Bile acids and sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 2 in hepatic lipid metabolism
- PMID: 26579441
- PMCID: PMC4629213
- DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2014.12.009
Bile acids and sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 2 in hepatic lipid metabolism
Abstract
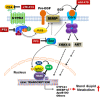
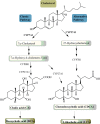
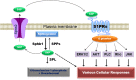
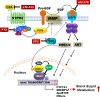
The liver is the central organ involved in lipid metabolism. Dyslipidemia and its related disorders, including non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), obesity and other metabolic diseases, are of increasing public health concern due to their increasing prevalence in the population. Besides their well-characterized functions in cholesterol homoeostasis and nutrient absorption, bile acids are also important metabolic regulators and function as signaling hormones by activating specific nuclear receptors, G-protein coupled receptors, and multiple signaling pathways. Recent studies identified a new signaling pathway by which conjugated bile acids (CBA) activate the extracellular regulated protein kinases (ERK1/2) and protein kinase B (AKT) signaling pathway via sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 2 (S1PR2). CBA-induced activation of S1PR2 is a key regulator of sphingosine kinase 2 (SphK2) and hepatic gene expression. This review focuses on recent findings related to the role of bile acids/S1PR2-mediated signaling pathways in regulating hepatic lipid metabolism.
Keywords: ABC, ATP-binding cassette; AKT/PKB, protein kinase B; BSEP/ABCB11, bile salt export protein; Bile acid; CA, cholic acid; CBA, conjugated bile acids; CDCA, chenodeoxycholic acid; CYP27A1, sterol 27-hydroxylase; CYP7A1, cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase; CYP7B1, oxysterol 7α-hydroxylase; CYP8B1, 12α-hydroxylase; DCA, deoxycholic acid; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; ERK, extracellular regulated protein kinases; FGF15/19, fibroblast growth factor 15/19; FGFR, fibroblast growth factor receptor; FXR, farnesoid X receptor; G-6-Pase, glucose-6-phophatase; GPCR, G-protein coupled receptor; HDL, high density lipoprotein; HNF4α, hepatocyte nuclear factor-4α; Heptic lipid metabolism; IBAT, ileal sodium-dependent bile acid transporter; JNK1/2, c-Jun N-terminal kinase; LCA, lithocholic acid; LDL, low-density lipoprotein; LRH-1, liver-related homolog-1; M1–5, muscarinic receptor 1–5; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; NAFLD, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; NK, natural killer cells; NTCP, sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide; PEPCK, PEP carboxykinse; PTX, pertussis toxin; S1P, sphingosine-1-phosphate; S1PR2, sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 2; SHP, small heterodimer partner; SPL, S1P lyase; SPPs, S1P phosphatases; SRC, proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase; SphK, sphingosine kinase; Sphingosine-1 phosphate receptor; Spns2, spinster homologue 2; TCA, taurocholate; TGR5, G-protein-coupled bile acid receptor; TNFα, tumor necrosis factor α; VLDL, very-low-density lipoprotein.
Figures

References
-
- Zakim D, Boyer TD. Hepatology: A Textbook of Liver Disease. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders 1996.
-
- Parks DJ, Blanchard SG, Bledsoe RK, Chandra G, Consler TG, Kliewer SA. Bile acids: natural ligands for an orphan nuclear receptor. Science. 1999;284:1365–1368. - PubMed
-
- Makishima M, Okamoto AY, Repa1 JJ, Tu H, Marc Learned R, Luk A. Identification of a nuclear receptor for bile acids. Science. 1999;284:1362–1365. - PubMed
-
- Wang H, Chen J, Hollister K, Sowers LC, Forman BM. Endogenous bile acids are ligands for the nuclear receptor FXR/BAR. Mol Cell. 1999;3:543–553. - PubMed
-
- Schaap FG, Trauner M, Jansen PL. Bile acid receptors as targets for drug development. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014;11:55–67. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

