Inhibition of the angiopoietin/Tie2 axis induces immunogenic modulation, which sensitizes human tumor cells to immune attack
- PMID: 26579226
- PMCID: PMC4647578
- DOI: 10.1186/s40425-015-0096-7
Inhibition of the angiopoietin/Tie2 axis induces immunogenic modulation, which sensitizes human tumor cells to immune attack
Abstract
Background: The angiopoietin/Tie2 pathway is an attractive target for cancer therapy due to its well-known role in regulating angiogenesis. Trebananib, a recombinant peptide-Fc fusion protein, or peptibody, that binds to angiopoietin-1 (Ang1) and Ang2 to block their interaction with the Tie2 receptor, is under active clinical investigation. We investigated whether suppressing the angiopoietin/Tie2 pathway, using the preclinical version of Trebananib (mL4-3 and L1-7(N)), could increase the sensitivity of human tumor cells to immune-mediated lysis through immunogenic modulation, which would make Trebananib a promising candidate for combination with immunotherapy.
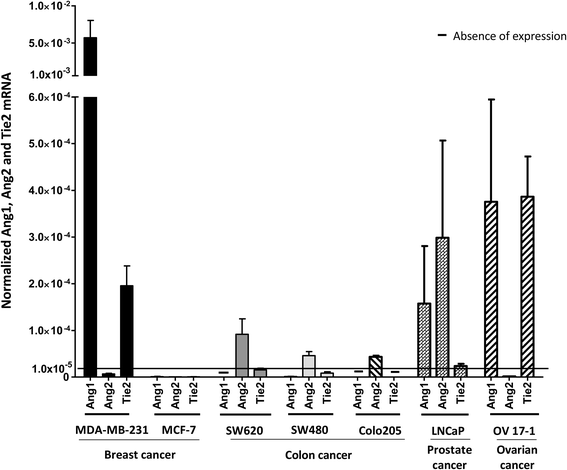
Methods: We assessed human carcinoma cells for expression and activation of Ang1 and Ang2 and their receptor tyrosine kinase Tie2. In vitro, we exposed tumor cell lines expressing Tie2 to the peptibodies mL4-3 and L1-7(N), which inhibit the binding of Ang1 and Ang2 to Tie2, and assessed the cells for changes in viability, proliferation, surface phenotype, and sensitivity to attack by antigen-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs).
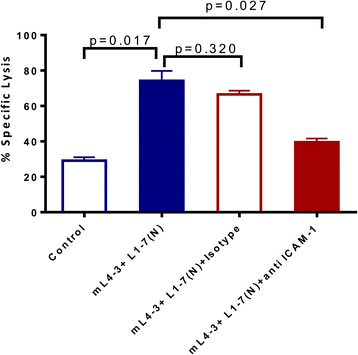
Results: Suppression of the angiopoietin/Tie2 pathway using mL4-3 and L1-7(N) had no effect on the proliferation or viability of tumor cells. However, these inhibitors markedly altered tumor cell phenotype, rendering tumor cells significantly more sensitive to antigen-specific CTL killing. ICAM-1 was shown to be mechanistically involved in these inhibitors' ability to sensitize tumor cells to immune-mediated attack by functional blocking studies.
Conclusion: Our findings provide a rationale for the combination of agents targeting the angiopoietin/Tie2 pathway with cancer immunotherapies.
Keywords: Angiopoietin; Immunogenic modulation; Immunotherapy; Tie2.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Context-dependent role of angiopoietin-1 inhibition in the suppression of angiogenesis and tumor growth: implications for AMG 386, an angiopoietin-1/2-neutralizing peptibody.Mol Cancer Ther. 2010 Oct;9(10):2641-51. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-10-0213. Mol Cancer Ther. 2010. PMID: 20937592 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a biosensor-based immunogenicity assay capable of blocking soluble drug target interference.J Immunol Methods. 2013 Oct 31;396(1-2):44-55. doi: 10.1016/j.jim.2013.07.010. Epub 2013 Aug 6. J Immunol Methods. 2013. PMID: 23933325
-
Ligand oligomerization state controls Tie2 receptor trafficking and angiopoietin-2-specific responses.J Cell Sci. 2012 May 1;125(Pt 9):2212-23. doi: 10.1242/jcs.098020. Epub 2012 Feb 22. J Cell Sci. 2012. PMID: 22357955
-
Targeting Tie2 in the Tumor Microenvironment: From Angiogenesis to Dissemination.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Nov 16;13(22):5730. doi: 10.3390/cancers13225730. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34830883 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Angiopoietin-2 and TIE Pathway as a Therapeutic Target for Enhancing Antiangiogenic Therapy and Immunotherapy in Patients with Advanced Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 18;21(22):8689. doi: 10.3390/ijms21228689. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33217955 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dual Inhibition of Angiopoietin-TIE2 and MET Alters the Tumor Microenvironment and Prolongs Survival in a Metastatic Model of Renal Cell Carcinoma.Mol Cancer Ther. 2020 Jan;19(1):147-156. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-18-1202. Epub 2019 Oct 3. Mol Cancer Ther. 2020. PMID: 31582532 Free PMC article.
-
Natural Born Killers: NK Cells in Cancer Therapy.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Jul 31;12(8):2131. doi: 10.3390/cancers12082131. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32751977 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunometabolic Network Interactions of the Kynurenine Pathway in Cutaneous Malignant Melanoma.Front Oncol. 2020 Feb 3;10:51. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00051. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32117720 Free PMC article.
-
Ang-2/VEGF bispecific antibody reprograms macrophages and resident microglia to anti-tumor phenotype and prolongs glioblastoma survival.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Apr 19;113(16):4476-81. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1525360113. Epub 2016 Apr 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27044098 Free PMC article.
-
The Cancer Cell Dissemination Machinery as an Immunosuppressive Niche: A New Obstacle Towards the Era of Cancer Immunotherapy.Front Immunol. 2021 Apr 13;12:654877. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.654877. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33927723 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kwilas AR, Ardiani A, Donahue RN, Aftab DT, Hodge JW. Dual effects of a targeted small-molecule inhibitor (cabozantinib) on immune-mediated killing of tumor cells and immune tumor microenvironment permissiveness when combined with a cancer vaccine. J Transl Med. 2014;12(1):294. doi: 10.1186/s12967-014-0294-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
