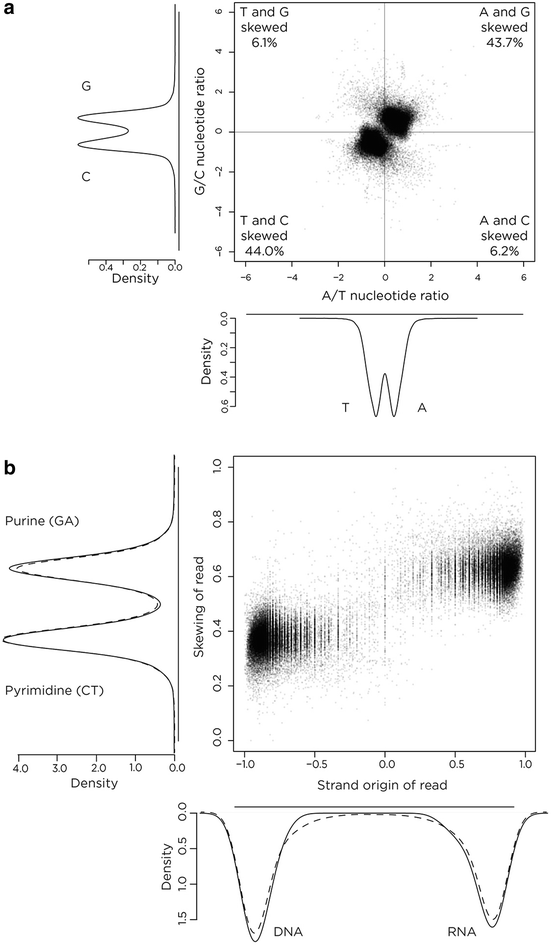
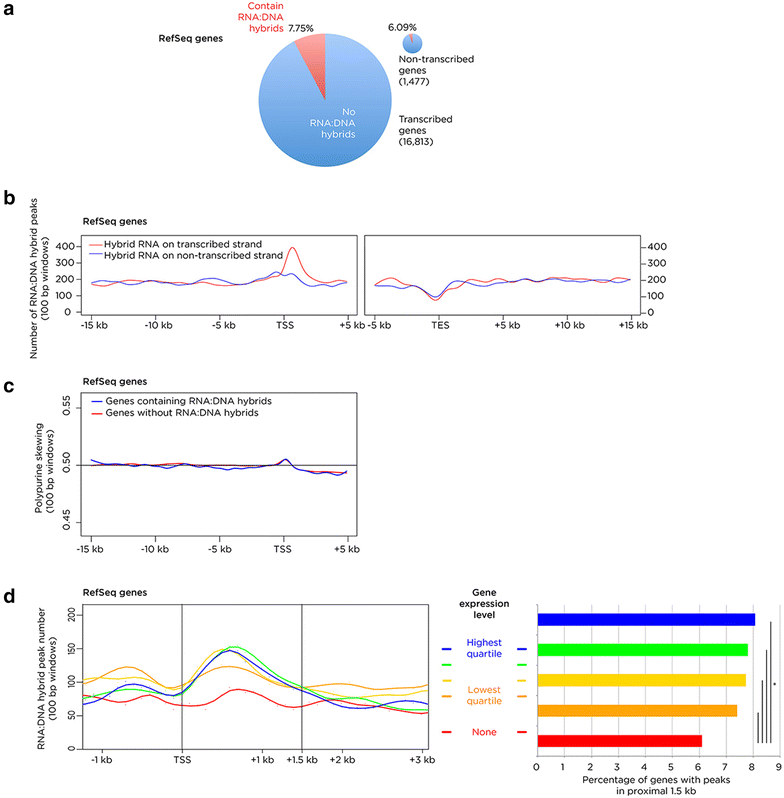
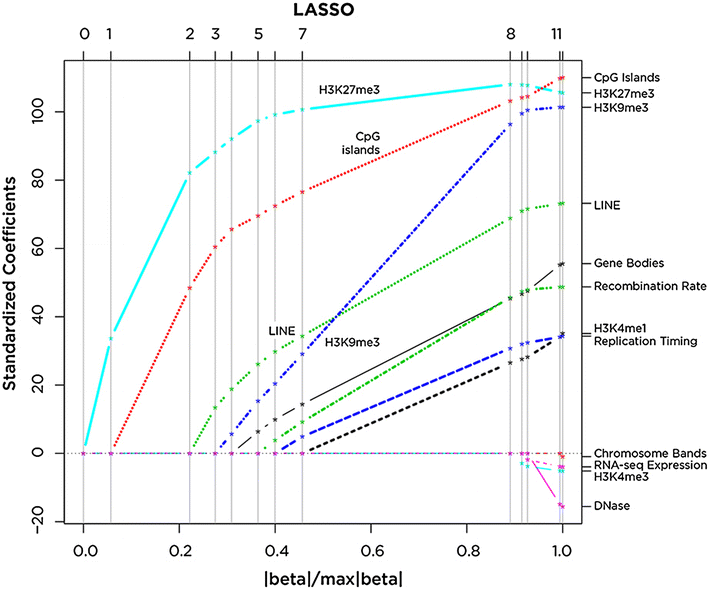
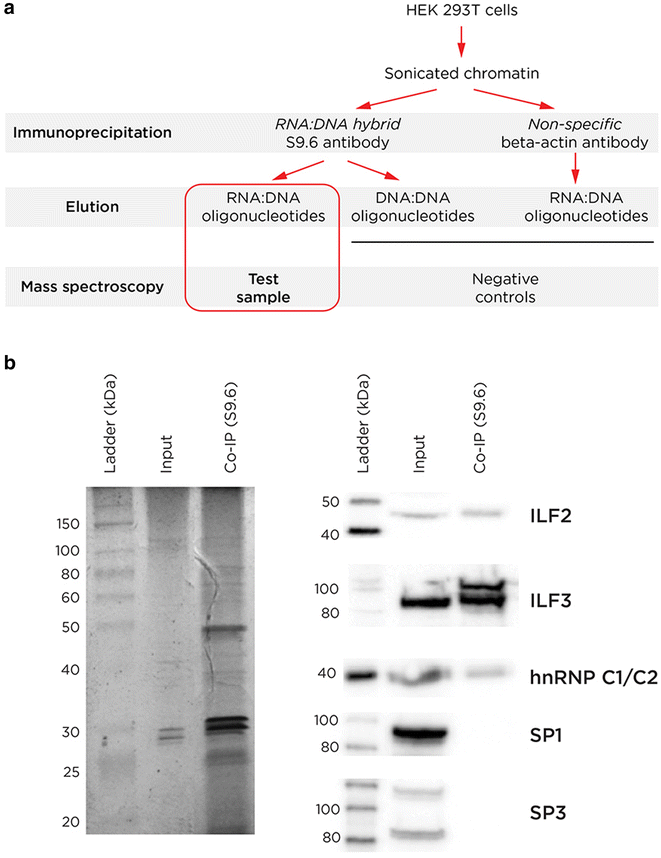
Results: We find RNA:DNA hybrids to occupy millions of base pairs in the human genome. A directional sequencing approach shows the RNA component of the RNA:DNA hybrid to be purine-rich, indicating a thermodynamic contribution to their in vivo stability. The RNA:DNA hybrids are enriched at loci with decreased DNA methylation and increased DNase hypersensitivity, and within larger domains with characteristics of heterochromatin formation, indicating potential transcriptional regulatory properties. Mass spectrometry studies of chromatin at RNA:DNA hybrids shows the presence of the ILF2 and ILF3 transcription factors, supporting a model of certain transcription factors binding preferentially to the RNA:DNA conformation.
Conclusions: Overall, there is little to indicate a dependence for RNA:DNA hybrids forming co-transcriptionally, with results from the ribosomal DNA repeat unit instead supporting the intriguing model of RNA generating these structures in trans. The results of the study indicate heterogeneous functions of these genomic elements and new insights into their formation and stability in vivo.
Keywords: Chromatin; DNA methylation; Mass spectrometry; Non-coding RNA; R-loop; RNA:DNA hybrid; Transcription; Transcription factor.
Figures



Similar articles
-
DNA-RNA hybrid formation mediates RNAi-directed heterochromatin formation.Genes Cells. 2012 Mar;17(3):218-33. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2443.2012.01583.x. Epub 2012 Jan 27. Genes Cells. 2012. PMID: 22280061
-
Hybrid oligomer duplexes formed with phosphorothioate DNAs: CD spectra and melting temperatures of S-DNA.RNA hybrids are sequence-dependent but consistent with similar heteronomous conformations.Biochemistry. 1998 Jan 6;37(1):61-72. doi: 10.1021/bi9713557. Biochemistry. 1998. PMID: 9425026
-
Roles for Pbp1 and caloric restriction in genome and lifespan maintenance via suppression of RNA-DNA hybrids.Dev Cell. 2014 Jul 28;30(2):177-91. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2014.05.013. Dev Cell. 2014. PMID: 25073155
-
