Myelolipomas and other fatty tumours of the adrenals
- PMID: 26579309
- PMCID: PMC4150587
- DOI: 10.1016/j.aju.2011.10.003
Myelolipomas and other fatty tumours of the adrenals
Abstract
Background: Lipomatous tumours of the adrenals are almost always benign. The importance of recognising their characteristic radiological features, leading to their correct treatment, is fundamental, as there has been an increase in the identification of these lesions. Our goal was to review all lipomatous tumours of the adrenal glands, particularly myelolipomas, their imaging methods and surgical management, updated in 2011.
Methods: This was a retrospective review of articles published in the USA and Europe, from 1979 to date. The sites from which information was retrieved covered PubMed, Medscape, Clinical Imaging, Histopathology, Urologia Internationalis, Archives of Surgery, JACS, the American Urological Association, BMJ, Medline, and Springer Link. We report areas of controversies in addition to well established guidelines.
Results: We reviewed 45 articles, that confirmed, with a high level of evidence-based medicine, that the diagnosis of a lipomatous adrenal tumour is made by various imaging procedures, particularly computed tomography (CT). We emphasise the importance to their management of the initial size of the adrenal mass, its increase in size over time, in addition to the presence of symptoms.
Conclusion: Lipomatous tumours of the adrenals are most frequently benign. The diagnosis is usually made by various techniques, in particular CT. The fundamental characteristics indicating the necessity of surgical intervention are the symptoms presented, volume of the tumoral mass (>5 cm), and the increase in size of the tumour as shown in two consecutive imaging studies.
Keywords: Adrenal glands; CAH, congenital adrenal hyperplasia; Conservative management; HU, Hounsfield unit; Laparoscopic adrenalectomy; Myelolipomas; US, ultrasonography.
Figures
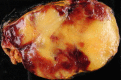

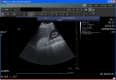
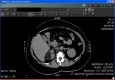
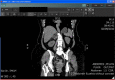
Similar articles
-
Bladder leiomyoma: Presentation, evaluation and treatment.Arab J Urol. 2013 Mar;11(1):54-61. doi: 10.1016/j.aju.2012.11.007. Epub 2012 Dec 25. Arab J Urol. 2013. PMID: 26579246 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipomatous tumors of the adrenals--a report on 18 cases and review of the literature.Clin Imaging. 2007 Sep-Oct;31(5):335-9. doi: 10.1016/j.clinimag.2007.06.022. Clin Imaging. 2007. PMID: 17825742 Review.
-
Giant myelolipomas and inadvertent bilateral adrenalectomy in classic congenital adrenal hyperplasia.Endocrinol Diabetes Metab Case Rep. 2015;2015:150079. doi: 10.1530/EDM-15-0079. Epub 2015 Aug 28. Endocrinol Diabetes Metab Case Rep. 2015. PMID: 26527321 Free PMC article.
-
Clinicopathological Characteristics of Four Cases of Adrenal Myelolipomas: A Rare Surgical Entity.World J Oncol. 2012 Dec;3(6):294-297. doi: 10.4021/wjon600w. Epub 2013 Jan 4. World J Oncol. 2012. PMID: 29147323 Free PMC article.
-
Retroperitoneoscopic partial adrenalectomy for small adrenal tumours (< or =1 cm): the Ruijin clinical experience in 88 patients.BJU Int. 2010 Mar;105(6):849-53. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2009.08878.x. Epub 2009 Sep 14. BJU Int. 2010. PMID: 19751254
Cited by
-
Adrenocortical adenoma with myelolipomatous metaplasia: a potential diagnostic pitfall: a case report and review of the literature.J Med Case Rep. 2021 Jul 4;15(1):333. doi: 10.1186/s13256-021-02937-9. J Med Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 34217375 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pheochromocytoma in a patient with heterotaxy syndrome: a case report.BMC Endocr Disord. 2025 Mar 10;25(1):65. doi: 10.1186/s12902-024-01829-5. BMC Endocr Disord. 2025. PMID: 40065330 Free PMC article.
-
Case report: Adrenal myelolipoma resected by laparoscopic surgery.Front Oncol. 2022 Dec 5;12:1058211. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1058211. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36544699 Free PMC article.
-
Adrenal extramedullary hematopoiesis associated with beta-thalassemia trait in an adult woman: a case report and review of literature.Int J Surg Case Rep. 2016;24:83-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2016.05.024. Epub 2016 May 19. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2016. PMID: 27232291 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Adrenal Collision Tumor in a Patient with Cushing's Syndrome.Case Rep Endocrinol. 2020 Dec 14;2020:7415762. doi: 10.1155/2020/7415762. eCollection 2020. Case Rep Endocrinol. 2020. PMID: 33414970 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Grumbach M.M., Biller B.M., Braunstein G.D., Campbell K.K., Carney J.A., Godley P.A. Management of clinically inapparent adrenal mass (‘incidentaloma’) Ann Intern Med. 2003;138:424–429. - PubMed
-
- Bellantone R., Ferrante A., Raffaelli M., Boscherini M., Rubino F., Crucciti F. Incidental discovery of adrenal neoplasm: our experience. Ann Ital Chir. 1995;66:439–448. - PubMed
-
- Song J.H., Mayo-Smith W.W. Incidentally discovered adrenal mass. Radiol Clin N Am. 2011;49:361–368. - PubMed
-
- Lam K.Y. Adrenal tumours in Chinese. Virchows Arch a Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1992;421:13–16. - PubMed
-
- Geelhoed G.W., Druy E.M. Management of the adrenal ‘incidentaloma’. Surgery. 1982;92:866–874. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
