Percutaneous endoscopic nephropexy with a percutaneous suture passed through the kidney
- PMID: 26579248
- PMCID: PMC4442924
- DOI: 10.1016/j.aju.2013.01.002
Percutaneous endoscopic nephropexy with a percutaneous suture passed through the kidney
Abstract
Objectives: To report a technique of percutaneous endoscopic nephropexy, using a polyglactin suture passed through the kidney, in patients with nephroptosis.
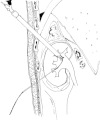
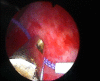
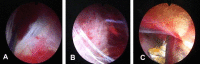
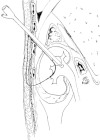
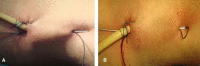
Patients and methods: Four women presenting with symptomatic right nephroptosis underwent a percutaneous endoscopic nephropexy. An upper-pole calyx was accessed percutaneously and a 24-F working sheath was placed. Another needle access was made through a lower-pole calyx and a #2 polyglactin suture was passed into the renal pelvis. It was then pulled out through the upper-pole tract using the nephroscope. A retroperitoneoscopy was performed and the tip of the nephroscope was used to cause nephrolysis. After inserting the nephrostomy tube the polyglactin suture was passed into the subcutaneous tissue and then tied without too much tension, to avoid cutting the parenchyma.
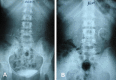
Results: The operative duration was 33 min and the hospital stay after surgery was 3.5 days. The nephrostomy catheter was removed 5 days after surgery. There were no complications, especially no haemorrhagic, infectious, lithiasic or thoracic complications. The four patients were relieved of their initial symptoms, with a mean follow-up of 28 months. Ultrasonography and/or intravenous urography showed the kidney at a higher location with the patient standing.
Conclusions: This technique combines the nephrostomy tract used in percutaneous techniques with the suture and nephrolysis used in laparoscopic techniques. Moreover, this procedure seems to be safe, with satisfactory anatomical and clinical results and a lower morbidity. However, a larger series will be necessary to establish its long-term morbidity and success rate.
Keywords: Kidney; Lateral modified position; Nephropexy; Nephroptosis; Percutaneous surgery.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Percutaneous nephrostomy for symptomatic hypermobile kidney: a single centre experience.Wideochir Inne Tech Maloinwazyjne. 2014 Dec;9(4):501-4. doi: 10.5114/wiitm.2014.44168. Epub 2014 Jul 22. Wideochir Inne Tech Maloinwazyjne. 2014. PMID: 25561985 Free PMC article.
-
Modified percutaneous nephropexy for nephroptosis: Technical description and short-term results.Curr Urol. 2025 May;19(3):168-172. doi: 10.1097/CU9.0000000000000238. Epub 2024 Mar 12. Curr Urol. 2025. PMID: 40376470 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term followup after laparoscopic nephropexy for symptomatic nephroptosis.J Urol. 2001 Aug;166(2):449-52. J Urol. 2001. PMID: 11458045
-
Do's and don't's of percutaneous nephrostomy.Acad Radiol. 1999 Jun;6(6):370-7. doi: 10.1016/s1076-6332(99)80233-5. Acad Radiol. 1999. PMID: 10376069 Review.
-
Clinical reappraisal and state of the art of nephropexy.Urologia. 2018 Nov;85(4):135-144. doi: 10.1177/0391560317749191. Epub 2018 Apr 11. Urologia. 2018. PMID: 29637838 Review.
Cited by
-
A Systematic Review on Spinal Asymmetries in Case Studies of Unilateral Nephroptosis from a Viscerosomatic Point of View.Healthcare (Basel). 2022 Nov 30;10(12):2422. doi: 10.3390/healthcare10122422. Healthcare (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36553946 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Srirangam S.J., Pollard A.J., Adeyoju A.A., O’Reilly P.H. Nephroptosis: seriously misunderstood? BJU Int. 2009;103:296. - PubMed
-
- Khan A.M., Holman E., Toth C. Percutaneous nephropexy. Scand J Urol Nephrol. 2000;34:157–161. - PubMed
-
- Castillo Rodríguez M., Larrea Masvidal E., Hernández Silverio D., Carauna Valdes-Gómez A., Labrada Rodríguez M.V., Cuesta Megias T. Percutaneous nephropexy in the treatment of renal ptosis. Arch Esp Urol. 1999;52:250–256. - PubMed
-
- Székely J.G. Re. Laparoscopic nephropexy: Washington University experience (letter to the editor) J Urol. 1997;157:266. - PubMed
-
- Hoenig D.M., Hemal A.K., Shalhav A.L., Clayman R.V. Percutaneous nephrostolithotomy, endopyelotomy and nephropexy in a single session. J Urol. 1998;160:826–827. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