Comparison of the thermodynamic stabilities and solution conformations of DNA.RNA hybrids containing purine-rich and pyrimidine-rich strands with DNA and RNA duplexes.Biochemistry. 1996 Sep 24;35(38):12538-48. doi: 10.1021/bi960948z. Biochemistry. 1996. PMID: 8823191
-
Transcriptional regulation mechanism mediated by miRNA-DNA•DNA triplex structure stabilized by Argonaute.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Nov;1839(11):1079-83. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2014.07.016. Epub 2014 Jul 30. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 25086339 Review.
Cited by
-
Ribonuclease H2 Subunit A Preserves Genomic Integrity and Promotes Prostate Cancer Progression.Cancer Res Commun. 2022 Aug 25;2(8):870-883. doi: 10.1158/2767-9764.CRC-22-0126. eCollection 2022 Aug. Cancer Res Commun. 2022. PMID: 36923313 Free PMC article.
-
Spliceosomal components protect embryonic neurons from R-loop-mediated DNA damage and apoptosis.Dis Model Mech. 2018 Feb 26;11(2):dmm031583. doi: 10.1242/dmm.031583. Dis Model Mech. 2018. PMID: 29419415 Free PMC article.
-
Senataxin resolves RNA:DNA hybrids forming at DNA double-strand breaks to prevent translocations.Nat Commun. 2018 Feb 7;9(1):533. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-02894-w. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 29416069 Free PMC article.
-
T helper cell-mediated epitranscriptomic regulation via m6A RNA methylation bridges link between coronary artery disease and invasive ductal carcinoma.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2022 Dec;148(12):3421-3436. doi: 10.1007/s00432-022-04130-x. Epub 2022 Jul 1. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35776197 Free PMC article.
-
Hot spots of DNA double-strand breaks in human rDNA units are produced in vivo.Sci Rep. 2016 May 10;6:25866. doi: 10.1038/srep25866. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27160357 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yip KY, Cheng C, Bhardwaj N, Brown JB, Leng J, Kundaje A, Rozowsky J, Birney E, Bickel P, Snyder M, Gerstein M. Classification of human genomic regions based on experimentally determined binding sites of more than 100 transcription-related factors. Genome Biol. 2012;13:R48. doi: 10.1186/gb-2012-13-9-r48. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

