Recoverability of renal function after relief of chronic partial unilateral ureteric obstruction: The effect of an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor (enalapril)
- PMID: 26579271
- PMCID: PMC4149048
- DOI: 10.1016/j.aju.2011.03.016
Recoverability of renal function after relief of chronic partial unilateral ureteric obstruction: The effect of an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor (enalapril)
Abstract
Objectives: We evaluated the effect of an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor (enalapril) on renal function during and after the relief of partial unilateral ureteric obstruction (UUO).
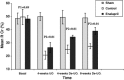
Materials and methods: Thirty-two male mongrel dogs were classified into three groups: sham (eight), control (12; left partial UUO + no medication) and study (12; left partial UUO + enalapril). Dogs in the study and control groups were subjected to 4 weeks of partial UUO. After that, the dogs were re-opened and subjected to Lich-Gregoir vesico-ureteric re-implantation, and were killed humanely by the end of the eighth week after relief of obstruction. The study and control groups were evaluated at baseline, after 4 weeks of obstruction and at 4 and 8 weeks after relief of obstruction, by measuring selective creatinine clearance (CCr), selective renographic clearance (RCr) and renal resistive index (RI). The sham group had sham surgery at 4 and 8 weeks and was evaluated as the other two groups.
Results: Sham surgery showed no significant effect on any of the evaluated variables. Compared with the control, enalapril offset the reductions of CCr and RCr by an extra 11% and 12% of the basal values by the end of the fourth week of obstruction, respectively. Moreover, compared with the control, enalapril enhanced the recovery of CCr by an extra 10% and of RCr by an extra 23% of the basal values at 8 weeks after relief of the 4-week obstruction. In addition, the increase in RI was significantly less in the enalapril group.
Conclusion: Enalapril decreases the deterioration of renal function in partial UUO and enhances the recoverability of renal function after relief of obstruction.
Keywords: (U)UO, (unilateral) ureteric obstruction; ACE, angiotensin-converting enzyme; CCr, creatinine clearance; DUS, Doppler ultrasonography; Enalapril; RAS, renin-angiotensin system; RCr, renographic clearance; RI, resistive index; Recoverability of renal function; Ureteric obstruction.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Renoprotection against complete unilateral ureteric obstruction: Is there an ultimate choice?Arab J Urol. 2012 Jun;10(2):199-206. doi: 10.1016/j.aju.2011.11.004. Epub 2012 Jan 28. Arab J Urol. 2012. PMID: 26558026 Free PMC article.
-
Recoverability of renal function after relief of chronic partial unilateral ureteral obstruction: study of the effect of angiotensin receptor blocker (losartan).Urology. 2010 Apr;75(4):848-52. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2009.07.1217. Epub 2009 Oct 24. Urology. 2010. PMID: 19854474
-
Recoverability of renal functions after relief of partial ureteric obstruction of solitary kidney: impact of ferulic acid.BJU Int. 2012 Sep;110(6):904-11. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2011.10848.x. Epub 2012 Mar 1. BJU Int. 2012. PMID: 22381210
-
[Molecular mechanisms of nephro-protective action of enalapril in experimental chronic renal failure].Ann Acad Med Stetin. 1999;Suppl 52:1-93. Ann Acad Med Stetin. 1999. PMID: 10589103 Review. Polish.
-
The therapeutic approaches of renal recovery after relief of the unilateral ureteral obstruction: A comprehensive review.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2020 Nov;23(11):1367-1373. doi: 10.22038/ijbms.2020.41984.9926. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 33235692 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Treatment Response to Idiopathic Retroperitoneal Fibrosis-associated Hydronephrosis With a Focus on IgG4/IgG3 Serum Concentration Ratio.J Rheum Dis. 2021 Jan 1;28(1):38-44. doi: 10.4078/jrd.2021.28.1.38. J Rheum Dis. 2021. PMID: 37476393 Free PMC article.
-
Renoprotection against complete unilateral ureteric obstruction: Is there an ultimate choice?Arab J Urol. 2012 Jun;10(2):199-206. doi: 10.1016/j.aju.2011.11.004. Epub 2012 Jan 28. Arab J Urol. 2012. PMID: 26558026 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of IL-1β by Aliskiren Improved Renal AQP2 Expression and Urinary Concentration Defect in Ureteral Obstruction and Release.Front Physiol. 2019 Sep 13;10:1157. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.01157. eCollection 2019. Front Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31572210 Free PMC article.
-
Renoprotective effect of local sildenafil administration in renal ischaemia-reperfusion injury: A randomised controlled canine study.Arab J Urol. 2019 Apr 18;17(2):150-159. doi: 10.1080/2090598X.2019.1600995. eCollection 2019. Arab J Urol. 2019. PMID: 31285928 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Klahr S., Morrissey J. Comparative effects of ACE inhibition and angiotensin II receptor blockade in the prevention of renal damage. Kidney Int Suppl. 2002;82:23–26. - PubMed
-
- Klahr S., Morrissey J. Comparative study of ACE inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor antagonists in interstitial scarring. Kidney Int Suppl. 1997;63:S111–S114. - PubMed
-
- Chevalier R.L., Chung K.H., Smith C.D., Ficenec M., Gomez R.A. Renal apoptosis and clusterin following ureteral obstruction. The role of maturation. J Urol. 1996;156:1474–1479. - PubMed
-
- Chevalier R.L., Cachat F. Role of angiotensin II in chronic ureteral obstruction. Contrib Nephrol. 2001;135:250–260. - PubMed
-
- Gonçalves R.G., Biato M.A., Colosimo R.D., Martinusso C.A., Pecly I.D. Effects of mycophenolate mofetil and lisinopril on collagen deposition in unilateral ureteral obstruction in rats. Am J Nephrol. 2004;24:527–536. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
