Pharmacokinetic study of salvianolic acid D after oral and intravenous administration in rats
- PMID: 26579453
- PMCID: PMC4629266
- DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2015.03.015
Pharmacokinetic study of salvianolic acid D after oral and intravenous administration in rats
Abstract
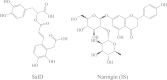
A sensitive, specific and rapid LC-MS method was developed and validated for the determination of salvianolic acid D (SalD) in rat plasma. This method used a single quadrupole mass spectrometer with an electrospray ionization (ESI) source. A single ion monitoring scanning (SIM) mode was employed. It showed good linearity over the concentration range from 3.3 to 666.7 ng/mL for the determination of SalD. The R.S.D.% of intra-day and inter-day precision values were no more than 7.69%, and the accuracy was within 91%-104% at all quality control levels. This LC-MS method was applied to the pharmacokinetic study of SalD in rats. A two-compartmental model analysis was employed. The plasma concentrations at 2 min (C 2min) were 5756.06±719.61, 11,073.01±1783.46 and 21,077.58±5581.97 μg/L for 0.25, 0.5 and 1 mg/kg intravenous injection, respectively. The peak plasma concentration (C max) was 333.08±61.21 μg/L for 4 mg/kg oral administration. The area under curve (AUC0-t ) was 14,384.379±8443.184, 22,813.369±11,860.823, 46,406.122±27,592.645 and 8201.740±4711.961 μg/L·h for intravenous injection (0.25, 0.5 and 1 mg/kg) and oral administration (4 mg/kg), respectively. The bioavailability of SalD was calculated to be 4.159%±0.517%.
Keywords: AUC, the area under curve; Analysis method; Bioavailability; CI, confidence interval; CL, clearance; Cmax, peak plasma concentration; Danshen; Dose proportionality; ECE-1, endothelin converting enzyme 1; ESI, electrospray ionization; IS, internal standard; LC-MS; LLOQ, lower limit of quantification; Pharmacokinetics; QC, quality control; R.E., relative error; R.S.D., relative standard deviation; SIM, single ion monitoring; SalB, salvianolic acid B; SalD, salvianolic acid D; Salvia miltiorrhiza; Salvianolic acid D; TCM, traditional Chinese medicine; ULOQ, upper limit of quantification.
Figures
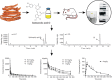


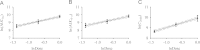
Similar articles
-
Enantioselective determination of ornidazole in human plasma by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry on a Chiral-AGP column.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2013 Dec;86:182-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2013.07.048. Epub 2013 Aug 12. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2013. PMID: 24004635
-
Determination of salvianolic acid C in rat plasma using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry and its application to pharmacokinetic study.Biomed Chromatogr. 2016 Mar;30(3):376-83. doi: 10.1002/bmc.3558. Epub 2015 Aug 19. Biomed Chromatogr. 2016. PMID: 26173992
-
[UPLC-MS/MS determination of tanshinone ⅡA, salvianolic acid B and ginsenoside Rg₁ in Fufang Danshen preparation in rat plasma and brain tissues].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2017 Feb;42(3):580-586. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.2017.0014. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 28952268 Chinese.
-
Pharmacokinetic study of salvianolic acid A in beagle dog after oral administration by a liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry method: a study on bioavailability and dose proportionality.J Ethnopharmacol. 2013 Jul 9;148(2):617-23. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2013.05.013. Epub 2013 May 21. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23707334
-
Simultaneous determination and pharmacokinetic study of four phenolic acids in rat plasma using UFLC-MS/MS after intravenous administration of salvianolic acid for injection.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2017 Feb 5;134:53-59. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2016.10.017. Epub 2016 Nov 5. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2017. PMID: 27875788
Cited by
-
Development and Validation of a Novel UHPLC-MS/MS Method for the Quantification of Plinabulin in Plasma and Its Application in a Pharmacokinetic Study with Leukopenic Rats.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Aug 14;16(8):1153. doi: 10.3390/ph16081153. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37631067 Free PMC article.
-
Salvia miltiorrhiza Bge. (Danshen) in the Treating Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Based on the Regulator of Metabolic Targets.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Apr 22;9:842980. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.842980. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35528835 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Salvianolic acid B in cancer therapy: pharmacokinetic profile, anticancer mechanisms and translational potential.Med Oncol. 2025 Jul 18;42(8):347. doi: 10.1007/s12032-025-02892-1. Med Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40679646 Review.
-
The Applications and Features of Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry in the Analysis of Traditional Chinese Medicine.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016;2016:3837270. doi: 10.1155/2016/3837270. Epub 2016 Nov 10. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016. PMID: 27956918 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacokinetic study of gallocatechin-7-gallate from Pithecellobium clypearia Benth. in rats.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2016 Jan;6(1):64-70. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2015.10.001. Epub 2015 Nov 29. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2016. PMID: 26904400 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li M.H., Li Q.Q., Zhang C.H., Zhang N., Cui Z.H., Huang L.Q. An ethnopharmacological investigation of medicinal Salvia plants (Lamiaceae) in China. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2013;3:273–280.
-
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission . 2010 ed. vol. 1. China Medical Science Press; Beijing: 2010. Pharmacopoeia of the People׳s Republic of China.
-
- Ai C.B., Li L.N. Salvianolic acids D and E: two new depsides from Salvia miltiorrhiza. Planta Med. 1992;58:197–199. - PubMed
-
- Pan C.S., Lou L.X., Huo Y.Q., Singh G., Chen M., Zhang D.M. Salvianolic acid B and Tanshinone IIA attenuate myocardial ischemia injury in mice by NO production through multiple pathways. Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis. 2011;5:99–111. - PubMed
-
- Xue L., Wu Z., Ji X.P., Gao X.Q., Guo Y.H. Effect and mechanism of salvianolic acid B on the myocardial ischemia–reperfusion injury in rats. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2014;7:280–284. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

