The antiviral effect of jiadifenoic acids C against coxsackievirus B3
- PMID: 26579396
- PMCID: PMC4629087
- DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2014.06.008
The antiviral effect of jiadifenoic acids C against coxsackievirus B3
Abstract
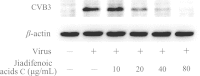
Coxsackievirus B type 3 (CVB3) is one of the major causative pathogens associated with viral meningitis and myocarditis, which are widespread in the human population and especially prevalent in neonates and children. These infections can result in dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) and other severe clinical complications. There are no vaccines or drugs approved for the prevention or therapy of CVB3-induced diseases. During screening for anti-CVB3 candidates in our previous studies, we found that jiadifenoic acids C exhibited strong antiviral activities against CVB3 as well as other strains of Coxsackie B viruses (CVBs). The present studies were carried out to evaluate the antiviral activities of jiadifenoic acids C. Results showed that jiadifenoic acids C could reduce CVB3 RNA and proteins synthesis in a dose-dependent manner. Jiadifenoic acids C also had a similar antiviral effect on the pleconaril-resistant variant of CVB3. We further examined the impact of jiadifenoic acids C on the synthesis of viral structural and non-structural proteins, finding that jiadifenoic acids C could reduce VP1 and 3D protein production. A time-course study with Vero cells showed that jiadifenoic acids C displayed significant antiviral activities at 0-6 h after CVB3 inoculation, indicating that jiadifenoic acids C functioned at an early step of CVB3 replication. However, jiadifenoic acids C had no prophylactic effect against CVB3. Taken together, we show that jiadifenoic acids C exhibit strong antiviral activities against all strains of CVB, including the pleconaril-resistant variant. Our study could provide a significant lead for anti-CVB3 drug development.
Keywords: Antiviral activity; CAR, coxsackievirus and adenovirus receptor; CPE, cytopathic effect; CVB3; CVB3, coxsackievirus B type 3; CVBs, coxsackie B viruses; DAF, decay accelerating factor; DCM, dilated cardiomyopathy; IC50, 50% inhibitory concentration; IRES, internal ribosomal entry site; Jiadifenoic acids C; MOI, multiplicity of infection; NTR, non-translated region; RBV, ribavirin; RdRp, RNA-dependent RNA polymerase; SI, selectivity index; Vero, African green monkey kidney cells.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Heparan sulfates and coxsackievirus-adenovirus receptor: each one mediates coxsackievirus B3 PD infection.J Virol. 2003 Sep;77(18):10071-7. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.18.10071-10077.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12941917 Free PMC article.
-
Early Treatment of Coxsackievirus B3-Infected Animals With Soluble Coxsackievirus-Adenovirus Receptor Inhibits Development of Chronic Coxsackievirus B3 Cardiomyopathy.Circ Heart Fail. 2019 Nov;12(11):e005250. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.119.005250. Epub 2019 Nov 13. Circ Heart Fail. 2019. PMID: 31718319
-
A decay-accelerating factor-binding strain of coxsackievirus B3 requires the coxsackievirus-adenovirus receptor protein to mediate lytic infection of rhabdomyosarcoma cells.J Virol. 1997 Dec;71(12):9844-8. doi: 10.1128/JVI.71.12.9844-9848.1997. J Virol. 1997. PMID: 9371658 Free PMC article.
-
A Kidnapping Story: How Coxsackievirus B3 and Its Host Cell Interact.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2019;53(1):121-140. doi: 10.33594/000000125. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2019. PMID: 31230428 Review.
-
Antiviral activity of Bifidobacterium adolescentis SPM1605 against Coxsackievirus B3.Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip. 2014 Jul 4;28(4):681-688. doi: 10.1080/13102818.2014.945237. Epub 2014 Oct 20. Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip. 2014. PMID: 26019554 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Novel N-benzenesulfonyl sophocarpinol derivatives as coxsackie B virus inhibitors.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2015 Jan 7;6(2):183-6. doi: 10.1021/ml500525s. eCollection 2015 Feb 12. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2015. PMID: 25699158 Free PMC article.
-
Purification of Houttuynia cordata Thunb. Essential Oil Using Macroporous Resin Followed by Microemulsion Encapsulation to Improve Its Safety and Antiviral Activity.Molecules. 2017 Feb 15;22(2):293. doi: 10.3390/molecules22020293. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28212296 Free PMC article.
-
Research Progress in the Pharmacological Activities, Toxicities, and Pharmacokinetics of Sophoridine and Its Derivatives.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2022 Jan 18;16:191-212. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S339555. eCollection 2022. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2022. PMID: 35082485 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kim D.S., Nam J.H. Characterization of attenuated coxsackievirus B3 strains and prospects of their application as live-attenuated vaccines. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2010;10:179–190. - PubMed
-
- Koho T., Koivunen M.R., Oikarinen S., Kummola L., Makinen S., Mähönen A.J. Coxsackievirus B3 VLPs purified by ion exchange chromatography elicit strong immune responses in mice. Antiviral Res. 2014;104:93–101. - PubMed
-
- Martin U., Jarasch N., Nestler M., Rassmann A., Munder T., Seitz S. Antiviral effects of pan-caspase inhibitors on the replication of coxsackievirus B3. Apoptosis. 2007;12:525–533. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

